Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Knee (Human Anatomy): Function, Parts, Diseases, Treatments
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
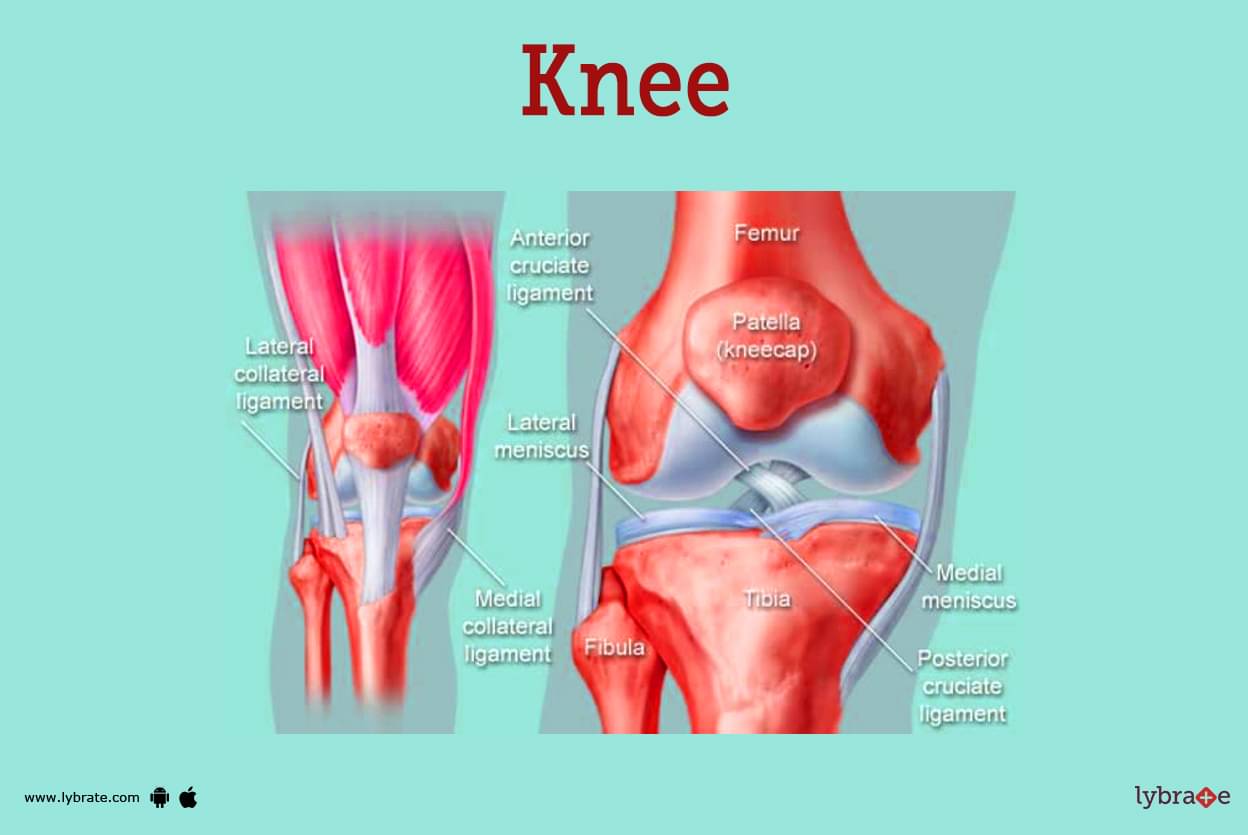
Knee Image
- The knee joint is one of the most complicated and largest joints in our body. It connects the largest bone, the femur, to the smaller bones of the shin, the tibia and the fibula. The kneecap, also known as the patella, can be found in the leg.
- Tendons are a type of connective tissue that connects the muscles of the leg to the bones of the knee, whereas ligaments are responsible for providing the knee joint with stability by connecting other muscles that are located in close proximity to the joint.
- The anterior cruciate ligament is the one that prevents the femur from sliding posteriorly on the tibia, and the posterior cruciate ligament is the one that prevents the femur from sliding anteriorly. Both of these ligaments are located in the middle of the knee joint. The medial and lateral collateral ligaments prevent the femur from sliding in either direction when they are in place.
- The shock absorber cartilage in the knee joint is made up of the medial meniscus as well as the lateral meniscus cartilage. Both of these are located in the knee joint. These two cartilages contribute to the C-shaped appearance of the knee joint.In the knee joint, there are a number of bursae as well as fluid-filled sacs, both of which contribute to the knee's ability to move easily and without friction.
Knee Functions
The knee is a hinge joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). It is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body, and it plays a vital role in movement and stability. The main functions of the knee are as follows:-
- Knee support the weight of the body: The knee is responsible for supporting the weight of the body, particularly when standing, walking, running, or jumping. It does this by distributing the load across the joint and the surrounding muscles and ligaments.
- Allow for movement: The knee is a hinge joint, which means that it allows for movement in one plane (flexion and extension). This allows us to perform activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
- Knee Provide stability: The knee is also responsible for providing stability to the leg and preventing it from collapsing. It does this through the use of muscles, ligaments, and tendons, which work together to keep the joint aligned and stable.
- Knee Absorb shock: The knee is designed to absorb shock, particularly when we walk or run on uneven surfaces. It does this through the use of cartilage, which cushions the joint and helps to distribute the load evenly across the bone.
- Knee Helps in Maintain balance: The knee plays a role in maintaining balance, particularly when we are standing or moving. It does this by coordinating with the other joints and muscles in the leg and adjusting the position of the leg to maintain a stable base of support.
Knee Conditions
- chondromalacia patella: This condition is also referred to as patellofemoral syndrome in some circles. When this condition is present, the patient will have complaints of irritation in the cartilage that is located around the kneecap. Therefore, resulting in discomfort in the knee. It is the factor that contributes to knee discomfort in younger people the most frequently
- Osteoarthritis Of The Knee: Osteoarthritis is almost always brought on by arthritis. Knees are the typical joint affected by osteoarthritis. The most common cause of osteoarthritis is simply getting older, which leads to cartilage degeneration and wear and tear. Pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee are the three symptoms of knee osteoarthritis that are most commonly experienced.
- Knee Effusion: knee effusion is a condition that affects the knees and is characterised by inflammation brought on by the buildup of fluid within the joint, which can be the result of an injury or arthritis.
- Meniscal Tear: A meniscal tear is a condition that affects the knee and is characterised by damage to the meniscus cartilage of the knee. This damage most commonly results from twisting the knee, because the meniscus cartilage functions as a shock absorber. Should there be significant damage, the knee joint may become immobilised as a result.
- A Strain On The Acl: A strain or tear of the anterior cruciate ligament is another name for this condition. In light of the fact that the anterior cruciate ligament is responsible for providing the knee joint with stability, any damage to this ligament may result in the knee bulging out, a condition that can only be remedied through surgical intervention.
- Pcl Strain: The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) has been damaged as a result of the strain. When an injury occurs in the posterior cruciate ligament, the most common symptoms that manifest themselves are a loss of knee stability, swelling, and pain. On the other hand, tears of the ACL are far more common than this injury. When treating an injury of this nature, physical therapy is the more effective course of action than surgical intervention.
- Mcl Tear: A tear in the medial collateral ligament (also known as an MCL tear) occurs when the ligament sustains an injury.The two most common symptoms associated with this condition are knee pain and instability on the inner aspect of the affected knee.
- Patellar Subluxation: Patellar subluxation is a condition in which extreme knee pain is experienced as a result of an abnormal dislocation of the knee cap from its normal position toward the thigh bone. This dislocation is brought on by some kind of activity.
- Patellar Tendonitis: Patellar tendonitis is an inflammation that occurs in the tendon that connects the patella to the shin bone. This condition is known as a knee tendonitis. This condition manifests itself most frequently in athletes who participate in high jump competitions.
- Knee Bursitis: Bursitis of the knee is characterised by pain, inflammation, and warmth in the bursae that are located in the knee. This condition is known as knee bursitis. Bursitis is almost always the result of an injury of some kind.
- Baker's Cyst: Baker's cyst is a condition of the knee in which a collection of fluid occurs in the posterior region of the knee. This condition is known as Baker's cyst. This is due to the constant effusion that can be caused by conditions such as arthritis.Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a form of arthritis that can affect any joint, but most commonly affects the knee joint. It is an autoimmune disorder that causes arthritis. In the event that this condition is not treated, it has the potential to cause irreversible damage to the knee joint.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis that causes an accumulation of crystals made of uric acid in the knee joint, which results in excruciating pain and swelling of the knee joint. Gout is one of the varieties of arthritis.
- Pseudogout: It is a form of arthritis that is typically very similar to gout; however, it is caused by the accumulation of crystals of calcium as well as pyrophosphate in the knee joint, which results in excruciating pain and inflammation of the knee joint.
- Septic Arthritis: Septic arthritis is a type of arthritis that can be caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection inside of the knee joint. This type of arthritis causes the knee to become inflamed, painful, and swollen, and it can make it difficult to move the knee. If these diseases are not treated, the conditions quickly deteriorate into a more serious state.
- Patellar: A knee injury caused by a direct blow that results in immobilisation of the knee joint.
- Genu Valgum: It is knock knees, according to Genu Valgum. The normal range between the ages of 4 and 7 years old.
- Popliteal: Posterior knee dislocation, tibial plateau fracture
- Lumbosacral Radiculopathy (L3 -L4): Herniations typically occur posterolaterally, affecting nerve root below level of disc herniation, which results in Weakness of knee extension and weak patellar reflexes. Lumbosacral Radiculopathy (L3 -L4), Herniations usually occur posterolaterally, affecting nerve root below level of disc herniation.
- Radiculopathy (L3 -L4): Herniations usually occur posterolaterally, affecting nerve root below level of disc herniation.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS): It is an overuse injury of the lateral knee. Athletes, runners, and cyclists are prone to developing this condition.
- Patellofemoral Pain: Pain in the patellofemoral joint, which is located behind the patella, is a common source of knee pain, especially in young adults.
Knee Joints Test
- Physical Examination: Examine the patient's knee and look around the area for any swelling or abnormal movement as part of the physical exam to determine the source of the patient's knee pain. During this examination, the doctor will collect all of the information about the factors that contribute to the knee joint becoming damaged or stressed.
- Drawer Test: It is the condition in which the physician makes the patient bend the knee join by pulling which is anterior drawer test or by pushing which is posterior drawer test, the lower leg while holding the foot, which checks the stability of the knee ligaments of the ACL and PCL.
- Valgus Stress Test: This refers to a condition in which the doctor will push the calf muscle outward while maintaining a stable position with the thigh in order to locate the injury in the medial collateral ligament (MCL).
- Varous Test: Pushing the calf muscle inward is one of the many tests that can be performed to determine whether or not there is an injury to the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
- Knee X-Rays: These X-rays are bombarded on the knee to determine the condition of the knee's joints in the early stages of treatment. Because X-rays cannot penetrate bones, they are used in this manner.
- M.R.I: Imaging by means of magnetic resonance is a common name for it. In this procedure, the knee joint is subjected to a barrage of high-energy magnetic waves in order to obtain a clear image of the knee joint. In order to get a clear picture of the injuries sustained by the ligaments and meniscus, an MRI is typically performed.
- Knee Arthrocentesis: In some circles, it is also referred to as joint aspiration. In this test a needle is inserted in knee joint space by the physician and the fluid present inside is drawn out to diagnose the various types of arthritis of knee joint.
- Arthroscopy: It is a surgical procedure of the knee joint that allows the physician to examine the knee joint through the use of an endoscope. This procedure is known as arthroscopy.
- Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan: This test, known as a computerised tomography (CT) scan, is able to diagnose diseases such as gout even when there is no inflammation present in the joints. During this test, high frequency waves will be bombarded, and a clear picture will be obtained with the assistance of a computer.Ultrasound: The ultrasound procedure involves the application of sound waves to the knee joint in order to obtain a real-time image of the soft tissues that surround the knee joint.
Knee Treatments
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Surgical procedures using an arthroscope: The purpose of this operation is to treat damaged cartilage, to remove loose tissue from the body, and to reconstruct torn ligaments. It is performed by practitioners. During this procedure, a tiny incision is first made, then a fibre optic camera is inserted into the joint, and finally the procedure itself is carried out.
- Partial Knee Replacement Surgery: Surgery for a partial knee replacement involves replacing only the most severely damaged portion of the knee with artificial components made of plastic or metal. In most cases, this is accomplished by making a very small incision. The knee's damaged tissues will heal more quickly as a result of this process.
- Total Knee Replacement: During total knee replacement surgery, the surgeon replaces the patient's damaged bone (the shin bone, tibia, fibula, or patella) with an artificial metal, alloy, or plastic joint. This procedure is intended to restore the patient's knee to its normal function.
- Osteotomy: This is a surgical procedure that is typically done to alleviate the pain of arthritis. If performed at the appropriate time, this procedure can prevent the need for a total knee replacement. During this procedure, either the shin bone or the femur will be cut out and realigned in order to correct alignment issues that may be causing knee problems.
- Compression: In this treatment method, a bandage is applied and wrapped around the area of the knee that is inflamed. This helps ensure that everything is aligned correctly. Aids in the speedy recovery of wounds. In addition to this, it helps in the process of eliminating inflammation.
- Elevation: During this stage of the procedure, the patient's leg is propped up at an angle, which improves blood circulation in the leg. Therefore, as a consequence, this leads to a reduction in the inflammation around the knee joint.
- Heat: Patients who are experiencing knee inflammation may find some temporary relief if heat packs are applied to the area around the joint.
- Ice: The application of ice as part of a therapeutic procedure can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. However, it is recommended. However, it is recommended that you do not continue doing it for longer than 20 minutes because it may cause damage to the skin or nerves that are associated with that area.
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation: In this procedure the cells of cartilage are collected and multiplied in the laboratory and implanted in the damaged area of the knee which helps in healing.
Knee Medicines
- Corticosteroids: In this treatment, an injection containing corticosteroid is injected into the knee joint. This helps to reduce the inflammation that is present in the knee joint. It can also be used to alleviate certain types of arthritis. Having said that, there are times when it is beneficial.
- Hyaluronic Acid: This is a viscous fluid that is comparable to the fluid that is present in tissue and is known as hyaluronic acid. This treatment with hyaluronic acid helps in the knee joint to move more easily and is performed by injecting fluid into the knee joint. In addition, it assists in relieving the pain that is associated with the knee joint. It might even last as long as half a year.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a combination of many growth factors that are injected into the knee joint. This helps to get rid of inflammation, and it also promotes the healing of damaged tissues. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a combination of many growth factors. Osteoarthritis, according to some reports, is another condition that can benefit from PRP treatment.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are a type of medication that belongs to the class of drugs that are prescribed by medical professionals to treat conditions that are brought on by bacteria. Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic medicine that is used to halt the progression of bacterial illness.
- Antiviral Medications: Medications like darunavir, atazanavir, and ritonavir are used to treat viral diseases and the deformities that are associated with them, such as when they affect the knee joint.
- Antifungal Medications: This medicine belongs to a certain class and are typically prescribed for the treatment of fungal infections of the leg. Both nystatin (also known as Nystatin) and amphotericin are examples of medications that belong to this class.
- Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is an excellent medication for relieving the discomfort associated with mild knee aches.
- NSAIDs: NSAIDs, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are a category of medication that is used to treat aches and pains in the knee as well as in other areas of the body. In our bodies, it can also be used as a treatment for fevers. Ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium are examples of typical medications that fall into this category.
- Ointments and Creams: These creams are intended to be applied topically to the skin. This medicine provides pain relief that is effective but only lasts for a short period of time. Medicines belonging to this class that are commonly used include salicylates, counterirritants, and capsaicin.
- DMARDs: DMARDs, which stands for disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. This class of medication is prescribed to patients suffering from autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis in order to alleviate their pain. Common disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) that are currently on the market include methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib.
- Nutritional Supplements: Physicians provide nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin to decrease the pain of person and boosten the healing process in joints.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the parts of the knee?
The four basic components of your knee are bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
What are the common problems with knee?
Tendonitis, cartilage tears, sprained or strained ligaments, and arthritis are all common knee issues.
What are 4 causes of knee pain?
Age-related issues, injuries, or repetitive stress on the knee are the most frequent causes of knee discomfort.
What kind of knee pain is serious?
If there is significant swelling along with your knee discomfort or if it was brought on by a particularly hard hit, redness, warmth and tenderness around the joint, it is necessary to see the doctor right away.
What are signs of knee damage?
The symptoms of knee damage include swelling and stiffness, redness and warmth to the touch, weakness or instability, popping or crunching noises, and the inability to fully straighten the knee.
What is the fastest way to relieve knee pain?
With the proper physical treatment, knee discomfort can be swiftly relieved without the use of uncomfortable injections or medications.
How can I strengthen my knees?
Your knees can be strengthened by performing knee bends, thigh contractions, straight leg raises, and hamstring stretches while contracting your thighs.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously