Biceps (Human Anatomy): Function, Diagram, Conditions, & More
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
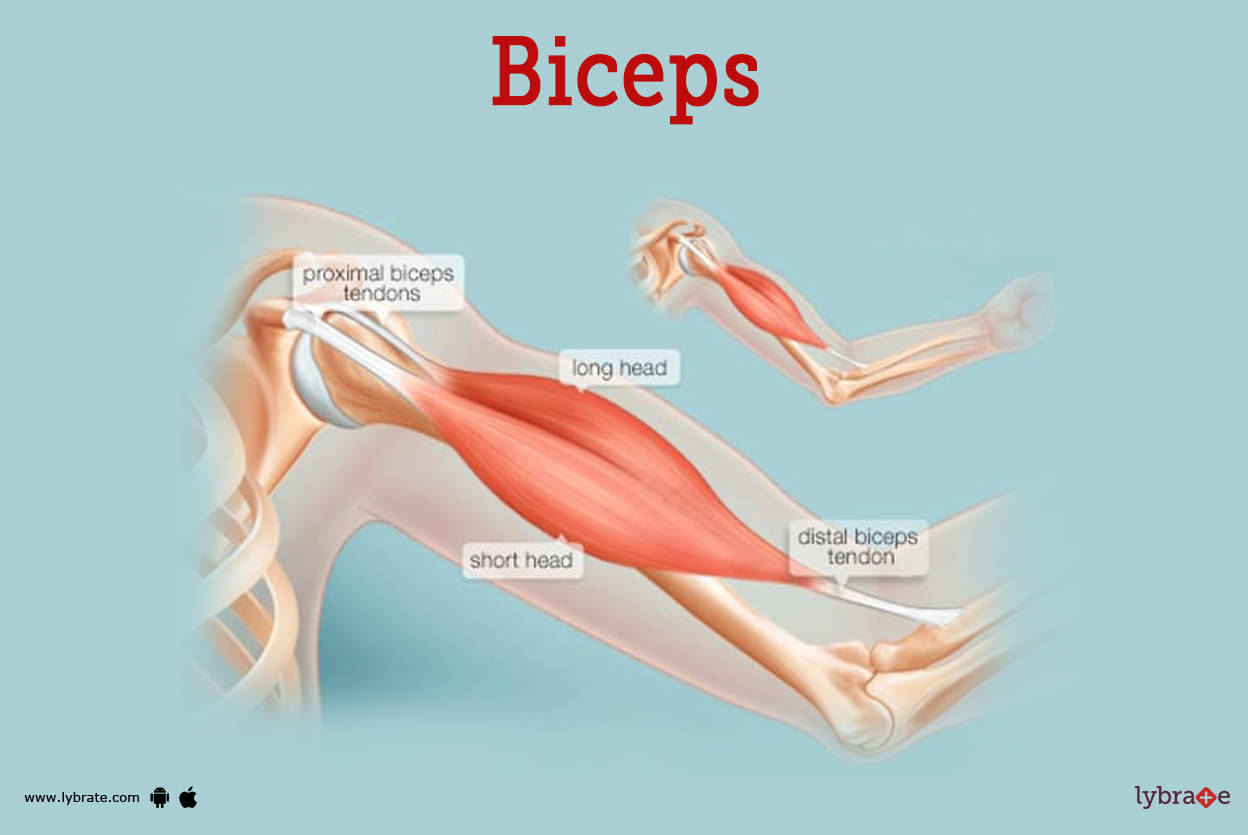
Biceps Image
The biceps is an upper arm muscle on its front/anterior part. The biceps have 2 heads mainly that are a 'short head' and a 'long head' both working as a single muscle.
The biceps is attached to the arm bones by what are called tendons which are made up of tough connective tissues. Tendons connecting the biceps muscle to the shoulder joint in two places are the proximal biceps tendons and the tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the forearm bones that are radius and ulna is called the distal biceps tendon. At the time of contraction of biceps, it pulls the forearm up and rotates it outward.
Biceps Functions
Biseps are responsible for several important functions in the body, including:-
- Flexion of the elbow joint: The biceps muscle helps to bend the elbow joint, bringing the lower arm towards the upper arm. This movement is important for activities such as lifting, carrying, and climbing.
- Supination of the forearm: The biceps muscle also helps to rotate the forearm so that the palm faces upwards. This movement is important for activities such as turning a doorknob or holding a cup.
- Stabilization of the shoulder joint: The biceps muscle helps to stabilize the shoulder joint by attaching to the scapula (shoulder blade) and helping to keep the arm in place when it is being used for activities such as lifting or throwing.
- Maintaining posture: The biceps muscle helps to maintain good posture by pulling the shoulder blade down and inwards, helping to keep the shoulders from slumping forward.
How do the different muscles in Biceps work?
The biceps are made up of a pair of muscles that only have two joints between them where they may move together. At the shoulder joint, the two muscle heads interact in a way that is somewhat antagonistic to one another.
When the long head is present, the arm will abduct (move away from the trunk) and rotate inwards (inward rotation). On the other hand, when the short head is present, the arm will adduct (move toward the trunk) (adduction). Because both heads are contracting at the same time, the arms will bend as a result (flexion).
The muscle is responsible for flexing (bending) the elbow and rotating (turning) the forearm outward at the shoulder (supination). Supination is performed most effectively with the elbow in a flexed position.
In addition to their involvement in the movement, the biceps contribute to the stability of the humeral head within the shoulder joint by helping to maintain its position. The triceps brachii, which may be located in the rear of the upper arm, is the muscle that acts as its antagonist.
Biceps Conditions
- Biceps strain: A pulled biceps results from overstretching and tearing some of the biceps muscle fibers and/or tendons. Pain and sometimes swelling are the usual symptoms.
- Proximal biceps tendon rupture: A condition in which one of the two biceps tendons in the shoulder is torn away from the bone. Symptoms like sudden shoulder pain and an odd-shaped bulge in the biceps are commonly observed.
- Distal biceps tendon rupture: A tear of the biceps tendon at the forearm due to some injury is unusual. Symptoms like sudden pain over the front of the elbow and forearm weakness are commonly observed.
- Proximal biceps tendinitis (tendonitis): The Repeated use of the biceps or continuous problems in the shoulder can irritate the proximal biceps tendon causing Pain in the shoulder and the biceps.
- Biceps contracture: A condition in which the biceps remains in a permanent contracted state along with the elbow bent. A Biceps contracture may occur after a severe stroke.
- Biceps bruise: Muscle bruises occur when something hits the muscle with force without damaging the skin. They may occur when a person presses their arm against something during a workout. They could also be the result of a fall. Symptoms like swelling, stiffness, weakness, bluish and bruised coloring and a lump over the injury site.
- Brachial plexus injury: The brachial plexus is a group of nerves in the neck, arm, and hand that are responsible for feeling and movement. Damage to the musculocutaneous nerve, which runs down the length of the arm, can result in bicep pain and weakness. Symptoms like pain, weakness, numbness, severe loss of movement and pain throughout the arm and hands is usually seen.
- Humerus fracture: The humerus is the bone in the upper arm. A fracture of this bone can result in pain. It may also prevent arm movement. Symptoms likea person with a humerus fracture may experience in the upper arm and surrounding areas can be intense pain, swelling,stiffness and a feeling of weakness in the hand or wrist.
- Popeye deformity: This is due to the overuse of biceps muscle, repetitive motion of your biceps, sports injury and injury from a fall.The bulge in your arm will be visible if you have a complete tear in the biceps tendon.
Biceps Tests
- Physical examination: A healthcare clinician might learn more about a patient's biceps status by observing and palpating (feeling) the muscle in different situations.
- Computed tomography (CT scan): A computed tomography (CT) scan requires the use of a machine that takes a series of X-ray images, which is referred to as a CT scanner. After that, a computer uses the X-rays to create images of the biceps and the structures that are located nearby.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan): An MRI scan, which is another name for magnetic resonance imaging, is a diagnostic procedure that uses a strong magnet and a computer to produce detailed images of the biceps and the areas of the body that are adjacent to it. These images are used to diagnose medical conditionsSpeed’s test: When a health care provider applies pressure to an arm, the patient often grips hands with the provider and bends their elbow to a right angle. If you feel pain in your shoulder throughout the exam, it may be biceps tendinitis.
- Yergason’s test: When a health care provider applies pressure to an arm, the patient often grips hands with the provider and bends their elbow to a right angle. If you feel pain in your shoulder throughout the exam, it may be biceps tendinitis.
- Biceps ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves are generated by reflecting a device placed on the skin off of the biceps' components. Medical professionals are able to observe internal body structures thanks to the signals being translated into visuals on a video screen. An ultrasound of the biceps might potentially reveal issues with the tendon.
- SERUM calcium test: The concentration of calcium in your blood is what a blood test for the mineral reveals. Bone illness, thyroid disease, parathyroid abnormalities, renal disease, and other medical diseases can all be indicators of either high or low blood calcium levels.
- Serum Urea and creatinine: They help identify the nitrogenous chemicals produced as a metabolic byproduct. The breakdown of ingested and cellular protein mostly results in the production of urea. Bone density is decreased when it collects as crystals in the bone.
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody: They are often high in rheumatoid arthritis, but can be high in other rheumatologic illnesses associated with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Computed tomography (CT scan)1: A blood test can detect the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF). Rheumatoid factor is an autoantibody produced by the immune system. Autoantibodies, such as RF, mistakenly attack healthy cells and tissues instead of pathogens.
- Computed tomography (CT scan)3: C-reactive protein (CRP) is an inflammatory marker that has been linked to increased fracture risk; however, earlier investigations on CRP and bone mineral density (BMD) have shown mixed results.
- Computed tomography (CT scan)5: A blood test can tell you how much vitamin D is in your body, so you can make sure you have enough for maximum health. Vitamin D is essential for healthy bones and teeth. In addition to improving your overall health, doing out on a consistent basis also keeps your muscles, nerves, and immune system in top shape.
- Computed tomography (CT scan)7: The most common and accurate way is with a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. DEXA uses low-dose x-rays.
- Bone mineral density (BMD): IT IS A test measures how much calcium and other types of minerals are in an area of your bone. This test helps your health care provider
Biceps Treatments
- Open reduction and internal fixation: It is a technique done when distal 1/3 of the humerus is fractured then the bone is displaced from its position due to which open reduction and internal fixation of the bone is done with exploration of the nerve to prevent its injury
- Closed reduction and slab: When fracture of humerus is occurred primary approach of treatment would be reduction of the fractured Part to it's original position and application of a slab two inhibit its further moment till the injury has been recovered
- Physiotherapy for myositis: Pressure and relaxation physical therapy is performed when there is inflammation of muscles of biceps it is only done by expert physiotherapist and it gives a result of a better prognosis even for those patients who have long time of injury
- Aeroplane splint: It is a splint used for treatment of erbs paralysis and klumpkes paralysis visually caused by neuropaxia . In this sort of treatment a split is placed and hand is glided in the motion of an airplane tilted upwards away from the medial position.
Biceps Medicines
- Antifungal medicines for biceps myositis: Antifungal drugs that can be either orally or administered topically to the affected area are effective in treating this condition. The antifungal medications luliconazole, itraconazole, clotrimazole, fluconazole, and others are a few examples.
- NSAIDs for reducing pain due to biceps pain: These medicines are prescribed for the relief of pain in different parts of the body. Common drugs such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium fall within this group. Anti-inflammatory drugs including ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, ketorolac, diclofenac, meloxicam, and celecoxib.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for osteomyelitis of humerus: Injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) into a joint, often the foot, release a cocktail of growth factors. PRP is commonly abbreviated as 'PRP.' Not only does this aid in inflammation reduction, but it also encourages the body's natural capacity to repair injured tissue.
- DMARDs for reducing pain of biceps: disease-modifying Rheumatic illnesses are remedied with anti-rheumatics. Disease progression can be halted by treatment. This medication is used to treat autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis. Medications including methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib fall under the category of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Nutritional supplements for promoting bone growth of humerus: Joint pain may be alleviated and the healing process sped up with the use of nutritional supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin, which are commonly given by doctors. Calcium and vitamin D supplements could be suggested. In the form of chole-calciferol.
- Pregabalin for reducing peripheral pain of biceps : It is an anticonvulsant used to alleviate neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia symptoms. It is effective in the treatment of both generalised and partial-onset seizures when taken in conjunction with other anticonvulsants.
- Bisphosphonates for bone growth in biceps : They are a class of drugs that can halt or markedly delay the deterioration of bone mass, a process that these drugs target. Bisphosphonates are used primarily to block the activity of osteoclasts, the bone cells responsible for the resorption and reabsorption of minerals like calcium (the process is known as bone resorption). Zolidronic acid. In addition, alendronate and risedronate are frequently used.
- Hyperuricemia treatment drugs for treating gout symptoms of biceps : There is a family of medications that can prevent or significantly slow the loss of bone mass. The primary function of bisphosphonates is to inhibit the function of osteoclasts, the cells in bone responsible for the removal and replacement of minerals like calcium (the process is known as bone resorption). Common treatments include the use of drugs like risedronate, alendronate, and zoledronic acid.
- Antibiotics for osteomyelitis and myositis of biceps: Antibiotics are used to treat myositis and other bacterial illnesses that affect the muscles of the foot. One of the most common reasons patients need antibiotics is cellulitis. Antibiotics like vancomycin and the cephalosporins are two common types.
- Corticosteroids for biceps : In some cases, doctors will prescribe cortisone-like drugs like prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone to patients with certain forms of myositis that manifest in the foot muscle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What 3 muscles make up the biceps?
What are the types of biceps?
What are the symptoms of bicep tendonitis?
What causes bicep tenosynovitis?
How to Increase biceps?
How fast do biceps grow?
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors