Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Parathyroid Gland (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
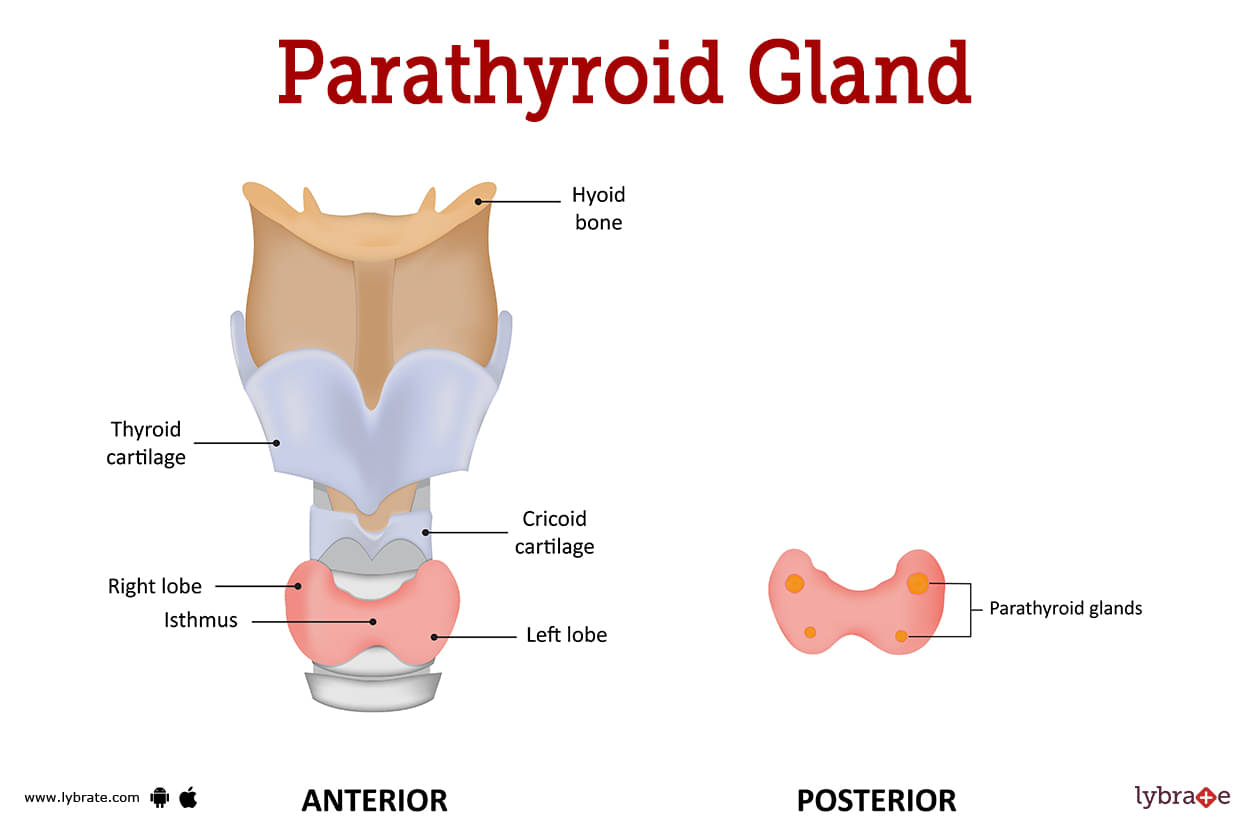
Parathyroid Gland Image
These glands, situated near the base of your neck beneath the thyroid, are roughly the size of a grain of rice. The parathyroid hormone generated by the thyroid glands aids in the maintenance of a normal calcium balance in the circulation and in tissues that rely on calcium for optimal function.
Parathyroid Gland Functions
- The following are some of the functions that are stimulated by the parathyroid hormone:
- Calcium is released from the bones and into the bloodstream.
- Absorption of calcium from food via the intestinal tract.
- Calcium storage accomplished via the kidneys.
- This causes the kidney cells to convert less potent forms of vitamin D into the form that is best able to absorb calcium from the intestines, and it does this by stimulating the cells.
Parathyroid Gland Conditions
- Hyperparathyroidism: Hyperparathyroidism (HPT for short) is the most prevalent disorder that may harm the parathyroid glands. People who have HPT may have hyperactive glands. PTH is produced in excess by the glands in response. In certain situations, this might result in hypercalcemia, a condition characterised by an abnormally high blood calcium concentration. The great majority of instances of hyperparathyroidism are caused by benign gland tumours.
- Hypercalcemia: Hypercalcemia is a condition in which there is an excess of calcium in the blood, which may lead to a hypercalcemic crisis, which can end in organ failure, unconsciousness, or even death.
- Hypocalcemia: Hypocalcemia is characterised as a blood calcium level that is unusually low, which might cause convulsions or tetany (severe muscle spasms).Cancer of the Parathyroid Glands: Parathyroid cancer causes HPT. This rare illness mostly affects 50-year-olds. Recurrence is when the cancer returns after treatment. Regulating blood calcium slows disease development. Early diagnosis is crucial. Hypercalcemia's health dangers and complications are often worse than cancer's.
- Hypoparathyroidism: Hypoparathyroidism is a lack of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Insufficient blood calcium results. Common reasons include neck surgery and parathyroid gland injury. Autoimmune gland attacks may potentially cause it.
- Hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands: Don't mix hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands with the illness known as hyperparathyroidism. All four parathyroid glands develop with hyperplasia, although there is no malignant growth (adenoma) present. The reason for this phenomena is unknown. Long-term usage of the psychiatric medication lithium has been associated with an increased risk of hyperplasia.
- Primary hypoparathyroidism: Primary hypoparathyroidism causes low parathyroid hormone levels. Hypoparathyroidism patients frequently have hyperparathyroidism (PTH). PTH regulates and maintains a healthy calcium and phosphorus balance in the body.
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: This kind of hyperparathyroidism arises when another disorder reduces calcium levels. As the body maintains a normal calcium level, parathyroid hormone levels grow. This is a frequent sign of renal failure and bowel problems.
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism: PHP, also known as pseudohypoparathyroidism, is an inherited disorder in which the body does not react correctly to parathyroid hormone. Hypoparathyroidism may occur in conjunction with hyperparathyroidism. This disease is characterised by insufficient parathyroid hormone production.
- DiGeorge syndrome: The fallopian tube is only one of several bodily systems affected by the chromosomal disorder known as DiGeorge syndrome. There is a wide range of diversity even among members of the same family.
Parathyroid Gland Test
- One densitometry (also known as DEXA or DXA): Bone densitometry, also known as dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or digital subtraction x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), creates photographs of the body's interior (often the lower spine and hips) to assess bone loss. We can determine whether or not the patient has osteoporosis using these photos. DXA is simple to use and produces no pain to the patient.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to create pictures of organs and structures within the body. Because ultrasound is non-invasive and does not entail the use of radiation, it is risk-free.
- Body computed tomography (CT): CT scans produce three-dimensional (3-D) images by combining x-rays and computer technologies. In certain cases, a contrast agent may be delivered to a patient before to a CT scan. A CT scan involves the patient lying down on a table that slides into a tube-like machine where they are exposed to x-rays.
- M.R.I.: The phrase 'body MRI' refers to a form of magnetic resonance imaging that uses radio waves, a massive magnetic field, and a computer to create high-resolution pictures of the interior of a patient's body.
- Blood test for 25-hydroxyvitamin D: Primary HPT patients usually have inadequate vitamin D levels. With the use of this test, your doctor will be able to monitor the levels of vitamin D in your blood and decide whether you need supplements.
- Four-dimensional computed tomography: Four-dimensional computed tomography, or 4DCT, is a more thorough imaging tool for assessing the parathyroid gland than standard CT. This is made feasible by administering contrast material at a specified rate and for a particular period of time. When earlier imaging examinations have failed to reveal the abnormal gland, 4DCT may be quite useful.
Parathyroid Gland Treatment
- Parathyroidectomy: this is a special form of surgery in which The surgeon will remove the overactive gland after making a tiny incision in the patient's neck. Local anaesthetic or general anaesthesia may be used. As a consequence of this procedure, the patient will feel less pain. It also offers a quicker recovery period when compared to more invasive operations.
- Lymphadenectomy: Lymph nodes are taken from the neck during a neck dissection, commonly known as a lymphadenectomy. If the imaging tests show that the lymph nodes are cancerous, the surgeon will do this surgery. Any bigger lymph nodes that are discovered during surgery will be removed.
- Replacement of fluids: Rehydrating the body with fluids helps alleviate dehydration (the loss of too much water). Dehydration is a common symptom of hypercalcemia patients. After the patient has been rehydrated, diuretics such as furosemide are often administered to increase the amount of calcium that is passed out of the kidneys and into the urine.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation treatment kills cancer cells by exposing them to high-energy radiation or particles. It is not a frequent therapy for parathyroid gland cancer. In most cases, radiation treatment is ineffective in treating parathyroid cancer (it is not radiosensitive). However, since parathyroid carcinoma is so rare, it is impossible to say if radiation treatment may assist treat certain forms of the illness. This is due to the fact that researchers can only investigate a limited number of patients at one time.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells by employing cytotoxic chemicals. It's a rare parathyroid cancer therapy. Chemotherapy seldom cures parathyroid cancer. It might also be used to treat metastatic or recurrent parathyroid cancer in patients who cannot undergo surgery. Chemotherapy helps achieve remission, but only temporarily.
Parathyroid Gland Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Parathyroid Gland: Drugs having anti-inflammatory qualities, such as the corticosteroids methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone, and dexamethasone, reduce inflammation, particularly in the parathyroid gland region, by limiting the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to regions of cellular and tissue damage.
- Analgesics for pain in Parathyroid Gland: You may find some relief from the pain associated with inflammation of the parathyroid gland by taking an analgesic, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen.
- Antibiotics for infection in Parathyroid Gland: Drugs called antibiotics are given to patients with bacterial infections that have spread to the parathyroid gland supporting muscles in the neck. Vancomycin for Gram-positive staining bacteria, third-generation cephalosporins for Gram-negative staining bacteria, and other options can also be used
- Supplements for promotion of growth at the time of fracture of Parathyroid Gland: Vitamin B complex, cyanocobalamin, and lycopene are all examples of nutritional supplements that may also be used medicinally.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Parathyroid Gland: Rhinitis and other rhinovirus infections are treated with antiviral medications like oseltamivir or inhaled zanamivir.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Parathyroid Gland: The drugs used in this chemotherapy regimen include cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and 5-fluorouracil. After that, radiation therapy will be administered to the chest.
- Diuretics: Drugs in this class are used to treat a variety of conditions, including edema, cirrhosis, and hypertension, that cause fluid retention. Diuretics including aldactone, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and metolazone are often used by doctors to treat parathyroid edema.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do you fix parathyroid disease?
Parathyroid diseases can be fixed by medications, home remedies and surgery.
How does parathyroid disease make you feel?
Parathyroid diseases may cause symptoms like weakness, irritation, fatigue and pain.
What is the treatment for parathyroid?
Surgery is the treatment for parathyroid.
How do you treat parathyroid gland naturally?
Parathyroid can be treated naturally by taking a healthy diet, doing exercises, and avoiding smoking and drinking.
Is parathyroid disease serious?
The parathyroid condition is indeed dangerous.
What causes high parathyroid?
A calcium deficit, vitamin D insufficiency, and kidney issues can all contribute to high parathyroid levels.
What diseases affect the parathyroid gland?
Diseases affecting the parathyroid gland are high blood pressure, osteoporosis, stones and heart problems.
What are the signs and symptoms of parathyroid disease?
Symptoms of parathyroid disease are abdominal pain, kidney bones, fatigue, joint pain, weakness and osteoporosis.
How long does parathyroid gland take to heal?
It takes approximately a month to heal the parathyroid gland.
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Endocrinologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously