Concussion: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 06, 2023
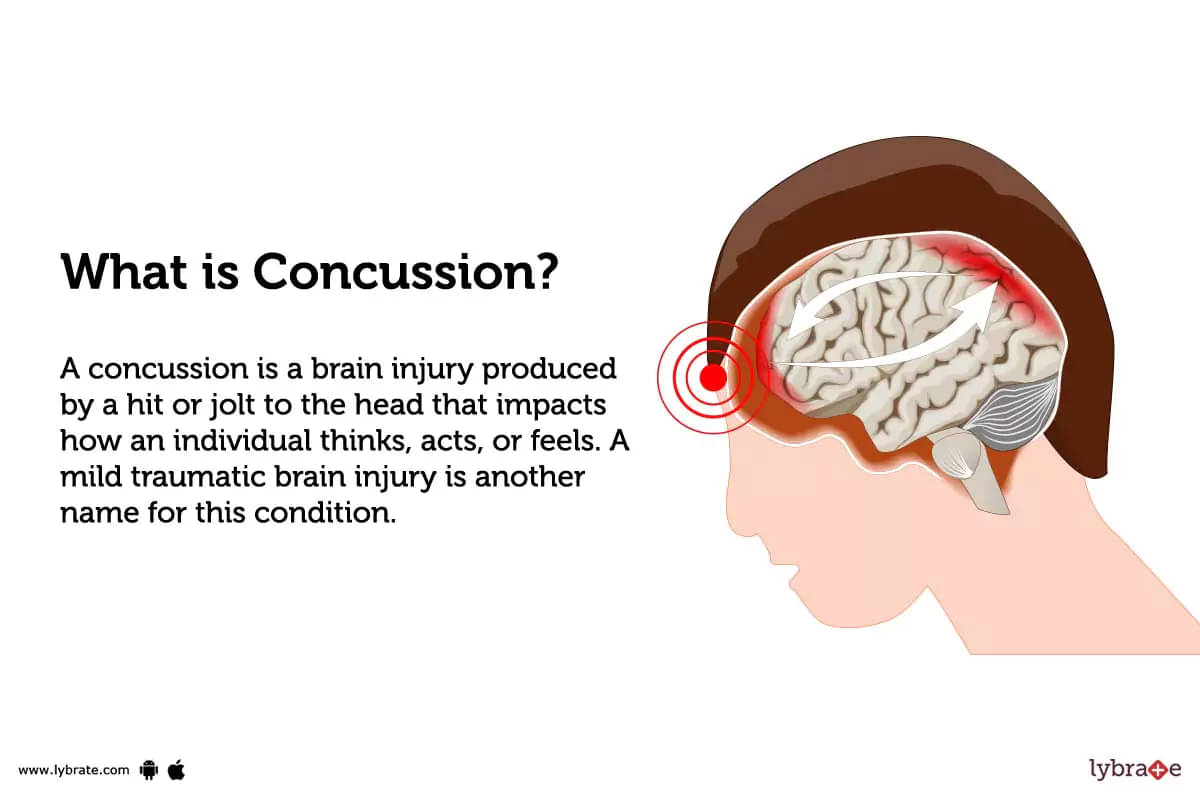
What is Concussion?
A concussion is a brain injury produced by a hit or jolt to the head that impacts how an individual thinks, acts, or feels. A mild traumatic brain injury is another name for this condition.
Types of Concussion
There are two types of concussion that can occur: simple or complex. Simple Concussion: A simple concussion is caused when a person has a minor head injury which causes brief confusion and dizziness, often with no hospital stay being required. In most cases, patients have symptoms for just a brief period of time before making a full recovery.
It may cause symptoms such as headache, dizziness, fatigue, confusion and memory problems.
Complex Concussion: A complex concussion is more serious and can cause long-lasting complications, such as difficulty thinking clearly or recognizing words. Symptoms may include difficulty concentrating or remembering things, confusion, loss of consciousness (even briefly), altered mental states, vision changes, hearing difficulties and balance problems. Treatment for complex concussions may require hospitalisation and rehabilitation to help the person recover more quickly.
What causes Concussion?
A bump, blow, or shock to the head that causes a disruption in the normal activity of the brain may cause the occurrence of a concussion.Common causes include vehicle accidents, falls, sports-related impacts such as football tackles and blows to the body that cause the head and brain to shake violently.Concussion can also be caused by objects flying through the air and striking a person in the head.
What are the symptoms of Concussion?
- Headache: Experiencing pain in the head along with pressure.
- Balance Problems: Dizziness and difficulty with coordination.
- Cognitive Impairment: Trouble with concentration, memory and confusion.
- Physical Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, tiredness, and light and sound sensitivity.
- Behavioural Changes: Irritability, mood swings and increased emotional reactions.
- Sleep Issues: Drowsiness, Insomnia or sleeping more than usual.
How can you prevent Concussion?
- Helmets and other safety gear should be used while playing sports.
- Increase awareness and understanding of concussion by educating students, parents and coaches.
- Teach correct body checking and tackling techniques in contact sports like football, hockey, etc.
- Avoid playing when feeling any symptoms of being concussed or after being knocked unconscious.
- Immediately report symptoms to a medical professional if they persist or worsen over time.
Concussion - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical exam: The physical exam in a concussion will usually focus on checking the person's vision, balance, coordination, strength and sensation. The doctor may also check the eyes for any signs of bleeding or bruising due to impact as well as reflexes to ensure they are working properly.
- Neuroimaging scans: Concussion neuroimaging scans typically involve magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans to detect changes in the brain due to a concussion. They can also be used to identify any abnormality or damage related to the concussion and assess the severity of the injury. Neuroimaging can help determine if there is any swelling, bleeding, tissue damage, or other potential signs of a concussion — all of which may be difficult for a practitioner to spot on their own.
- EEG: EEG, or electroencephalogram, is a test that measures the electrical activity of the brain. In the case of suspected concussion, an EEG can help determine whether or not there has been any trauma to the brain and detect any potential signs of long-term damage.
What are possible complications of Concussion?
- Cognitive complications: The most common cognitive effects of a concussion include difficulty with problem solving, memory, confusion, and slowed reaction times.
- Physical Symptoms: Physical symptoms like headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and sensitivity to noise or light can also result from a concussion.
- Emotional Issues: Some individuals with mild concussions may have emotional difficulties such as anxiety and sadness.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty sleeping is another potential side effect of getting a concussion.
- Secondary Injury: If a person sustains a second head injury before the concussion has fully healed it can cause much more serious and even permanent damage to the brain or death in some cases.
Home Remedies for Concussion
- Drink warm water mixed with a teaspoon of turmeric 3 times a day.
- Have a teaspoon of triphala powder at night before going to bed with lukewarm water.
- Consume nutmeg and almonds paste in warm milk daily as it reduces headaches and vertigo symptoms caused by concussion.
- Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as fish, walnuts, and flaxseed oil for reducing inflammation in the brain tissues post-concussion.
- Steam inhalation with cumin seeds helps to reduce headache due to concussion and its symptoms like vertigo, nausea, and dizziness.
- Apply sandalwood paste on the forehead for relief from headache due to concussion injury.
What to eat in Concussion?
- To recover from a concussion, healthy eating habits are essential.
- The recommended diet contains lean proteins, fruits and vegetables, healthy grains, good fats, and lots of water.
- Consume four to six smaller meals throughout the day for better nutrient absorption and to avoid feeling overwhelmed by large portions.
- Incorporate brain-supporting foods such as omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, flaxseed), glucosamine (shellfish), vitamins B12/B6 (chicken or tuna) & antioxidants (blueberries or dark chocolate) into the diet to help heal and protect the brain from concussion damage.
What not to eat in Concussion?
- Caffeine: Can worsen symptoms of a concussion, making it last longer.
- Alcohol: Increases the chance of another head injury, should be avoided.
- Greasy and processed foods: Lack of beneficial nutrients that can help speed recovery.
- High cholesterol foods: Can increase inflammation and prolong healing time.
- Sugary snacks and drinks: Can lead to fatigue, restlessness and disrupted sleep.
- Spicy Foods: May cause headaches or exacerbate current ones.
Concussion Treatment
- Medicine: Pain-relieving medication may be prescribed for headaches, but there is limited use for other symptoms of a concussion.
- Physical activity: Gradually increase physical activity as directed by your doctor until the person can return to regular activities of daily living or athletic participation without any concussion symptoms lingering.
- Cognitive behavioural therapy: Concussion cognitive behavioural therapy (CCBT) is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals who experience cognitive, emotional and physical issues related to a concussion. It works by teaching individuals coping strategies and techniques to better manage their thoughts, feelings, behaviour and overall wellness in the wake of a concussion. CCBT techniques may include psychoeducation, relaxation training, stress management techniques, problem-solving skills and communication skills.
- Surgery: In extreme cases, surgery may be necessary to repair physical damage sustained from a traumatic head injury and/or reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with repeated concussions.
Which doctor to consult for Concussion?
- The best type of doctor to consult for a concussion is a neurologist.
- Neurologists are medical experts who specialise in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of brain and nervous system disorders. They are experts in identifying the symptoms and
- underlying causes of a concussion and develop personalized treatment plans that can reduce long-term effects.
- Other doctors that may be consulted include primary care physicians and emergency room physicians.
Which are the best medicines for Concussion?
- Pain medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen may provide pain relief and help decrease swelling. Acetaminophen can also be used to help ease headaches and other minor aches associated with a concussion.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are a kind of anti-inflammatory medicine that is often used to treat concussion symptoms. They help to reduce swelling, pain, and headaches associated with the condition. Corticosteroids may also be beneficial for improving healing times by encouraging faster recovery from head trauma.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants are drugs that are used to treat mental disorders including anxiety, depression, and other associated conditions. In the case of a concussion, antidepressant medication may be used in addition to other treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes to reduce symptoms of psychological distress associated with concussion.
How long does it take to recover from Concussion?
- Concussions, or mild traumatic brain injuries, are notoriously difficult to treat and highly individualistic; therefore the amount of time it takes to fully recover from a concussion can vary between individuals, incidents and circumstances.
- Generally speaking, recovery may take anywhere from 7-10 days for mild cases to several weeks or even months in severe ones.
- Symptoms such as confusion, headaches and nausea typically dissipate in the first few days but may linger for some time, depending on the severity of the concussion.
- There are also certain milestones that indicate progression towards full recovery, such as returning to physical activities followed by school or work activity.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
- The outcome of treatment for a concussion varies from person to person and the effects may be permanent or temporary.
- Some might experience a full recovery with no recurrence of symptoms, while others might have lingering issues that may need ongoing management.
- The focus of treatment is to help the individual manage the symptoms and restore as much normal functioning as possible.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
The following are post-treatment recommendations for concussions:
- Refraining from physical activity such as sports or contact activities, even if the symptoms improve.
- Gradually increasing physical activity as tolerated, but stopping if any symptoms recur.
- Making sure to get plenty of rest, avoid activities that require extended cognitive and mental effort, and follow the doctor's recommendations for taking medication or supplements when necessary.
- If any new or worse concussion related symptoms occur after physical activity or play, seek medical attention immediately.
- Having a follow-up appointment with the doctor to monitor a patient's recovery process and adjust treatment if needed.
What is the cost of Concussion treatments in India?
The cost of concussion treatments in India can vary greatly depending on the patient's specific needs, the severity of the concussion, and the medical facility providing the services.
Generally speaking, treatment for a mild concussion can range from Rs. 500-2,500, for a moderate concussion between Rs. 3,000-6,000 and for a severe concussion up to Rs.10-20,000 or more. The cost may also include medications and physiotherapy sessions as well.
What are side-effects of Concussion treatments?
- Headache: Pressure, throbbing or aching pain.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or disorientation.
- Fatigue: Increased feeling of lethargy and exhaustion.
- Difficulty concentrating: Challenges performing mental tasks.
- Sleep disturbances: Problems sleeping or difficulty staying asleep.
- Irritability & emotional changes: Easily agitated or sad/depressed mood.
- Sensitivity to sound & light: Discomfort due to sensitivity to sound and bright lights.
Concussion - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any symptoms relating to concussion then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'cognitive complications, physical symptoms, emotional issues' in which treatment courses can span from a few months to years based on the severity of the condition.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find General Physician near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors