Tinnitus - Know More About It!
Tinnitus (tin-ih-tus) is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. A common problem, tinnitus affects about 1 in 5 people. Tinnitus isn't a condition itself — it's a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury or a circulatory system disorder.
Although bothersome, tinnitus usually isn't a sign ofv something serious. Although it can worsen with age, for many people, tinnitus can improve with treatment. Treating an identified underlying cause sometimes helps. Other treatments reduce or mask the noise, making tinnitus less noticeable.
Symptoms
Tinnitus involves the annoying sensation of hearing sound when no external sound is present. Tinnitus symptoms include these types of phantom noises in your ears:
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- Roaring
- Clicking
- Hissing
The phantom noise may vary in pitch from a low roar to a high squeal, and you may hear it in one or both ears. In some cases, the sound can be so loud it can interfere with your ability to concentrate or hear actual sound. Tinnitus may be present all the time, or it may come and go.
There are two kinds of tinnitus.
1. Subjective tinnitus is tinnitus only you can hear. This is the most common type of tinnitus. It can be caused by ear problems in your outer, middle or inner ear. It also can be caused by problems with the hearing (auditory) nerves or the part of your brain that interprets nerve signals as sound (auditory pathways).
2. Objective tinnitus is tinnitus your doctor can hear when he or she does an examination. This rare type of tinnitus may be caused by a blood vessel problem, a middle ear bone condition or muscle contractions.
You develop tinnitus after an upper respiratory infection, such as a cold, and your tinnitus doesn't improve within a week.
See your doctor as soon as possible if:
Causes-
A number of health conditions can cause or worsen tinnitus. In many cases, an exact cause is never found.
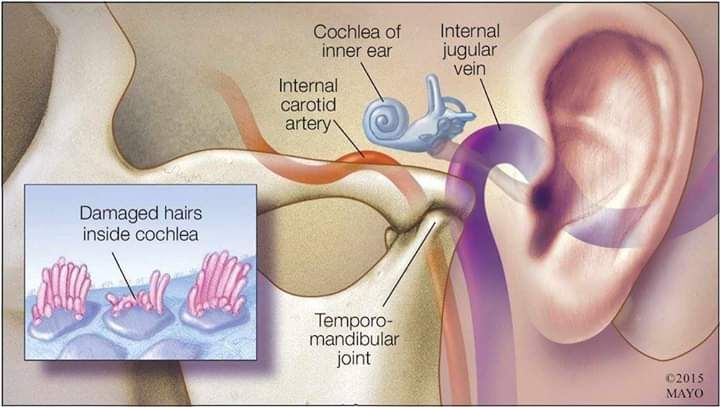
A common cause of tinnitus is inner ear cell damage. Tiny, delicate hairs in your inner ear move in relation to the pressure of sound waves. This triggers ear cells to release an electrical signal through a nerve from your ear (auditory nerve) to your brain. Your brain interprets these signals as sound. If the hairs inside your inner ear are bent or broken, they can" leak" random electrical impulses to your brain, causing tinnitus.Other causes of tinnitus include other ear problems, chronic health conditions, and injuries or conditions that affect the nerves in your ear or the hearing center in your brain.
Common causes of tinnitus
In many people, tinnitus is caused by one of these conditions:
- Age-related hearing loss. For many people, hearing worsens with age, usually starting around age 60. Hearing loss can cause tinnitus. The medical term for this type of hearing loss is presbycusis.
- Exposure to loud noise. Loud noises, such as those from heavy equipment, chain saws and firearms, are common sources of noise-related hearing loss. Portable music devices, such as mp3 players or ipods, also can cause noise-related hearing loss if played loudly for long periods. Tinnitus caused by short-term exposure, such as attending a loud concert, usually goes away; long-term exposure to loud sound can cause permanent damage.
- Earwax blockage. Earwax protects your ear canal by trapping dirt and slowing the growth of bacteria. When too much earwax accumulates, it becomes too hard to wash away naturally, causing hearing loss or irritation of the eardrum, which can lead to tinnitus.
- Ear bone changes. Stiffening of the bones in your middle ear (otosclerosis) may affect your hearing and cause tinnitus. This condition, caused by abnormal bone growth, tends to run in families.
Other causes of tinnitus
Some causes of tinnitus are less common, including:
- Meniere's disease- Tinnitus can be an early indicator of meniere's disease, an inner ear disorder that may be caused by abnormal inner ear fluid pressure.
- Tmj disorders- Problems with the temporomandibular joint, the joint on each side of your head in front of your ears, where your lower jawbone meets your skull, can cause tinnitus.
- Head injuries or neck injuries- Head or neck trauma can affect the inner ear, hearing nerves or brain function linked to hearing. Such injuries generally cause tinnitus in only one ear.
- Acoustic neuroma- This noncancerous (benign) tumor develops on the cranial nerve that runs from your brain to your inner ear and controls balance and hearing. Also called vestibular schwannoma, this condition generally causes tinnitus in only one ear.
- Blood vessel disorders linked to tinnitus- In rare cases, tinnitus is caused by a blood vessel disorder. This type of tinnitus is called pulsatile tinnitus. Causes include:
- Atherosclerosis- With age and buildup of cholesterol and other deposits, major blood vessels close to your middle and inner ear lose some of their elasticity — the ability to flex or expand slightly with each heartbeat. That causes blood flow to become more forceful, making it easier for your ear to detect the beats. You can generally hear this type of tinnitus in both ears.
- Head and neck tumors- A tumor that presses on blood vessels in your head or neck (vascular neoplasm) can cause tinnitus and other symptoms.
- High blood pressure- Hypertension and factors that increase blood pressure, such as stress, alcohol and caffeine, can make tinnitus more noticeable.
- Turbulent blood flow- Narrowing or kinking in a neck artery (carotid artery) or vein in your neck (jugular vein) can cause turbulent, irregular blood flow, leading to tinnitus.
- Malformation of capillaries- A condition called arteriovenous malformation (avm), abnormal connections between arteries and veins, can result in tinnitus. This type of tinnitus generally occurs in only one ear.
Medications that can cause tinnitus
A number of medications may cause or worsen tinnitus. Generally, the higher the dose of these medications, the worse tinnitus becomes. Often the unwanted noise disappears when you stop using these drugs. Medications known to cause or worsen tinnitus include:
- Antibiotics
- Cancer medications,
- Water pills (diuretics),
- Quinine medications used for malaria or other health conditions
- Certain antidepressants may worsen tinnitus
- Aspirin taken in uncommonly high doses (usually 12 or more a day)
Risk factors
Anyone can experience tinnitus, but these factors may increase your risk:
- Loud noise exposure- Prolonged exposure to loud noise can damage the tiny sensory hair cells in your ear that transmit sound to your brain. People who work in noisy environments — such as factory and construction workers, musicians, and soldiers — are particularly at risk.
- Age- As you age, the number of functioning nerve fibers in your ears declines, possibly causing hearing problems often associated with tinnitus.
- Gender- Men are more likely to experience tinnitus.
- Smoking- Smokers have a higher risk of developing tinnitus.
- Cardiovascular problems- Conditions that affect your blood flow, such as high blood pressure or narrowed arteries (atherosclerosis), can increase your risk of tinnitus.
Complications
Tinnitus can significantly affect quality of life. Although it affects people differently, if you have tinnitus, you also may experience:
- Fatigue
- Stress
- Sleep problems
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory problems
- Depression
- Anxiety and irritability
Treating these linked conditions may not affect tinnitus directly, but it can help you feel better.
Prevention
In many cases, tinnitus is the result of something that can't be prevented. However, some precautions can help prevent certain kinds of tinnitus.
Use hearing protection. Over time, exposure to loud noise can damage the nerves in the ears, causing hearing loss and tinnitus. If you use chain saws, are a musician, work in an industry that uses loud machinery or use firearms (especially pistols or shotguns), always wear over-the-ear hearing protection.
Turn down the volume. Long-term exposure to amplified music with no ear protection or listening to music at very high volume through headphones can cause hearing loss and tinnitus.
Take care of your cardiovascular health. Regular exercise, eating right and taking other steps to keep your blood vessels healthy can help prevent tinnitus linked to blood vessel disorders.
Homeopathic remedies
1. Calcarea carbonica- When this remedy is indicated, tinnitus may be experienced alone or with vertigo. The person may have hearing problems, or cracking and pulsing sensations in the ears. People who need this remedy are usually chilly, easily fatigued, crave sweets, and feel overwhelmed and anxious when unwell.
2.Chininum sulphuricum- Buzzing, ringing, and roaring sounds that are loud enough to impair the person's hearing suggest a need for this remedy. The person may also have a tendency toward chills and vertigo, during which the tinnitus is often worse.
3. Graphites- This remedy may be beneficial to a person who has tinnitus with associated deafness. Hissing and clicking sounds are often heard in the ears (or even louder sounds like gunshots). People who need this remedy may also have a tendency toward constipation, poor concentration, and cracking skin eruptions.
4. Lycopodium- A humming and roaring in the ears, along with impairment of hearing, suggest the use of this remedy. Sounds may also seem to echo in the ears. People needing lycopodium often have a tendency toward ear infections with discharge, as well as chronic digestive problems or urinary tract complaints.
5. Carbo vegetabilis- This remedy may be useful if ringing in the ears occurs during flu or other conditions involving vertigo and nausea. The symptoms may be worst in the evening and at night. The person may feel cold and faint, but usually has a craving for fresh and moving air. Carbo vegetabilis is also helpful when an illness has been prolonged or recovery is slow.
6. China (also called cinchona officinalis)- This remedy is often helpful to people who feel touchy, weak, and nervous with sensitivity to noise and tinnitus. It is often indicated after fluids have been lost through vomiting, diarrhea, heavy sweating, and surgery or other conditions involving blood loss.
7. Cimicifuga- People likely to respond to this remedy are very sensitive to noise, along with tinnitus, and often have pain and muscle tension in the neck and back. They are usually energetic, nervous, and talkative, but become depressed or fearful when not feeling well. Headaches and problems during menstrual periods are often seen in people who need this remedy.
8. Coffea cruda- This remedy may be helpful to an excitable, nervous person with tinnitus accompanied by extremely sensitive hearing and a buzzing feeling in the back of the head. People who need this remedy often have insomnia from mental overstimulation.
9. Kali carbonicum- Tinnitus with ringing or roaring, accompanied by cracking noises and itching in the ears, may be relieved with this remedy. Vertigo experienced on turning is another indication. People who need this remedy are often quite conservative, with a rigid code of ethics. They tend to feel anxiety in the region of the stomach.
10. Natrum salicylicum- This remedy may be beneficial if ringing in the ears is like a low, dull hum. Loss of hearing related to bone conduction, as well as nerve interference and vertigo, may be involved. Natrum salicylicum is a useful remedy when tinnitus and tiredness occur after influenza or along with meniere's disease.
11. Salicylicum acidum- This remedy is indicated for tinnitus with very loud roaring or ringing sounds, which may be accompanied by deafness or vertigo. The problem may have begun with flu, or occur in a person with meniere's disease. Salicylicum acidum may also be helpful if tinnitus has been caused by too much aspirin.
"Don’t use any homeopathic remedies without any prescription."


+1.svg)
