Brainstem (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
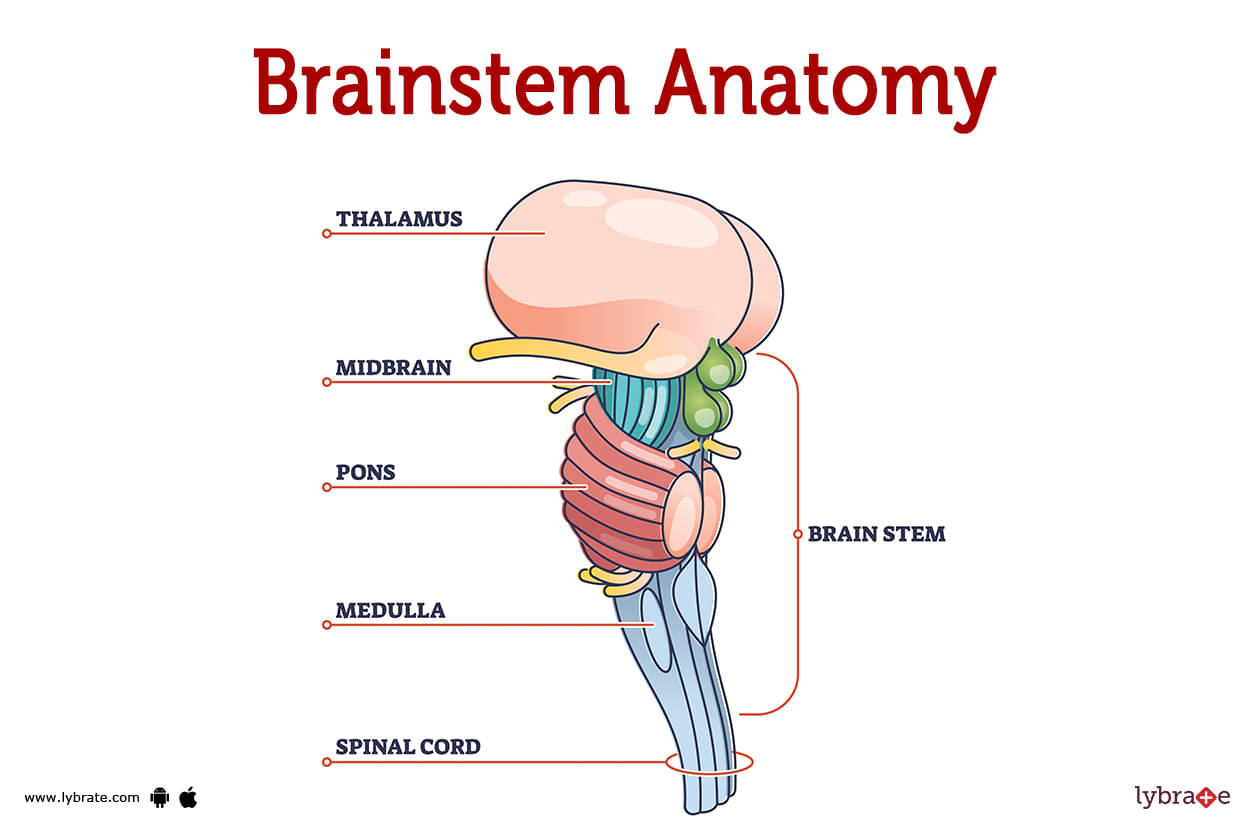
Brainstem Image
The brainstem is the structure in humans that resembles a stalk and is responsible for connecting the brain to the spinal cord (column of nerve tissue that runs down your spine). It is a component of your brain as well as your central nervous system, and it may be found down there.
The brainstem is the part of the brain that is in charge of managing many autonomic functions of the body, including breathing and heart rate. Your brain stem is responsible for your feeling of balance, as well as your coordination and reflexes.
What are the parts of the brainstem?
Between the two hemispheres of the cerebrum and the spinal cord is the thin brainstem. It has three primary components:
- The medulla oblongata: This is the brainstem's dorsal portion, and it regulates vital activities like heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
- The pons: Just above the medulla oblongata is a structure called the pons, which plays a role in sleep and wakefulness regulation and in relaying sensory and motor impulses to and from the rest of the brain and body.
- The midbrain: The midbrain, which sits above the pons, plays a role in motor control and the interpretation of sensory input from the eyes and ears.
Where is the brainstem located?
At the very back of your head, at the very base of your brain, is where you'll find something called your brainstem. It is reminiscent of the stalk that a flower would have. It acts as a connection between the brain and the spinal cord in your body.
Brainstem Functions
The brainstem is responsible for a wide variety of crucial processes, including:
- Rate of the heartbeat: The brainstem is responsible for regulating the rate at which the heart beats.
- Pressure in the blood vessels The brainstem plays a role in maintaining a healthy blood pressure by regulating the degree to which blood vessels constrict and relax.
- The regulation of the muscles that are responsible for breathing is carried out by the brainstem. The diaphragm and the intercostal muscles are both considered to be a part of these muscles.
- Swallowing: The brainstem is responsible for controlling all of the muscles that are involved in the swallowing process, including those in the throat and the oesophagus.
- A person's level of alertness is partially controlled by the brainstem, which also plays a role in regulating the person's level of consciousness.
- The brainstem plays a role in the processing of pain signals received from the body.
- Movement: The brainstem has a role in the regulation of movement, including eye movement, head movement, and neck movement.
How does your brainstem perform with your brain?
To guarantee that all of the body's systems are working as they should, the brainstem collaborates closely with the other portions of the brain. For instance, the brainstem may obtain signals from the cerebral cortex, which is the most superficial layer of the brain, and then transmit those signals to the spinal cord.
The spinal cord, in turn, may transmit those signals to the appropriate muscles or organs. In a similar manner, the brainstem may be the location where signals from the body are received before being sent to the brain for additional processing.
Brainstem Conditions and Disorders
Conditions and diseases of the brainstem are forms of illness that have an effect on the brainstem, which is a portion of the brain that is accountable for a great deal of the body's most fundamental processes. The following are some examples of illnesses and disorders that can affect the brainstem:
- Brainstem stroke: A form of stroke known as a brainstem stroke takes place when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brainstem, which in turn causes damage to the tissue of the brain.
- Brainstem glioma: The term 'brainstem glioma' refers to a specific type of brain tumour that originates in the brainstem. Headaches, nausea, and vomiting, as well as alterations in one's vision or hearing, are all potential symptoms of a brainstem glioma.
- Brainstem encephalitis: An infection of the brainstem, also known as brainstem encephalitis, is a form of inflammation that can be brought on by either a viral or bacterial illness. Fever, headache, trouble speaking or swallowing, and weakness or numbness on one side of the body are some of the possible symptoms of brainstem encephalitis. Other symptoms include encephalitis.
- Brainstem degeneration: Brainstem degeneration is a disorder in which the brainstem becomes injured or deteriorates over time, resulting in symptoms such as weakness, trouble speaking or swallowing, and abnormalities in vision or hearing. Brainstem degeneration can be caused by a number of different conditions.
- Brainstem injury: An injury to the brainstem can refer to any type of damage that occurs to the brainstem as a result of a traumatic event. Some examples of traumatic events include being in a car accident or falling down.Injuries to the brainstem can cause a variety of symptoms, some of which include trouble speaking or swallowing, paralysis or numbness on one side of the body, and difficulty moving the eyes.
- Brainstem cavernoma: A brainstem cavernoma is a form of aberrant blood vessel that can cause bleeding and edema in the area of the brainstem that it affects. Headaches, nausea, vomiting, and shifts in one's vision or hearing may all be indicators that a cavernoma has formed in the brainstem.
- Brainstem infarct: When a blood clot obstructs a blood vessel in the brainstem, this medical condition is known as a brainstem stroke, also known as a brainstem infarct. An infarct in the brainstem can cause a variety of symptoms, including trouble speaking or swallowing, numbness or weakness on one side of the body, and difficulties moving the eyelids.
- Brainstem ataxia: Brainstem ataxia is a disorder that affects the brainstem's capacity to govern movement, resulting in difficulties walking or coordinating movement.
- Brainstem demyelination: Brainstem demyelination is a condition in which the protective covering (myelin) around the nerve fibres in the brainstem becomes damaged or destroyed. This condition can also be referred to as brainstem demyelination. This can result in a wide variety of symptoms, some of which include trouble speaking or swallowing, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, and difficulty moving the eyes.
- Brainstem abscess: A brainstem abscess is a collection An accumulation of pus in the brainstem that is brought on by an infection is referred to as a brainstem abscess. Abscesses on the brainstem can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, and alterations in vision or hearing.
What is brainstem death?
A person is said to be brainstem dead when they no longer have any functions of the brainstem. It happens when something causes the brainstem to be damaged in a permanent way or when something shuts off the blood or oxygen flow to the brain.
A person who has experienced brainstem death is unable to restore consciousness since the brainstem is responsible for controlling key life functions. They are dependent on medical technology to help them stay alive. This illness is sometimes referred to as brain death in some circles.
Can you recover from a brainstem injury?
A lesion to the brainstem can have serious implications since the brainstem is responsible for controlling so many of the most fundamental functions of your body. However, patients with certain forms of brainstem injury can make a full recovery.The sooner you seek medical attention, the greater the likelihood that your healthcare specialists can limit the extent of the injury. After suffering an injury to your brain stem, you can require rehabilitation along with additional specialised forms of treatment.
Brainstem tests
There are several tests that may be used to diagnose brainstem conditions or disorders, including:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI creates detailed images of the brain and brainstem by combining strong magnets and radio waves in order to produce the images.
- Computed tomography: A computed tomography, or CT, scan creates comprehensive images of the brain and brainstem by using x-rays as the primary imaging modality.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan: A PET scan is a type of imaging technique that creates detailed images of the brain and brainstem by using a very small amount of radioactive material.
- Electroencephalography: Electroencephalography, which is more often referred to as an EEG, is a method that records the electrical activity of the brain by connecting electrodes to the scalp of a patient. It is possible that any anomalies in brain activity, including those in the brainstem, might be identified with its help.
- Cerebral Angiogram: An angiography of the brain, also known as a cerebral angiogram, is a diagnostic procedure that creates in-depth pictures of the blood arteries in the brain, including those in the brainstem, by using a specialised dye and x-rays.
- Lumbar Puncture: A diagnostic operation known as a lumbar puncture, which is often referred to as a spinal tap, involves inserting a needle into the lower back in order to withdraw a sample of cerebrospinal fluid.
This treatment is also known as a spinal tap. Infections or other disorders that may be affecting the brain stem can be evaluated by using this fluid as a sample.
Brainstem treatments
There are several types of brainstem surgery that may be used to treat brainstem conditions or disorders. Some examples include:
- Brainstem tumour surgery: The removal of brainstem tumours typically requires a specific kind of surgery known as brainstem tumour surgery. Endoscopy and stereotactic surgery are two examples of minimally invasive surgical procedures that can be used to perform this procedure.
- Brainstem aneurysm surgery: Surgery for brainstem aneurysms is a type of operation that can be performed to either repair or remove brainstem aneurysms (abnormal bulges in blood vessels). You have the option of performing it using the more conventional method of open surgery or through more less invasive procedures such as endovascular surgery.
- Brainstem abscess surgery: Surgical removal of a brainstem abscess is accomplished through the performance of this particular kind of operation (a collection of pus in the brainstem caused by an infection). It might be performed using the more conventional method of open surgery, or it could be carried out through less invasive methods such as endoscopy.
- Brainstem decompression surgery: Brainstem decompression surgery is a type of operation that is performed to alleviate pressure that has been placed on the brainstem as a result of disorders such as hydrocephalus (a build-up of fluid in the brain). It may need the implantation of a shunt, which is a tiny tube, in order to redirect the flow of excess fluid away from the brain.
- Brainstem vascular surgery: The term 'brainstem vascular surgery' refers to a type of operation that is performed to repair or restore blood vessels in the brainstem that have been damaged. You have the option of performing it using the more conventional method of open surgery or through more less invasive procedures such as endovascular surgery.
- Physical therapy: Patients who suffer from illnesses or abnormalities of the brainstem may be advised to participate in physical therapy in order to help improve their strength and mobility.
- Occupational therapy: Individuals who have illnesses or abnormalities of the brainstem may be recommended to participate in occupational therapy in order to help them improve their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks and to live independently.
- Speech therapy: Speech therapy is a treatment option that may be suggested to patients who have illnesses or abnormalities affecting their brainstem that impact their ability to talk or swallow.
How can I keep my brain stem healthy?
There are several steps you can take to help maintain the health of your brainstem:
- Regular exercise can assist enhance blood flow to the brain and support brain health, so it's important to make time for it. Aim to engage in at least thirty minutes of moderately intense physical exercise on most days of the week. Some examples of such activities are walking and cycling.
- Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Eating a diet that is rich in these foods can help support the health of your brain. Avoid foods that have been processed and that are heavy in fat, and reduce the amount of sugary beverages and snacks that you consume.
- Sleep well- enough sleep is essential for maintaining healthy brain function. Aim to get between 7 and 9 hours of sleep each night.Maintaining appropriate brain and body function requires adequate hydration, which can be achieved by drinking a sufficient amount of water throughout the day.
- Moderate your usage of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products because excessive amounts of both can have a detrimental influence on the health of your brain. It is in everyone's best interest to restrict or avoid these substances whenever it is at all possible.
- Protect your noggin by donning a helmet whenever you engage in an activity that places you at a higher risk of suffering a head injury, such as skiing, skating, or cycling.
Brainstem Medicines
- Steroids for the treatment of brainstem inflammation: Prednisone and methylprednisolone are two examples of steroids that may be utilised in the treatment of brainstem inflammation. Other steroids, such as dexamethasone, may also be used.
- Analgesics for pain in the Brainstem: Important medicines that are useful for the management of pain in the brainstem include pain medications that can be purchased without a prescription, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, in addition to prescription pain medications, such as opioids.muscles relaxants for stiffness in the brainstem: It includes medications such as cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol, and tizanidine. These are all examples of important medicines that can be used to treat stiffness in the brainstem.
- Antibiotics for infection in brainstem: Penicillins, cephalosporins, and macrolides are some examples of important antibiotics that may be used to treat infections in the brainstem. Other possible treatments for brainstem infections include antifungals and immunomodulators.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in the Brainstem: Some nutritional supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, and chondroitin, may be used to reduce pain in the brainstem.
Table of content
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors