Radiculopathy: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 06, 2023
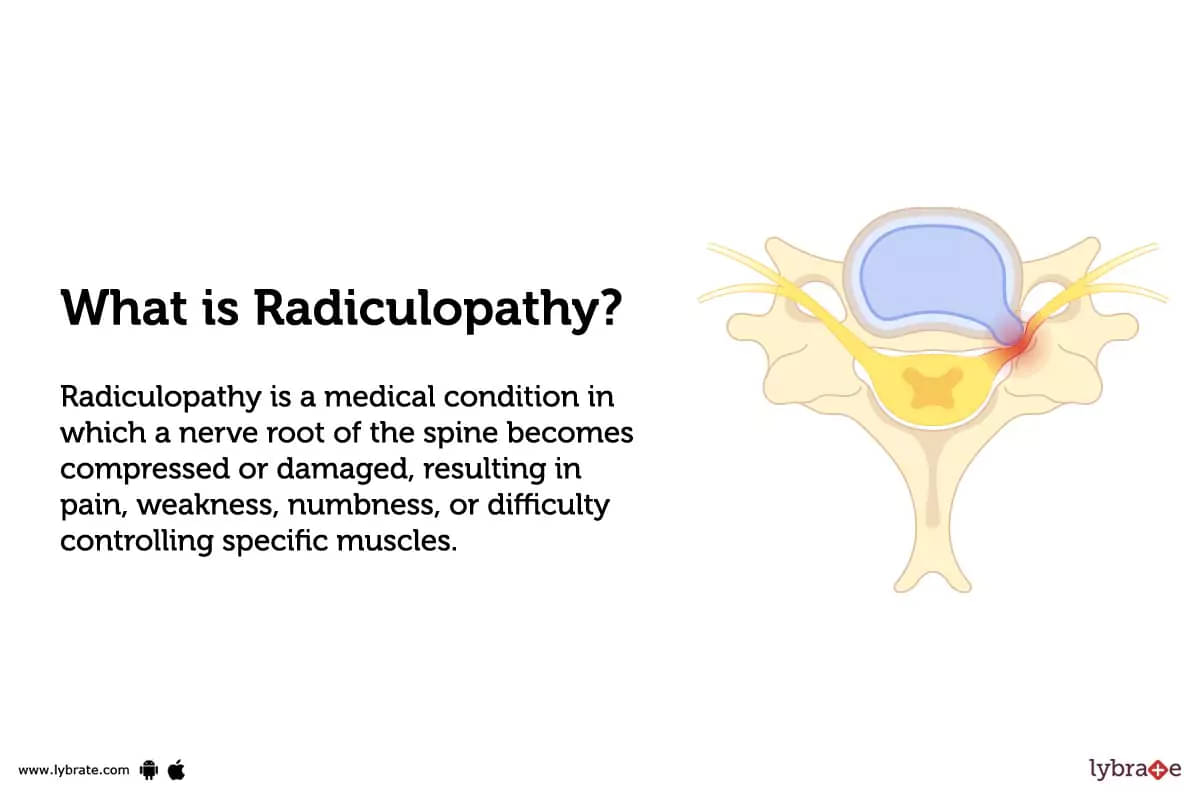
What is Radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy is a medical condition in which a nerve root of the spine becomes compressed or damaged, resulting in pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulty controlling specific muscles. It can occur as a result of spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, trauma, or tumors.
Types of Radiculopathy
Types of radiculopathy include:
- Cervical Radiculopathy: This is when a nerve root in your neck becomes compressed or irritated and can cause referred pain to your arms, shoulders or chest. This can be caused by a disc herniation or degenerative changes in the vertebrae of your neck.
- Lumbar Radiculopathy: This is when a nerve root in your lower back becomes compressed or irritated and causes referred pain to your buttocks, legs or feet. It can be caused by disc herniation as well as other degenerative changes within the vertebrae of your lower back.
- Thoracic Radiculopathy: This type affects nerves originating from vertebrae that are located within your mid-to-upper back region (thoracic spine).
What causes Radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy is caused by damage or disturbance of nerve roots in the spine.
This can be due to a number of factors, including trauma, spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, tumors, spondylolisthesis, infections, and inflammation.
In some cases, the exact cause may be unknown.
What are the symptoms of Radiculopathy?
Common symptoms of radiculopathy can include burning, sharp shooting pain; pain in the arms or legs that radiates from the lower back, leg muscle weakness, numbness and tingling sensations in the limbs, and difficulty controlling bladder or bowel movements.
Other general symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and mood changes can also occur due to decreased mobility and pain.
How can you prevent Radiculopathy?
- Incorporate regular exercise into daily routine to help maintain healthy spinal strength and flexibility.
- Engage in proper body mechanics while working, exercising, or lifting heavy objects in order to avoid straining the spine/nerves.
- Avoid smoking and practice good posture to promote healthy nerve functioning.
- Make effort to stay at a healthy weight, as excess body weight can put strain on the spine and surrounding nerves of the cord leading to radiculopathy symptoms.
Radiculopathy - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical Exam: A physical exam is used to assess muscle strength, sensation, and reflexes. If a doctor suspects radiculopathy, they may ask the patient to perform specific movements to bring out any pain or weakness in the affected area.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG tests measure the electrical activity of nerves and muscles. This can help identify damaged nerve roots or other nerve issues associated with radiculopathy.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): NCS tests measure how well electrical signals travel through the nerves, which can be affected by radiculopathy. This test can also identify if there is nerve damage or entrapment.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can help doctors diagnose radiculopathy by showing if there is any pressure on the nerves from a herniated disc or bone spur.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be used to check for inflammation or infection that could be causing radiculopathy symptoms.
What are possible complications of Radiculopathy?
- Loss of sensation, tingling and burning in the affected area.
- Weakness and loss of muscle strength in the affected area due to nerve damage.
- Painful and spasmodic muscular contractions in the affected region.
- Increased risk of developing infections along with other complications like foot drop or bladder and bowel problems.
- Difficulty controlling autonomic functions like body temperature, blood pressure etc due to nerve damage to specific areas of the body such as spine
- Inability to move a limb normally, as well as problems with coordination, fine motor skills, balance, or walking gait due to impaired motor function
Home Remedies for Radiculopathy?
- Ice or Heat Pack: Apply ice or heat in the form of a heat pad or a cold pack to provide relief from pain& swelling due to nerve irritation.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): It is an anti-inflammatory and analgesic herb used to reduce nerve pain and inflammation in cases of radiculopathy.
- Guggul (Commiphora mukul): It helps reduce nerve pain and inflammation associated with radiculopathy.
- Shilajit (Asphaltum puniabiunum): It is a mineral-rich ayurvedic remedy that can reduce pain, inflammation, and weakness caused by radiculopathy.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): It is an anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce nerve pain and inflammation in cases of radiculopathy.
- Ayurvedic Massage Therapy: Ayurveda recommends massaging the affected area with warm oil to reduce the discomfort associated with radiculopathy. Massaging with sesame oil or Mahanarayan oil can help soothe the inflamed nerves in the affected area and alleviate discomfort due to radiculopathy.
- Yoga: Doing gentle yoga postures such as forward bends, twists, backward bends, etc., can help improve flexibility of the spine while reducing stress on the affected nerves due to radiculopathy.
What to eat in Radiculopathy?
- Eating a well-balanced and nutritious diet can help improve symptoms associated with radiculopathy.
- Meal plans should include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins such as fish, poultry, nuts, and beans.
- Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, mackerel, flaxseed, olive oil can be beneficial for reducing inflammation and managing pain.
- Staying hydrated with fluids such as water or green tea is important to help the body flush out toxins.
- Eating foods rich in antioxidants like berries or dark leafy vegetables can help reduce free radical damage to cells in the affected area of the body.
What not to eat in Radiculopathy?
- Foods that are high in fat and cholesterol, including red meat and full-fat dairy products such as cheese and butter.
- Refined grains like white pasta and white bread, which can cause inflammation in the body.
- Spicy or processed foods as they can cause irritation to the nerves.
- Citrus fruits, tomatoes, alcohol, processed sugars and caffeine should be avoided as these may aggravate nerve pain related to Radiculopathy.
Radiculopathy Treatment
- Physical therapy: This includes stretching, strengthening, and aerobic exercises to reduce pain and maintain mobility.
- Surgery: A surgeon can decompress a nerve by removing tissues that put pressure on it or by cutting away bone.
- Nerve blocks or injections: An injection of steroids may help relieve chronic nerve-related pain for some people. Hot or cold compresses or electrical stimulation may also provide relief.
- Microdiscectomy: Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that removes the inflamed, herniated portion of an intervertebral disc and any associated bone spurs causing nerve root compression.
- Laminectomy: Laminectomy is surgical procedure in which the back of one vertebra is removed to create space for the spinal nerves and relieve compression from them due to conditions such as herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion involves fusing two adjacent vertebrae together in order to eliminate motion and stop pain signals from radiating along damaged nerve pathways and reduce the pressure on the nerves due to a herniated disc or other conditions causing radiculopathy.
- Foraminotomy: A foraminotomy is a surgery that removes bone and tissue around nerve rooting channels in your spine to provide a greater exit range and ease pinching of nerves which can cause radiculopathy pain.
Which doctor to consult for Radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy is a condition which affects the nerve roots and can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in an area of the body.
A neurologist is the best doctor to consult for Radiculopathy. They are specialists in diseases of the nervous system and are able to diagnose any underlying nerve or spinal cord conditions that may be causing symptoms associated with Radiculopathy.
Which are the best medicines for Radiculopathy?
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain associated with nerve root compression. Examples include ibuprofen (Advil), naproxen sodium (Aleve), and celecoxib (Celebrex).
- Analgesics: Analgesics are used to reduce pain resulting from nerve root compression. Examples include acetaminophen (Tylenol) and tramadol (Ultram).
- Muscle relaxants: Muscle relaxants reduce muscle spasms and tension in the affected area to help relieve pain associated with radiculopathy. Examples include cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and tizanidine (Zanaflex).
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants have been found to be effective in treating chronic pain caused by radiculopathy due to their ability to block pain signals from being sent to the brain. Examples include amitriptyline (Elavil) and nortriptyline (Pamelor).
- Corticosteroids : Corticosteroids can be used to treat radiculopathy caused by inflammation. They can be injected directly into the affected area or taken orally as a pill. Corticosteroids reduce inflammation, thus relieving nerve pain and other symptoms associated with radiculopathy.
How long does it take to recover from Radiculopathy?
Generally, milder cases can be treated with rest and physical therapy and may take several weeks-to-months to resolve.
More severe cases may require more aggressive treatment such as spinal injections or surgery, which can take several months-to-years to resolve.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of treatment depend on what type of treatment it is. Some treatments, such as surgery or radiation, may provide permanent results, while other treatments, such as medications or behavioral therapy, may provide temporary relief.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Avoid activities or movements that cause or increase discomfort.
- Adopt a gentle exercise program to help maintain flexibility and strength, with special emphasis on the muscles in the neck and shoulder girdle.
- Start gently, making sure not to overdo it or cause further injury.
- Avoid sudden movements that could strain your back and neck such as twisting and bending.
- Work on core strengthening exercises to target abdominal muscles as well as the pelvic floor muscles, which can help support the spine’s structures and reduce excessive force on nerves during movement.
- Regularly take time out for relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation and breathing exercises which can also target muscles related to chronic pain in radiculopathy patients such as depression and anxiety levels associated with chronic pain status have been significantly improved in patients following these practices regularly over time.
- Award appropriate medications when needed but be mindful of potential addiction issues associated with long-term use of certain drugs so that you can find an alternative treatment whenever possible
- Follow-up care should include regular check-ups by medical professionals so that any potential symptom progression like numbness, tingling sensations or muscular weaknesses can be monitored and attended to timely if necessary
What is the cost of Radiculopathy treatments in India?
Treatment for radiculopathy in India generally costs between ₹50,000 and ₹200,000 depending on the severity of the injury and complexity of treatment.
What are side-effects of Radiculopathy treatments?
Medication side effects can include nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, diarrhea, constipation and headaches.
Surgery side effects include pain management medications which can cause drowsiness and vomiting.
Physical therapy may cause temporary soreness due to stretching of the affected muscles and joints.
Radiculopathy - Conclusion
If you are suffereing from any complications relating radiculopathy then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can complications like ' cauda equina syndrome and severe lumbar radiculopathy 'in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors