Peripheral Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 09, 2023
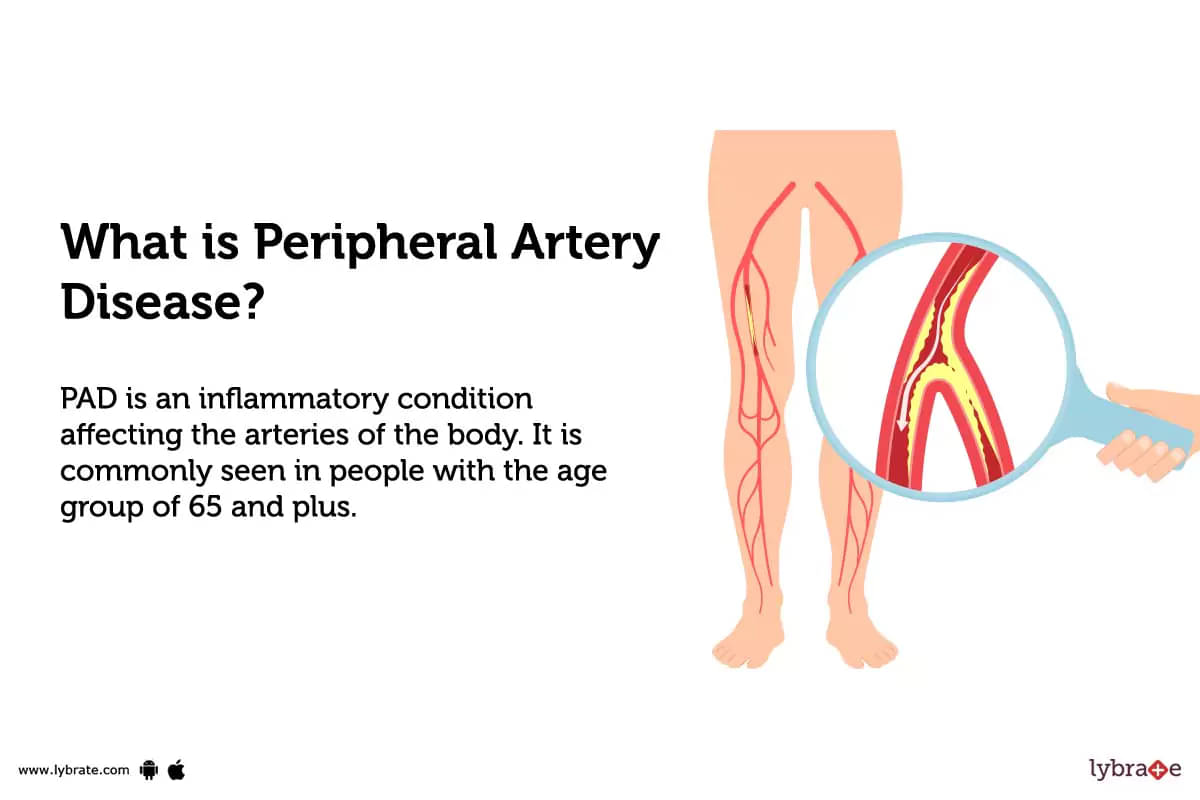
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
PAD is an inflammatory condition affecting the arteries of the body. It is commonly seen in people with the age group of 65 and plus. It is caused by a buildup of plaque on the artery walls, resulting in reduced blood flow to the legs, arms, and other organs.
Types of Peripheral Artery Disease
There are different types of PAD; some common ones include:-
- Atherosclerotic PAD: This type is caused due to accumulation of fat on the walls of arteries. It commonly affects older adults with high cholesterol or diabetes, as well as people who smoke.
- Mononuclear Cell PAD: This type occurs when cells from the immune system accumulate on artery walls and form lesions that block blood flow.
- Fibrointimal Hyperplasia: This type is caused by an overgrowth of tissues in narrowed arteries due to inflammation from bacteria or viruses such as HIV/AIDS which gain access through weakened portions of destroyed vessels due to prior surgery or trauma causing problems with healing processes.
- Buerger's Disease: This type occurs when blood vessels become inflamed due to smoking tobacco products containing nicotine which leads to narrowing/hardening with subsequent loss of circulation that causes damage throughout affected areas leading towards tissue death if left untreated.
What Causes Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure and smoking, high cholesterol can cause Peripheral Artery Disease.
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries is the most common cause of PAD.
- Over time, fatty deposits build up in the walls of arteries and eventually block or limit blood flow to the limbs.
- Other causes can be obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and certain medical conditions such as arterial trauma or an abdominal aneurysm.
What are the symptoms of Peripheral Artery Disease?
How can you prevent Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Increase physical activity: Regular exercise can help improve circulation, build strength and increase flexibility.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating balanced meals packed with fibre and lean proteins increase overall health and can help manage cholesterol levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of PAD due to toxic buildup in the arteries and veins, so avoiding nicotine is important.
- Lose weight: High body mass index is one of the major risk factors for PAD so making lifestyle changes are essential to preventing it.
- Monitor cholesterol: Tracking cholesterol levels helps doctors determine if there’s an increased risk for PAD, so regular visits to a doctor are important in managing this condition effectively.
Peripheral Artery Disease - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical examination:A physical exam which may include taking a pulse, listening to the arteries, and checking blood pressure throughout the body.
- Doppler ultrasound test:It uses sound waves to look for areas of narrowing or blockage in the arteries.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA):It uses powerful magnets and computers to create detailed images of the arteries.
- Angiogram:This is an invasive imaging test that involves inserting a small catheter into an artery to inject contrast dye and get pictures of your blood vessels.
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI):It measures how freely blood flows through your legs by comparing readings from two different places on each leg – usually at the ankle and behind your knee.
- Treadmill exercise test:Also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test, it is used to check how well blood flows through your heart while you are exercising and can help determine if there’s a blockage in your arteries.
- Pulse volume recording:Pulse volume recording (PVR) is a non-invasive test used to measure the blood flow in the legs or arms. It is a useful tool in determining if a patient has peripheral artery disease (or an artery blockage in their arteries).
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans:CTA scans use X-rays and computer processing power to create detailed 3D images showing any blockages in the major arteries of your body including those in your arms and legs.
What are possible Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Decreased blood flow to the legs- resulting in leg pain while walking (claudication).
- Poor wound healing leading to possible amputation of the affected limb.
- Increased risk of heart attack or stroke due to accumulated plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Kidney failure due to reduced blood flow in the kidney's arteries.
- Recurring infections due to decreased circulation and weakened immune system elsewhere in the body can occur with PAD as well, such as gangrene and sepsis (blood stream infection).
Home Remedies for Peripheral Artery Disease
- Horse Gram: Drink a glass of warm horse gram juice every morning on an empty stomach to improve blood circulation and reduce PAD symptoms.
- Garlic: Chew 3-4 raw garlic cloves with some water daily, it helps unclog arteries and improves blood flow in the body.
- Onion Juice: Extract some onion juice and mix one teaspoon of honey in it, drink it daily on an empty stomach to improve circulation throughout the body including the extremities affected by PAD.
- Ginger: Have less than one teaspoon of raw ginger along with water or mix it in meals daily to open clogged arteries and enhance blood flow throughout the body.
- Brahmi: Take Brahmi powder or Brahmi oil massage around affected arteries twice a week to reduce swelling and pain associated with Peripheral Artery Disease.
What to eat in Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet is important for people with peripheral artery disease (PAD).
- Foods high in fibre, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help improve circulation.
- Eating foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids like salmon and other fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds and canola oil can help decrease inflammation and may help with plaque formation.
- Complex carbohydrates such as oatmeal and whole grain bread can help regulate blood sugar levels which reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications that may result from various types of diabetes.
What not to eat in Peripheral Artery Disease?
- High cholesterol food:Foods high in cholesterol, like red meat and full-fat dairy products, should be avoided or eaten sparingly. This includes processed meats and frozen dinners with added fat or cholesterol.
- Foods high in saturated fat:Saturated fats like butter, shortening, lard, and fatty cuts of meat should be avoided as much as possible.
- Fried foods:Fried foods are unhealthy for everyone due to their high saturated fat content. This includes French fries, chips, and chicken nuggets.
- Foods high in sodium:Many convenience foods contain large amounts of sodium which can raise blood pressure and put strain on the arteries over time.
- Alcoholic beverages:Limiting or eliminating alcoholic beverage usage is highly recommended.
Peripheral Artery Disease Treatment
- Lifestyle changes:To reduce the symptoms of peripheral artery disease, certain lifestyle changes are important. These can include regular physical activity and exercise, smoking cessation, etc.
- Medications:To treat PAD, medications may be prescribed to help reduce risks of complications such as blood clots or stroke, lower cholesterol, and improve circulation.
- Angioplasty:Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked blood vessels in the legs caused by PAD.
- Atherectomy:Atherectomy is the removal of blockage in the peripheral artery using a rotating cutter or laser energy, enabling improved blood flow to limbs.
- Bypass Surgery:This procedure creates a detour around the blocked vessels and restores normal flow of blood to your leg muscles and other tissues.
- Stent Placement:A small metal device, called a stent, is placed in an artery near where it has been narrowed or clogged due to PAD, which helps open up blocked arteries.
Which doctor to consult for Peripheral Artery Disease?
The best doctor to consult for PAD is a vascular specialist or interventional cardiologist. They are experts in diagnosing and treating conditions related to artery blockages and can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Other healthcare professionals who may be involved in diagnosing PAD include general practitioners, family doctors, internists, and even cardiologists.
Which are the best medicines for Peripheral Artery Disease?
- Anticoagulants:These drugs are used to prevent the formation of blood clots, which can restrict blood flow in arteries affected by peripheral artery disease. Examples include warfarin (Coumadin) and heparin.
- Antiplatelet medications:These drugs work to lower the risk of blood clots that form on artery walls. Examples include aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Cholesterol-lowering medications:Drugs that help lower cholesterol levels can help improve outcomes in those with peripheral artery disease. Commonly prescribed medications are statins such as atorvastatin (Lipitor) and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
- Vasodilators:These drugs work to widen narrowed arteries by relaxing the muscles in their walls, replenishing circulation in the limbs with peripheral artery disease.
- Cilostazol:This drug works to inhibit an enzyme that’s involved in narrowing arteries; it also helps to lower how hard your heart needs to work by improving circulation throughout your body.
How long does it take to recover from Peripheral Artery Disease?
Generally speaking, it can take weeks to months to see noticeable results as lifestyle changes are incorporated and treatments begin.
Long-term recovery is typically achieved through ongoing lifestyle changes such as an exercise regimen, smoking cessation, etc.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
While the results of treatment are often effective in improving overall blood flow, they are not permanent solutions and individuals with PAD will likely need ongoing monitoring by a medical professional to ensure their condition does not worsen over time.
What are Post-treatment guidelines?
- Follow up with healthcare provider:Provide regular follow-ups with healthcare provider in order to monitor symptoms, progression and any side effects of medications.
- Exercise regularly:Participate in regular exercise like walking and other light activities to improve blood circulation, muscle strength, circulation problem in leg veins (rarely), as well as overall fitness and quality of life.
- Take medications:Follow doctor's instructions to take prescribed medicines; and avoid any over-the counter medicines that may worsen the condition further.
- Quit smoking:Smoking reduces oxygen flow to legs due to narrowing of veins; stopping smoking altogether can improve vascular health significantly for people with this disease.
What is the Cost of Peripheral Artery Disease Treatments in India?
The cost of treatment for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in India varies according to the severity of the disease, type and extent of treatment necessary.
For mild cases, cost can start at around Rs 10,000 and can increase if medication or further treatments are required.
Surgery may also be required in more serious cases and this could potentially range between Rs 30,000 to 1 lakh or more depending on the nature of procedure performed.
What are side-effects of Peripheral Artery Disease treatments?
- Bleeding:Treatment for PAD may involve medication or surgery and can cause a risk of bleeding.
- Infection:Some surgical treatments to restore blood flow carry a risk of infection in the area where they are performed.
- Pain:Pain at the site where the intervention has been done can be another potential side effect.
- Damage to surrounding tissues:Some treatments, including angioplasty and stent placement, may affect adjacent tissues in the affected artery and cause damage or complications such as clot formation.
- Allergic reactions:People may experience an allergic reaction to any medications used in treating PAD such as anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs and thrombolytics medications.
Peripheral Artery Disease - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are facing any of the complications related to peripheral artery disease then do consult a doctor nearby as if not treated on time it can cause complications like “claudication, kidney failure, heart attack” in which treatment courses can vary from a few months to years depending on the severity of the patient's situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors