Adipose tissue (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 16, 2023
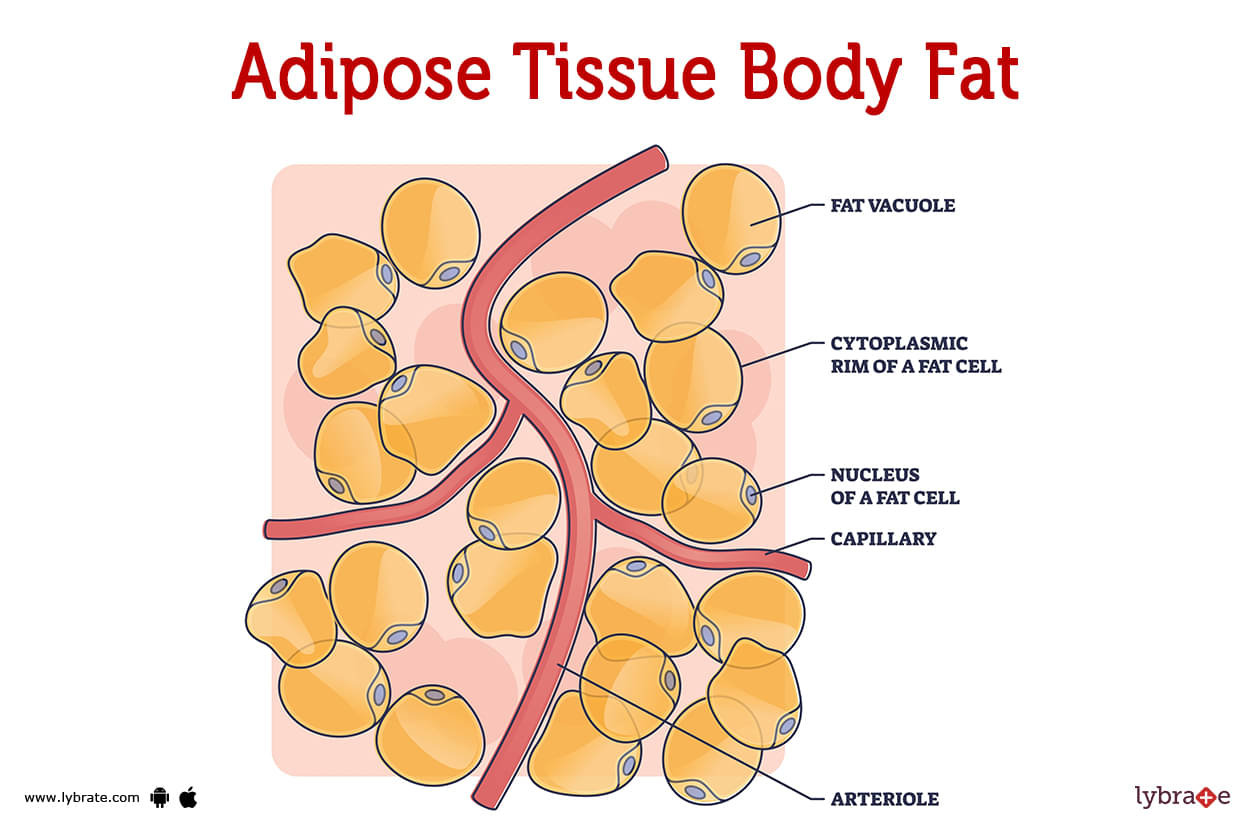
Adipose Tissue Image
Body fat, sometimes referred to as adipose tissue, is a connective tissue that covers every part of your body. It can be found in the spaces of the internal organs (visceral fat), beneath the skin (subcutaneous fat), and even inside the cavities of your bones (bone marrow adipose tissue).
Body fat is best known for storage and release of energy as well as providing insulation. Adipose tissue comprises nerve fibers and blood arteries and communicates with various organs across your body via hormone messages. It serves various vital functions in the regulation of overall health. However, if you do have excessive or insufficient amounts of it, it might cause problems.
Where is adipose tissue located?
The primary regions where adipose tissue is found are:
- Subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT): The fat that resides beneath the skin and muscles is this fat.
- Visceral adipose tissue (VAT): This would be the fat that lines the organs in your abdominal cavity.
Other areas includes of location of adipose tissue:
- In the bone marrow.
- In the breast tissue
- Among muscles.
- Close to your heart
- The sockets of your eyes.
- In the soles of your feet and the palms of your hands.
The amount of a particular type of adipose tissue, the brown variety, increases during infancy and decreases with aging. It is located in the upper back, close to the vertebrae, and above the clavicles.
What does adipose tissue look like?
Adipose tissue is classified into two types: white (WAT) and brown (BAT).
White adipose tissue
The most prevalent form is white adipose tissue, which can be found in the body as subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, and bone marrow fat. One lipid droplet (fat molecule) and a handful of cellular organelles make up the basic structure of white fat cells, or adipocytes.
They store energy, protect against harsh temperatures, and cushion soft organs. Other cell types known as stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells are also present in WAT.Collectively, those cells secrete hormones that control metabolism, inflammatory response, hunger and satiety, and energy balance.
Brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue is predominant in humans during childhood and diminishes with age. It mostly resides in your upper back. White adipocytes are simpler than brown adipocytes, which have a greater number of cellular organelles and many lipid droplets.
Iron included in these organelles is what gives brown fat cells their colour. These organelles help the brown adipocytes to generate large amounts of heat. The primary purpose of BAT would be to generate heat through a process known as non-shivering thermogenesis, which aids in the prevention of hypothermia in babies.
Adipose Tissue Functions
Body fat performs a variety of important functions, including:
- Storage and release of energy
- A barrier to heat and cold transfer. This provides padding for any soft internal organs.
- Modifying one's response to hunger and fullness.
- Protecting a neutral energy level.
- Modulation of Blood Glucose and Cholesterol Preserving your insulin sensitivities.
- Creating thermal energy through chemical or nuclear reactions.
- Aiding the body's natural defences. Hormones involved in sex are being broken down.
How does adipose tissue collaborate with other organs?
By secreting certain hormones or responding to others, adipose tissue communicates with other regions of the body and the central nervous system. It controls energy demand and supply by sending signals of hunger and satiety (being full). In response to insulin, it converts excess blood sugar to lipids and stores them for later use.
Sex hormones influence where fat is stored in your body. Adipose tissue also has active immune cells that respond to stimuli by removing dead fat cells or causing an inflammatory response. A failure in these activities leads to metabolic disorders.
Adipose tissue Conditions and Disorders
Adipose tissue disorders can be caused by a number of things, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. Some common adipose tissue disorders are obesity, diabetes, and fatty liver disease.
- Obesity: The most typical adipose tissue dysfunction is this one. It occurs when your body stores an excessive amount of fat in the tissues beneath your skin. Obesity, in addition to producing a variety of health issues, can contribute to cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetes: It affects blood sugar. Diabetes occurs when the body doesn't create enough insulin or when it doesn't act properly. Your body may have trouble using glucose for energy. Diabetes affects more than 200 million people worldwide.
- Fatty liver disease: Another typical adipose tissue dysfunction is this one. It occurs when the liver struggles to effectively break down the body's fat reserves. This may cause extra fat to be stored in the body's organs, including the liver.
- Insulin resistance disorder: Insulin resistance, a condition when the body does not react to insulin like it should, has diabetes as its primary cause. Diabetes, excessive blood sugar levels, as well as other health issues could result from this.
- Dysfunctional hunger and satiety signals, resulting in obesity: The idea that malfunctioning hunger and satiety signals play a key role in the emergence of obesity is supported by a growing body of studies. The brain produces dysfunctional hunger and satiety signals in response to a variety of inputs, including hunger, fullness, caloric content, and time. These signals may affect how much energy is consumed and used, which may result in overeating or undereating.
Adipose tissue Tests and Procedures
Tests and procedures that can be done to evaluate or treat adipose tissue include:
- MRI: This type of scan uses radio waves to create images of the body. It can be used to assess injuries and illnesses like obesity.
- CT scan: This scan uses X-rays to create images of the body. It can be used to diagnose conditions like herniation and bowel obstruction.
- Blood tests: Blood tests are used to diagnose conditions like obesity and diabetes.they are helpful in finding out levels of HDL and LDL.
- Ultrasound: A type of scan called an ultrasound makes use of sound waves to see inside the body. It can be used to evaluate conditions like obesity related herniation and bowel obstruction.
Adipose Tissue Treatment
Treatment for adipose tissue conditions and disorders includes:
- Weight loss surgery: Weight loss surgery is a procedure that uses surgical methods to lessen a person's body's fat tissue.
- Abdominal surgery: Abdominal surgery can be used to treat adipose tissue diseases in a number of different ways. These include visceral fat removal surgery, fat loss surgery, and liposuction.
- Liposuction: During the procedure, suction is used to remove fat from particular body parts. Typically, liposuction is performed on the stomach, hips, buttocks, arms, and legs. It's one of the most widely used cosmetic procedures today and can aid in weight loss or cellulite reduction.
- Visceral fat removal surgery (vaserlipo): It is a novel technique for removing visceral (internal) fat from body parts like the lower back and belly without first cutting through muscle or other tissues.
Adipose tissue Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Adipose tissue: Steroids can be employed to treat diseases like type 2 diabetes and obesity. for example, prednisone is a type of steroid that's used to treat conditions like arthritis and asthma.
- Analgesics for pain in Adipose tissue: A variety of analgesics are available for the treatment of pain in adipose tissue. Ibuprofen,diclofenac sodium and naproxen sodium, is an analgesic used to treat pain caused by conditions such as fat deposition & menstrual cramps.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Adipose tissue: diazepam is a type of muscle relaxant that's used to relieve pain from conditions like neck pain and headaches.
- Antibiotics for infection in Adipose tissue: Antibiotics can be utilised in a variety of different ways to treat infections that are found in adipose tissue. penicillin is used t treat infections of adipose tissue.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in Adipose tissue: There are a number of nutritional supplements that can be used to reduce pain in adipose tissue. For example, glucosamine and chondroitin are natural supplements that can help to reduce pain from conditions like arthritis.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Adipose tissue: There are a number of antiviral medications that can be used to treat infection in adipose tissue. For example, acyclovir is a type of antiviral medication that's used to treat conditions like herpes.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Adipose tissue: There are a number of chemotherapeutic medications that can be used to treat conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes. for example, doxorubicin is a type of chemotherapeutic medication that's used to treat conditions like cancer.
How should I take care of my adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue performs best when present in a normal level. The body mass index (BMI) can be helpful in providing recommendations for the amount you should aim for. However, it's only a generalised chart and not entirely accurate.
You can receive more individualised information, taking into consideration your fluid and fat levels, by visiting your usual healthcare physician. You could get assistance from your doctor in setting sensible objectives for weight gain or decrease.
But you don't have to become bogged down in statistics when providing general healthcare.This could be mowing the yard, going for a bike ride, swimming, or taking a fast stroll. Two or three times per week is plenty if you indulge in more strenuous exercise, such as running, aerobic dance, or strenuous yard work.
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors