Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Liver (Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, Tests, Treatments
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
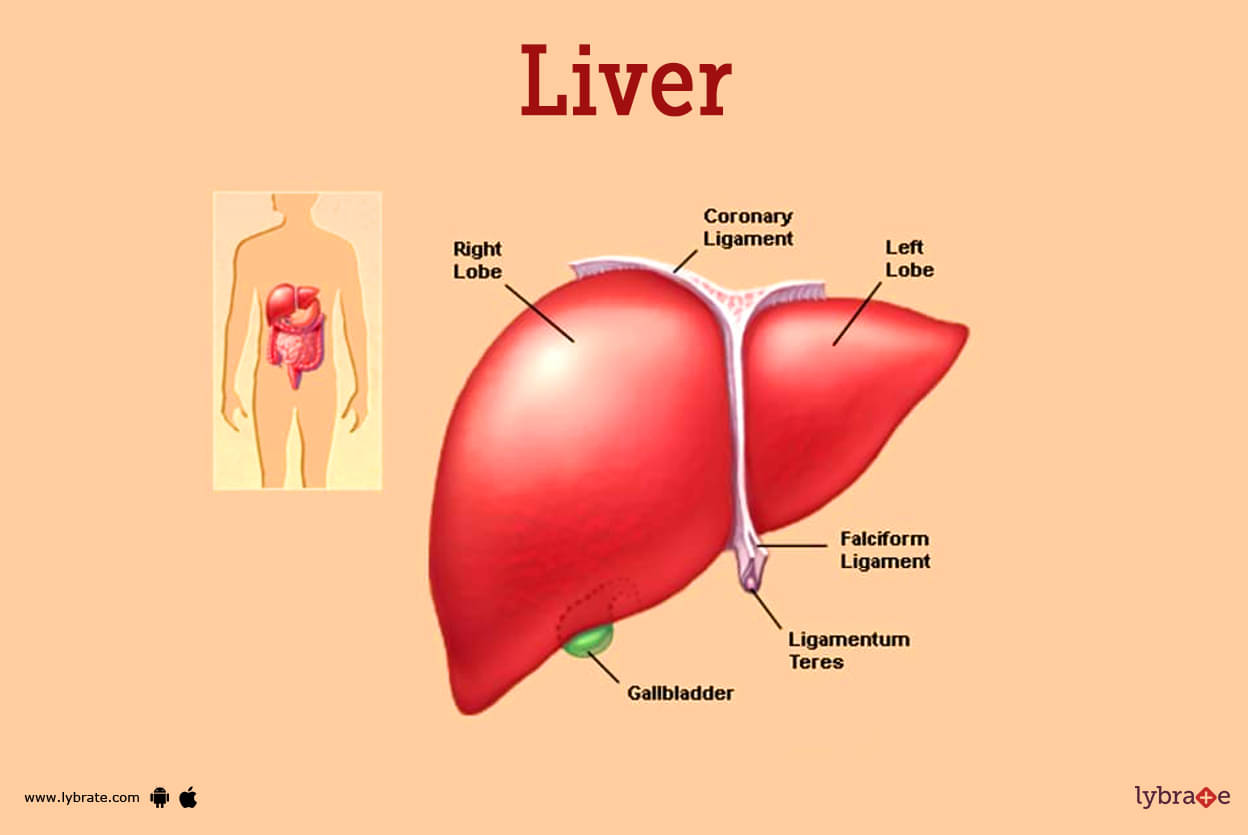
Liver Image
- The liver, also known as the largest gland of a human body, is situated above the stomach, right kidney, and in the upper right region of the abdominal cavity and also just below the diaphragm. It is a sizable organ . It is reddish-brown in its appearance and weighs roughly 3 pounds. It also looks rubbery in its texture too.
- The rib cage protects various organs from any kind of external damage, the liver is also protected due to coverance of the rib cage as a result of which it is difficult for us to feel it in a normal condition.
- Liver consists of two lobes,one is the right lobe and the other is the left lobe. Beneath the liver a portion of pancreas, intestines as well as the gallbladder is located. Along with these organs it helps in various body functions such as breakdown, assimilation and processing of food.
Liver Functions
The liver is a vital organ that performs a wide range of important functions in the body. Some of the main functions of the liver include:
- Strengthen the Metabolism: The liver helps to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, converting them into usable energy and storing it in the form of glycogen. It also metabolizes medications to make them more easily absorbed by the body.
- Helps in Detoxification: The liver's primary function is to filter blood arriving from the digestive system. The liver helps to filter out toxins, such as drugs and alcohol, from the bloodstream and break them down into substances that can be eliminated from the body through urine or feces.
- Production of bile which helps in fat digestion: The liver produces bile, a yellow-green fluid that helps to digest fats and absorb fat-soluble vitamins. The liver excretes bile and controls the majority of blood chemical levels. This aids in removing waste from the liver.
- Store Vitamins & Minerals: The liver stores a variety of substances, including vitamins, minerals, and sugars. It also stores iron, which is essential for the production of red blood cells.
- Helps in Production and Regulation of Hormones: The liver plays a role in the production and regulation of various hormones, including insulin and testosterone.
- Helps in Blood clotting: The liver produces substances that are essential for blood clottings, such as clotting factors and fibrinogen.
- Produce Nutrients: The liver receives all the blood that exits the intestines and stomach. This blood is processed by the liver, which also breaks, balances, and produces nutrients.
Overall, the liver is a crucial organ that performs a wide range of vital functions that are essential for maintaining good health.
Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis A: The hepatitis A virus is responsible for the highly contagious liver ailment known as hepatitis A. This particular hepatitis virus is one of many varieties that can inflame your liver and impair its capacity to operate.
- Hepatitis B: The hepatitis B virus, which causes hepatitis B, is a dangerous liver infection (HBV). Developing chronic hepatitis B raises your risk of getting liver cancer, liver failure, or cirrhosis, which causes the liver to become permanently scarred.
- Hepatitis C: A viral illness called hepatitis C can result in significant liver damage by inflaming the liver. Contaminated blood can spread the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- Hepatitis D: The hepatitis D virus (HDV), which depends on HBV for reproduction, causes hepatitis D, an inflammation of the liver. Absence of the hepatitis B virus prevents hepatitis D infection. The co-infection of HDV and HBV is regarded as the most severe type of chronic viral hepatitis because it leads to hepatocellular cancer and liver-related mortality more quickly.
- Hepatitis E: Hepatitis E is a disease by the hepatitis E virus that results in liver inflammation (HEV). The fecal-oral route of transmission of the virus is primarily through contaminated water.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is an late or advanced stage of liver scarring (fibrosis) brought on by a variety of liver disorders and conditions, including prolonged alcoholism and hepatitis.The type and extent of treatment depend on the cirrhosis's underlying cause. If the liver is failing, liver transplantation can be a possibility.
- Multiple Biliary Hamartomas: A rare cause of several benign hepatic lesions is multiple biliary hamartomas. Multiple bile duct hamartomas, von Meyenburg complexes, and biliary microhamartomas are other names for the disorder. When separating multiple biliary hamartomas from other sources of multiple liver lesion, especially metastases, they are frequently discovered incidentally and are asymptomatic.
- Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: An infection of the abdominal fluid, known as ascites, caused by spontaneous bacterial peritonitis does not originate from an evident area of the abdomen, such as an hole in the intestines or a buildup of pus. People with liver illness are frequently affected, and as the disease progresses, ascites is a common complication.
- Hepatorenal Syndrome: Hepatorenal syndrome, often known as HRS, is a form of kidney dysfunction that manifests itself in patients who have an advanced stage of liver disease.
- Variceal Bleeding: Varices have the potential to rupture as a result of excessive pressure (portal hypertension) and thinning of the walls of the varices. This results in bleeding within the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: People who drink very little to no alcohol but nevertheless have liver disorders and symptoms for those diseases are said to have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which is abbreviated as NAFLD. This is an umbrella term for a variety of liver ailments.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: Developing alcoholic hepatitis is typically a slow and gradual process that might take years. On the other hand, acute alcoholic hepatitis might appear out of nowhere. It can bring about liver failure and death in a short amount of time.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis, abbreviated as AIH, is a non-contagious, chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune illness in which a person's own immune system assaults healthy, normal liver cells. This disease can affect anyone at any age.
- Wilson's Disease: Copper can build up in your liver, brain, and other key organs if you have Wilson's disease, a rare genetic condition that can be passed down through families.
- Congestive Hepatopathy: Congestive hepatopathy is a term that is used to describe the symptoms that arise as a result of prolonged and passive congestion of the liver in the presence of heart failure.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Patients who already have an underlying chronic liver disease or cirrhosis are more likely to be diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (also known as HCC), which is a primary malignancy of the liver.
- Hepatic Adenoma: Hepatic adenomas, also known as hepatocellular adenomas, are benign epithelial tumours of the liver that are uncommon but frequently associated with women of reproductive age who are taking oral contraceptive pills containing exogenous estrogens.
- Cavernous Hemangioma: Cavernous hemangioma, also known as cavernous angioma, venous malformation, or cavernoma, is a type of venous malformation that is caused by endothelial dysmorphogenesis from a lesion that is present at birth. Other names for this condition are cavernous angioma and cavernous hemangioma.
- Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: Only hepatic hemangioma is more prevalent than the liver tumour known as focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH), which is the second most frequent type of liver tumour.
- Angiosarcoma: Any part of the body is susceptible to developing angiosarcoma, which is a type of cancer that affects the inner lining of blood vessels. The skin, breast, liver, spleen, and deep tissue are the most prevalent locations where the disease can be found.
- Liver Cysts: Cysts in the liver are sacs that can be filled with air, fluids, or semi-solid substances and have thin walls. Cysts in the liver affect around 5 percent of the general population.
- Pyogenic Liver Abscess: A liver abscess is a pus-filled mass in the liver that can form as a result of hepatic damage or an intraabdominal infection that has spread through the portal circulation.
- Liver Failure: Acute liver failure is the impairment of liver function which happens quickly, usually in a matter of days or weeks, and in people who do not already have liver disease.
- Drug Related Liver Failure: Most frequently, acetaminophen or the hepatitis virus are to blame. Compared to chronic liver failure, which manifests itself more gradually, acute liver failure is less frequent.
- Ascites: As cirrhosis progresses, the liver begins to leak fluid into the abdomen, causing it to swell and become heavy.
- Gallstones: In the gallbladder, gallstones are deposits of hardened digestive fluid. Hepatitis and bile duct infections (cholangitis) may develop if a gallstone becomes lodged in the bile duct that drains the liver.
- Hemochromatosis: This condition makes it possible for iron to accumulate in the liver, harming it. Additionally, the iron builds up all over the body, leading to several additional health issues.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: This uncommon condition, which has unknown aetiology, results in inflammatory changes in the bile ducts of the liver.
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: In this uncommon condition, the liver's bile ducts are slowly destroyed by an unknown cause cirrhosis, or permanent liver scarring, eventually appears.
Liver Tests
- Alpha-Fetoprotein Blood (AFP) Test: Individuals with liver problems, liver cancer, pregnancy, or other cancers can have elevated amounts of the protein AFP.
- Liver Function Panel: A liver function panel is a collection of numerous blood tests that evaluates the liver's functionality. An increased ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase) can assist diagnose liver illness or damage caused by a variety of conditions, including hepatitis.
- Alkaline Phosphatase: The liver's bile-secreting cells and bones both contain alkaline phosphatase. High levels frequently indicate restricted bile passage from the liver.
- Serum Bilirubin: High bilirubin levels point to a liver issue.
- Serum Albumin: Albumin, a component of total protein, provides information on the efficiency of the liver.
- Hepatitis A Viral Marker: If the doctor suspects hepatitis A, he or she will examine liver function and check for hepatitis A antibodies.
- Hepatitis B Viral Marker: Your doctor can check your antibody levels to see if you've ever had the hepatitis B virus.
- Hepatitis C Viral Marker: Blood tests can also examine your liver function and see if you have the hepatitis C virus in your system.
- Prothrombin Time (PT): To determine if someone is on the right dosage of the blood thinner warfarin, a prothrombin time, or PT, is frequently performed (Coumadin). It also looks for issues with blood coagulation.
- Ptt (Partial Thromboplastin Time): A PTT is performed to look for issues with blood coagulation.
- Abdomen Ultrasound: An abdominal ultrasound examination can check for a variety of liver disorders, such as cancer, cirrhosis, or issues brought on by gallstones.
- Transient Elastograph: a highly specialized ultrasound, can be used to assess the severity of liver injury.
- Computed Tomography: An abdominal CT scan (computed tomography) provides detailed images of the liver as well as other abdominal organ.
- Serum Ferritin: A common sign of both acute and chronic inflammation of liver, serum ferritin is considered an acute phase reactant.
- Right Upper Quadrant Ultrasound: It is typically used to diagnose liver gallbladder and pancreatic anomalies whether there is a presence of an Abscess or increased fat on the liver or the presence of milestones are any sort of obstruction in that cystic duct
- Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy is typically performed when results from another test, like a blood or ultrasound, point to a potential liver issue.
- Liver and Spleen Scan: This nuclear test employs radioactive material to help identify a variety of diseases, such as tumours, abscesses, and other issues with liver function.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): A long, flexible tube with a camera and equipment on the end is used in ERCP (Endocscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography), a procedure that allows doctors to diagnose and even treat some liver conditions.
- Meld Score: Patients with cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, acute liver failure, and patients with acute hepatitis have all been tested and validated to see whether or not the MELD Score is an accurate predictor of survival.
- Child Pugh Score: The Child-Pugh scoring system, which can also be referred to as the Child-Pugh-Turcotte score, was developed with the intention of determining the likelihood of death in cirrhosis patients.
- Hepascore: In hepatitis C patients, a model consisting of four blood indicators in addition to age and sex can provide information that is therapeutically valuable on the different stages of fibrosis.
Liver Treatments
- Endoscopic Banding Or Injection Sclerotherapy: In endoscopic sclerotherapy (EST), a sclerosant is injected directly into a varicose vein to cause thrombosis and obliteration of the vein.
- Balloon Tamponade: The double-lumen catheter of this tamponade balloon makes it possible to both inflate it with saline and drain blood from the liver. In order to stop variceal bleeding, balloon tamponade is only used sometimes today.
- TIPSS(Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Stent Shunting): TIPS, or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, is a procedure in which the portal vein is connected to the hepatic vein under imaging guidance.
- Open Cholecystectomy: Surgery in which the gallbladder is removed via an open incision in the abdomen is known as an open gallbladder removal.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Through four tiny incisions and the use of a camera, a cholecystectomy can be performed laparoscopically, earning it the name 'minimally invasive cholecystectomy.'
- Lobectomy: it is a procedure in which a portion of the liver, or the entire liver, is surgically removed. It is commonly used in cancer therapy.
- Liver Resection: In a liver resection, the liver is either completely or partially removed surgically. It's also known as a hepatectomy, either complete or partial.
- Liver Transplantation: Liver failure can be treated by removing the diseased organ and replacing it with a healthy one, a procedure known as a liver transplant.Paracentesis: In this procedure, a needle can be put it through skin to remove fluid from the abdomen when acute ascites, a swelling in the abdomen brought on by liver failure, causes discomfort.
Liver Medicines
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: Cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones, both of the third generation of antibiotics, are used to treat spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and other infectious illnesses of the liver.
- Antiviral Medications: Entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, adefovir, and telbivudine are just a few of the antiviral medications that can help in the fight against the virus and limit its propensity to destroy your liver.
- Hepatic Rejuvenation Medicine: Including n-acetyl cysteine, trypsin, and vitamin K, are used as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of a wide range of hepatocellular diseases.
- Diuretics: Conditions other than edoema that lead to fluid retention are also treated with these drugs, including cirrhosis and hypertension. Numerous medical professionals prescribe diuretics such aldactone, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and metolazone.
- Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Chemotherapy and radiation are effective treatments for liver cancer, despite the disease's untreatable nature. In extreme cases, the liver may be removed surgically or replaced with a donor organ.
- Statins: This class of drugs is known as lipid-lowering medicines, and it has other beneficial properties for slowing the development of acute or chronic liver disease, such as lowering oxidative stress and inflammation. Rosuvastatin, atorvastatin, etc., are all instances of statins.
- Corticosteroids: Drugs with anti-inflammatory properties work by preventing the recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to areas of cellular and tissue injury, hence reducing inflammation. Methylprednisolone is an example of an effective corticosteroid.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Gastroenterologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously