Integumentary System (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
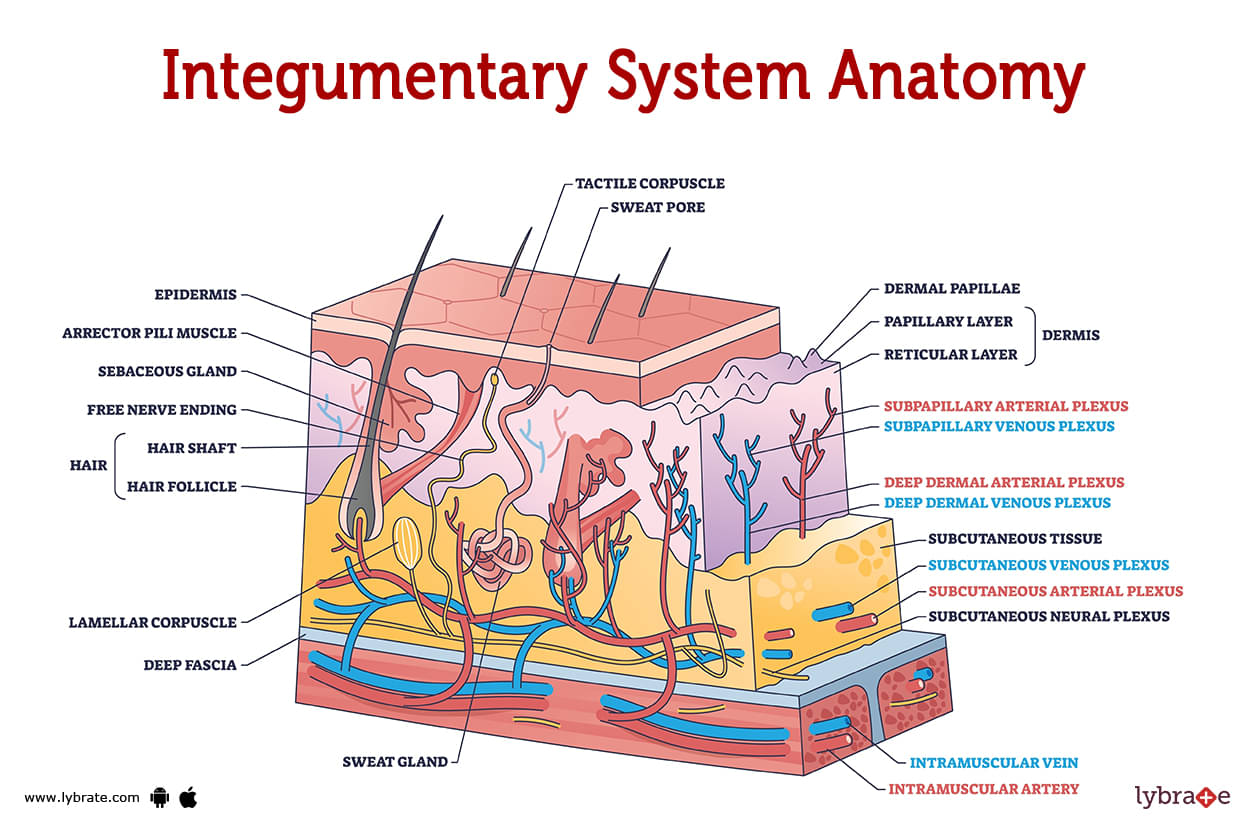
Integumentary System Image
The integumentary system is the layer of your body that is most exposed to the environment. It include the glands, hair, and nails in addition to the skin. These organs and structures serve as your first line of protection against bacteria and aid in injury and sun protection. Your integumentary system collaborates with other bodily systems to maintain balance.
Integumentary System Functions
Your integumentary system safeguards your body against infections and externally-caused injuries. It serves as the first protective barrier against viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms. It protects your body from damaging light and aids in temperature regulation.In addition to storing fat, water, glucose, and vitamin D, your integumentary system also plays a role in the immune system's ability to fend off disease.
Your integumentary system serves many crucial purposes, including the following:
- Offers physical defence against germs and bacteria.
- Absorbs and aids in the healing of cuts, abrasions, and other wounds.
- Defends your body against infection and cushions it.
- Shields you from sunburn and ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
- Keeps you cool by regulating your body temperature.
- Helps you detect other sensations, such as heat and cold.
- manufactures vitamin D.
Integumentary System Conditions and Disorders
- Eczema: Eczema is a condition that affects the skin and is characterised by itchy, red, and dry areas of skin. It is most frequent on the scalp, face, hands, and feet, as well as the neck and feet.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that manifests on the skin as red areas that are covered in silvery scales. A hyperactive immune system is the root cause of this condition, which manifests as a fast accumulation of skin cells on the surface of the skin.
- Skin Cancer: Cancer of the skin is a kind of illness that affects the skin. The majority of cases may be traced back to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or tanning beds.
- Dermatitis: Dermatitis is a broad term for any kind of skin inflammation. It is generally triggered by allergies or things that irritate the skin, and it can be short-term or long-term.
- Melanoma: It is a form of skin cancer that starts in the skin's pigment cells. It's the deadliest kind of skin cancer.
- Acne: Clogged pores, breakouts, blackheads, whiteheads, as well as other skin blemishes are hallmarks of acne, a common skin condition.
- Burns: Hot liquids, electricity, and scalding water are just a few of the many potential sources of burns.
- Scars and Keloids: Scars are marks on the skin that are left behind after a wound has healed. Keloids are scars that are raised and thick, and their disappearance may take several months or even years.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis causes red, scaly skin patches. Overactive immune system causes rapid skin cell buildup.
- Sunburn: Burning from too much exposure to the sun's ultraviolet radiation, also known as sunburn, is the medical term for this condition.
- Cold Sores: Cold sores are contagious lip ulcers. They're virus-caused and treatable with OTC drugs.
- Bedsores and Stretch Marks: Bedsores can develop on the lower back, buttocks, and thighs. Stretch marks appear when skin elasticity is damaged.
- Calluses: On the hands and feet, calluses are clumps of thick, hard skin. They typically result from ongoing friction with something rough, like a rock, branch, or tile.
- Lice and Nits: The parasitic, microscopic lice dwell on the hair. They may result in scalp issues and excruciating itching. Nits, which are microscopic louse egg fragments, are visible on the hair.
- Fungal (Tinea) Infections: Ringworm, athlete's foot, and jock itch are just a few of the many microorganisms that can result in fungal (tinea) infections, which are widespread.
- Calluses: Calluses are thick, rough skin patches that develop on the feet and hands. Continuous contact against anything rough, such as a rock, branch, or tile, frequently causes them.
- Impetigo: Impetigo is a skin illness that can be passed from person to person and is characterised by swollen, red areas of skin. The chest, the neck, and the face are the regions that are most frequently afflicted.
- Edema: Edema is a fluid accumulation in tissues and organs. Multiple illnesses, notably congestive heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease, can cause it.
- Diarrhoea: Diarrhoea is a condition marked by water and food (or occasionally blood) diarrhoea.
- Lymphedema: Lymphedema is a condition in which excess fluid collects beneath the surface of the skin.
- Petechiae: Petechiae are little, red patches that form on the skin after being injured. If the skin exhibits petechiae, it is bleeding. If you have been harmed and notice petechiae on your skin, do not try to cure them on your own. Instead, you should consult with your doctor as soon as possible.
- Sebaceous cyst: Sebaceous cysts are fluid-filled sacs that commonly manifest on the face, neck, and chest. Acne and other cosmetic issues are a direct result of enlarged sebaceous cysts. Surgery is the typical treatment for sebaceous cysts.
Integumentary System Tests
- Auscultation: Listening to the body's organs and tissues through a process called auscultation. Auscultation can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including fever, chest pain, and heart disease.
- Biopsy: A little piece of tissue is removed during surgery in a process known as a biopsy.To diagnose cancer or to check for skin cancer, for example, a biopsy may be necessary.
- Palpation: Palpation refers to the process of using one's hands to sense the the body's surface in order to diagnose and treat medical conditions. A person's temperature, the presence or absence of chest pain, and the presence or absence of a cardiac ailment can all be ascertained through the use of palpation.
- Capillary Refill Test: The CAPILLARY Refill test is a laboratory test that measures the amount of haemoglobin in the blood by using a very tiny amount of blood. The capillary refill test is employed for the purpose of making a diagnosis of hematologic conditions like anaemia and thrombocytopenia.
- Skin patch test: The skin patch test detects skin allergies with a little dose of medicine. The skin patch test can detect allergic rhinitis, asthma, or contact dermatitis.
- Wedge biopsy: A little piece of tissue is extracted from the centre of a lesion. A wedge biopsy may be required to diagnose a disease, malignancy, or skin cancer.
- Culture: The process of cultivating microorganisms involves the usage of a substance. Culture can be used to identify a disease's origin, identify a malignancy, or check for skin cancer.
- Diascopy: Using a microscope to view within the body is known as a diascopy. The results of a diascopy can be used to establish whether a patient has a fever, chest discomfort, or a cardiac disease.
- Dermoscopy: Dermoscopy is the examination of the skin's surface using a microscope. Dermoscopy can be employed to diagnose contact dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, or allergic asthma.Tzanck test: The Tzanck test is a laboratory test that employs a chemical to quantify the quantity of perspiration in sweat droplets. The Tzanck test is used to determine whether a sweat gland condition, such as apocrine hypersecretion or hyperhidrosis, exists.
Integumentary System Treatments
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a kind of treatment that employs a laser to remove acne-causing cells. Combining laser therapy with additional therapies, such as topical applications or surgery, is possible.
- Steroid therapy: Steroid therapy is a medical procedure that decreases the size of sebaceous cysts by using steroids. Combining steroid medication with other therapies, like the laser therapy or surgery, is possible.
- Skin graft: During a skin graft, a piece of skin from one part of the body is taken and put on the the skin's surface on another area of the body. A skin graft might be needed to fix a wound or replace a layer of skin that has been lost.
- Escharotomy: Escharotomy is a type of surgery in which a cut is made in the top layer of skin. Escharotomy might be used to get rid of a tumour, a cyst, or a piece of skin.
- Fluid resuscitation: Fluid resuscitation is giving a dehydrated person liquids like water or saline to get them back to normal. Fluid resuscitation may be required to alleviate dehydration caused by a disease, surgery, or the heat and humidity of summer.
- Moh's micrographic surgery: In Moh's micrographic surgery, a tiny slice of skin is removed and examined for cancer cells using a microscope. Moh's micrographic surgery may be required for lesion excision, cancer diagnosis, or skin cancer staging and evaluation.
- Surgical excision of sebaceous cyst: A lesion on the skin is eliminated by surgery known as surgical excision of sebaceous cyst. A sebaceous cyst may require surgical excision in order to be removed, to detect malignancy, or to be checked for skin cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy refers to a series of therapies for cancer that involve the use of chemicals to eliminate cancer cells. Combining chemotherapy with other therapies, such as radiation therapy or surgery, is often necessary in the fight against cancer.
- Radiotherapy: Radiotherapy is a form of treatment for cancer that involves the use of radiation in order to eliminate cancer cells. Combining radiotherapy with other types of treatment, such as chemotherapy or surgery, is one option that is available.
Integumentary System Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Integumentary System: Steroids shrink sebaceous cysts. Steroids can be utilised alongside laser therapy or surgery. Prednisone, dexamethasone, betamethasone, clobetasol, mometasone furoate are examples.
- Analgesics for pain in Integumentary System: Analgesics ease discomfort. Analgesics can be used alongside radiotherapy or surgery. Ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen, etc. are examples.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Integumentary System: Drugs called muscle relaxants lessen stiffness. The use of muscle relaxants in conjunction with other therapies, such as radiation therapy or surgery, is possible. A few popular muscle relaxants include lorazepam, vecuronium, and atracurium.
- Antibiotics for infection in Integumentary System: Medications that destroy germs include antibiotics. The use of antibiotics in conjunction with other therapies, such as surgery or radiation therapy, is possible. Cephalexin, erythromycin, doxycycline, and other commonly used antibiotics fall into this group.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in Integumentary System: Nutritional supplements are medications that are used to help the body perform better. Nutritional supplements could be combined with other therapies like radiation therapy or surgery. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulphate, MSM (methylsulfonylmethane), and other nutritional supplements are often utilised in this area.
- Supplements for growth promotion when the Integumentary System is injured: Supplements are medications that are consumed to enhance the body's function. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulphate, MSM (methyl sulfonyl methane), and other supplements are often used in this segment.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Integumentary System: Antivirals are medications that destroy viruses. Antivirals may be used with other therapies, such as radiation therapy or surgery. In this group, common antivirals include acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir, etc.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Integumentary System: Chemotherapeutic medications are those that eliminate cancer cells. Combining chemotherapy with other therapies, like as radiation therapy or surgery, is possible. Cisplatin, carboplatin, paclitaxel, and other chemotherapy drugs are often recommended in this group.
Table of content
Find Dermatologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors