Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Ankle (Human Anatomy): Picture, Function, Diseases, & More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
Ankle Image
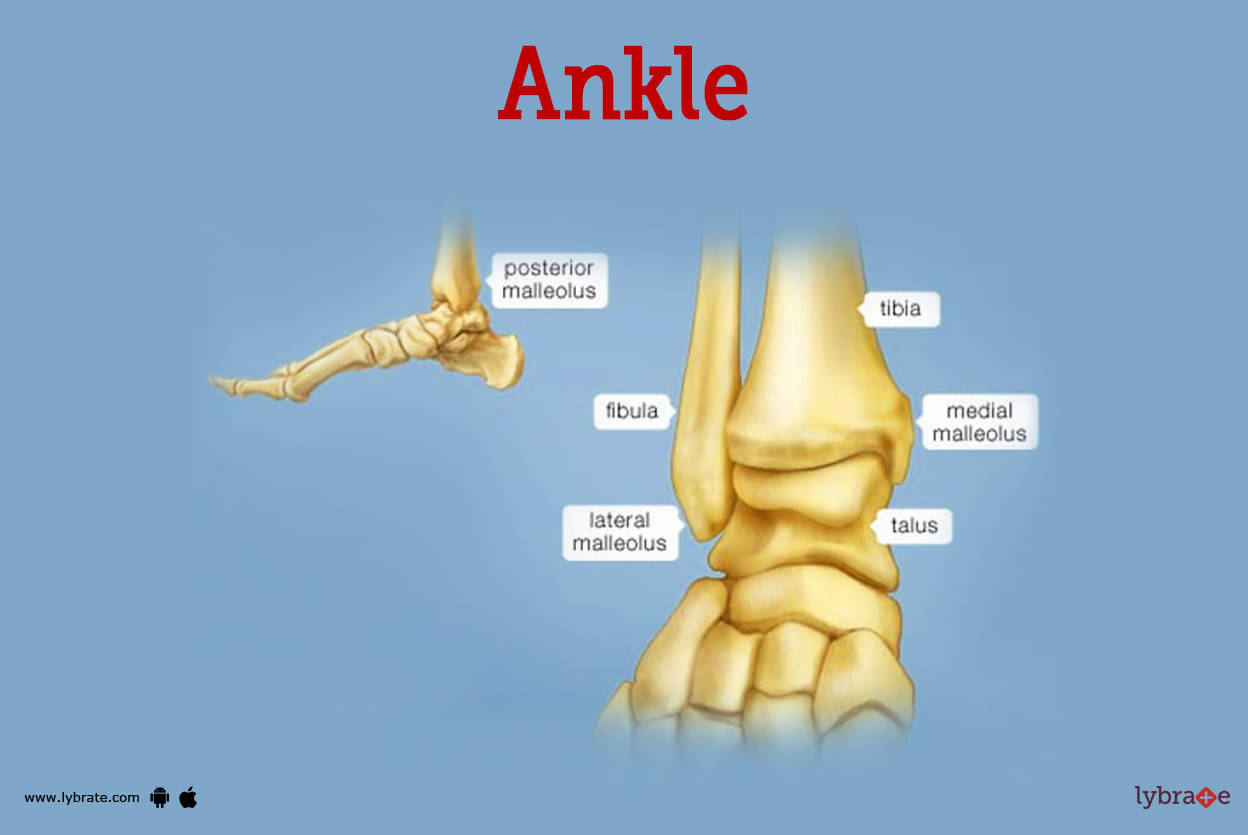
- The ankle, also known as the talocrural region or the jumping bone (informally), is the joint between the foot and the leg. The ankle is made up of three joints: the ankle joint proper, also known as the talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint.
- There are three bones that come together to form the big joint that is the ankle. The bone that is found in the shin is tibia. The thinner bone that runs parallel to the tibia medically known as the fibula.
- A further bone in the foot that can be found directly above the heel bone (talus). The bony protrusions (or bumps) that may be seen and felt on the ankle each go by their own specific nomenclature.
- You can feel the medial malleolus on the inside of your ankle. It is a component of the base of the tibia. The posterior malleolus, which you can feel on the rear of your ankle, is also a portion of the base of the tibia.You may feel the lateral malleolus, which is the low point of the fibula, on the outside of your ankle.
- The motion of the foot in an upward and downward direction is made possible by the ankle joint. The subtalar joint is located just below the ankle joint and enables the foot to move in a side-to-side motion.
- Around the actual ankle joint and the subtalar joint are a number of ligaments, which are tough bands of tissue with some degree of mobility. These ligaments are responsible for attaching the bones of the leg to each other as well as to the bones of the foot.
Ankle Functions
The main functions of the ankle include:
- Support Body Weight: The ankle helps to support the weight of the body, particularly when standing or walking.
- Maintain Balance: The ankle helps to maintain balance by allowing the foot to adjust to uneven surfaces and changes in movement.
- Propulsion: The ankle helps to propel the body forward when walking or running by pushing off the ground.
- Shock absorption: The ankle helps to absorb shock when the foot hits the ground, protecting the bones and joints of the foot and leg from impact.
Overall, the ankle is a crucial joint that plays a vital role in the movement and stability of the body.
Ankle Diseases
- Sprained Ankle: In most cases, a rapid movement of the foot is what causes a rupture in one of the ligaments that support the ankle. By making use of rehabilitative services in the future, one may be able to prevent experiencing pain and swelling.
- High Ankle Sprain: The lower leg bones (the tibia and the fibula) are connected by a ligament known as the syndesmotic ligament. This ligament, which has been injured, is responsible for connecting the two bones. A high ankle sprain and a true ankle sprain both induce pain and swelling in the ankle, however the recovery period for a high ankle sprain may be substantially longer than that of a real ankle sprain.
- Ankle Fracture: a broken bone in any of the three bones that make up the ankle (the talus, the talus, and the talus). The shin has both of these bones in separate locations.
- Ankle Arthritis: Even though it does not happen very often, osteoarthritis, which is the most prevalent form of arthritis, may cause damage to the ankle.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A kind of arthritis that is brought on by an autoimmune response in which the body attacks the tissue that surrounds the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling in the affected areas. Rheumatoid arthritis, which may manifest itself in any joint, can cause a variety of symptoms, including painful ankles.
- Gout: A kind of arthritis that is distinguished by the periodic deposition of crystals in the joints, which leads to considerable joint pain and swelling. This condition is known as gout. The ankle joint is a possible location for the manifestation of gout symptoms on occasion.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: There is a connection between psoriasis and this particular kind of arthritis, which is characterised by severe swelling of the joints. One of the joints that psoriasis has the potential to affect is the ankle joint. Psoriasis may also affect other joints.
- Septic Arthritis: This particular kind of arthritis advances quite quickly, and as a consequence, the afflicted ankle experiences severe pain, edoema, fever, and a restricted range of motion. It is speculated that bacterial infections that might manifest in the ankle are to blame for the condition.
- Tillaus-Chaput Avulsion Fracture: In most cases, the rotational or axial-loading stresses on the tibia bone that induce Tillaux fractures are the result of high-energy trauma, such as an accident involving a vehicle or motorcycle, a fall from a significant height, or an incident involving skiing.
- Gosselin Fracture: A fracture in the shape of a V in the distal tibia reaches all the way into the tibial plafond and separates the tibia into its anterior and posterior halves. The fracture can be found in the proximal region of the distal tibia.
- Pilon Fracture: Pilon fractures are breaks in the distal tibia that occur on the articular surface or the tibial plafond. These types of breaks are referred to as 'pilon fractures.' In most cases, the cause of these injuries is the axial stress that is placed on the weight-bearing surface of the tibia.
- Dupuytren Fracture: a fracture of the mid-distal fibula that is located above the syndesmosis and is accompanied by diastasis 1, an injury pattern that is now usually linked with further fractures.
- Bimallelar Fracture Of The Ankle: In order for a fracture to be classified as a bimalleolar equivalent, it is necessary for the medial (inside) ankle ligaments to be ruptured in addition to the malleoli.
- Salter Harris Fracture The growth plate in a child's bone may be broken, which is medically referred to as a Salter-Harris fracture. At the articular surfaces of the bones of a growing kid is an additional layer of developing tissue that is referred to as a growth plate. It is imperative that a diagnosis be established because of the possibility that it will have an effect on the growth of a kid.
- Shephards Fractures: The growth plate in a child's bone may be broken, which is medically referred to as a Salter-Harris fracture. It is imperative that a diagnosis be established because of the possibility that it will have an effect on the growth of a kid.
- Charcot Joints: Joint destruction known as Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy often begins with an injury to a nerve-damaged limb. Foot fractures and dislocations are possible consequences.
- Haglunds Deformity: For those unfamiliar, Haglund's deformity is a skeletal and soft-tissue foot anomaly characterised by an expansion of the bony portion of the heel at the site where the Achilles tendon enters.
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV): The developmental abnormality of the lower limb more often known as 'club-foot,' is rather prevalent but has received relatively little research attention. Fixation of the foot in the positions of adduction, supination, and varus that is, tilted inwards, axially rotated outwards, and pointing downwards is how it is referred to when discussing this condition.
Ankle Tests
- Physical Examination: An examination of the ankle by a medical professional may reveal the presence of an ankle fracture, a sprain, or another ailment.
- Ankle X-Ray: An X-ray film of the ankle is often taken while trying to diagnose a fracture, arthritis, or any number of other conditions that may affect the joint.
- Stress X-Ray: A film of an X-ray is taken as the physician applies pressure to an injured ankle. This procedure, which may identify ankle abnormalities that are not visible on standard X-rays, is also known as a stress film or a stress test.Magnetic Resonance Imaging (Mri Scan): The images of the ankle that are produced by an MRI scanner have a very high level of resolution since they are created using both a powerful magnet and a computer.
- Insall-Salvati Ratio: it is arguably the measurement that is utilised for determining patellar height more frequently than any other. It is impacted by the existence of tibial tuberosity anomalies (for example, Osgood-Schlatter disease, osteotomies), and when they are present, a different method may be necessary 4,5.
- Serum Calcium Test: A calcium blood test determines how much calcium is currently present in your blood. It is possible that a wide variety of medical issues, such as bone disease, thyroid illness, parathyroid abnormalities, renal disease, and other conditions, are present if the amount of calcium in the blood is either too high or too low.
- Serum Urea And Creatinine: They are useful in determining the nitrogenous compounds that are the final result of metabolism. Urea is the major metabolite that is formed from the turnover of protein in tissue and in the body's food. It accumulates in the bone in the form of crystals and reduces bone mineral density.
- Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (Anti-CCP) Antibody: Despite the fact that the levels can be high in other rheumatologic disorders linked with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, the levels are generally elevated in rheumatoid arthritis.
- RA Factor: The presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) can be determined using a blood test. The immune system creates an autoantibody called rheumatoid factor. Autoantibodies like RF target healthy cells and tissues rather than their intended targets, such as germs and viruses.
- CRP Levels: Despite the fact that prior research on CRP and bone mineral density (BMD) has produced mixed results, there is a correlation between increasing levels of the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (CRP) and an increased risk of fractures.
- SERUM VIT D3: To ensure adequate levels for optimal health, a blood test can determine the concentration of vitamin D in your system. Strong bones and teeth can only be maintained with enough vitamin D. In addition to its health benefits, regular exercise helps maintain your muscles, nerves, and immune system functioning regularly.
- Dexa Scan: A dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan is the method that is used most frequently and provides the most reliable results. Low-dose x-rays are used in DEXA imaging.
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD): Your health care practitioner can diagnose osteoporosis and estimate your likelihood of suffering a bone fracture with the help of this test. Your health care practitioner can diagnose osteoporosis and estimate your likelihood of suffering a bone fracture with the help of this test.
Ankle Treatments
- Rice Therapy: The acronym RICE refers to the treatment methods of Rest, Ice, Compression (using something like an athletic bandage), and Elevation. The RICE protocol is an effective first treatment for the majority of ankle injuries.
- Ankle Immobilization: For the majority of ankle fractures, immobilisation of the ankle, typically via the use of a cast is required. It is believed by certain professionals in the medical field that immobilisation may also aid with ankle sprains.
- Syndesmotic Screw: A screw is inserted by a surgeon to join the bones in the patient's lower leg. Because of this, the bones are held together, and the high ankle sprain is given time to heal. After the wound has healed, the screw will be removed.
- Ankle Arthroscopic Surgery: Ankle surgery in which instruments are placed via relatively tiny incisions in the patient's ankle. An endoscope is one of the instruments that gives the surgeon a view of the interior of the ankle joint that may be seen on a video screen.
- Ankle Fusion Surgery: The bones of the ankle will be fused together during surgery, therefore reducing the range of motion in the ankle. The excruciating agony of severe ankle arthritis might be alleviated via surgical fusion of the ankle.
- Ankle Replacement Surgery: In spite of the fact that certain orthopaedic doctors provide ankle replacement surgery, the procedure often yields less satisfactory outcomes than ankle replacement surgery.
- Chopart Amputation: Chopart amputation is a procedure that removes the forefoot and midfoot while leaving the talus and calcaneus intact; nevertheless, this procedure should not be performed in cases of ischemia
- Triple Arthrodesis: During a triple arthrodesis, the talocalcaneal (TC), talonavicular (TN), and calcaneocuboid (CC) joints of the foot are surgically fused together. This procedure is known as 'foot fusion.'. This surgery is also known as a talonavicular arthrodesis.
- Dilwyn Evans Procedure: In order to cure the mechanical instability of the lateral ankle ligaments, a surgical procedure known as the Evans method is performed. The Dilwyn Evans treatment is used to address clubfoot deformities (procedure).
- Pyogenic Osteomyelitis: Inflammation of the bone that is brought on by an infectious organism is referred to as acute pyogenic osteomyelitis. The staphylococcus aureus infection is the one that is most widely known.
- Ponseti Method: It has been suggested to use an expedited version of the Ponseti procedure, in which the manipulations, five casts, and Achilles tenotomy are all performed within a single week.
Ankle Medicines
- NSAIDs for Reducing Pain In The Ankle: As well as being used to treat aches and pains in other parts of the body, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are a family of medications that are used to address discomfort in the ankle. Examples of usual drugs that fit within this group are ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium. Naproxen Indomethacin with ibuprofen and also Diclofenac, Meloxicam and Celecoxib.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for Osteomyelitis Of Ankle: Platelet-rich plasma, often known as PRP, is a mixture of several growth factors that is injected into a joint, most commonly the ankle. This not only assists in reducing inflammation but also has a positive impact on the healing process of injured tissue.
- DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis Of Ankle: Patients who are suffering from autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis are often prescribed this class of drug in order to alleviate the pain that they are experiencing. Methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib are some of the disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (DMARDs) that are now available on the market.
- Nutritional Supplements for Fractured Ankle: Physicians provide nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin to decrease the pain of person and boosten the healing process in joints.Vitamin D and Calcium supplements are given as per age and deficiency of the requred elements for normal bone growth and metabolism.
- Pregabalin for Pain In Ankle Muscles: It is an anticonvulsant that is utilised in the treatment of fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. In combination with other anti-seizure medications, it can also be used to treat partial-onset seizures.
- Cortisone Injections For Reducing Osteomyelitis Of Ankle: When treating some types of ankle arthritis, cortisone injected into the ankle joint might be helpful. The inflammation in the ankle joint may be reduced and the associated pain alleviated with the use of cortisone.
- Bisphosphonates For Maintaining Bone Growth In Ankle: They belong to a class of drugs that can either stop or decrease the process of bone loss, making for stronger bones. Inhibiting osteoclasts, which are responsible for the removal and reabsorption of minerals such as calcium from bone, is the primary function of bisphosphonates. Some of the examples include zoledronic acid, alendronate and risedronate.
- Hyperuricemia Treatment Drugs For Reducing Gout Symptoms Of Ankle: Allopurinol, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Probenecid, which inhibits tubular resorption of uric acid in PCT Pegloticase, and Rasburicase, which is a Recombinant uricase that catalyses uric acid to water soluble, are all effective medications for the treatment of Gout as well as Tumour
- Antibiotics For Myositis And Osteomyelitis Of Ankle: Antibiotics are a type of drug that is used to treat bacterial disorders that affect the ankle, such as myosotis. Some of the drugs includes Vancomycin and Cephalosporin (or Cefepime if concern for Pseudomonas) and also azithromycin or doxycycline
- Corticosteroids For Ankle Pain And Osteomyelitis: Patients who suffer from specific kinds of myositis that present in the ankle muscles may be given prescriptions for cortisone-like medications such as prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone, as well as other pharmaceuticals that are comparable to cortisone.
- Antiviral Medicine For Viral Infection Of Ankle: ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet are just some of the medications that belong to this class that are frequently prescribed. These are the antivirals known to be used for infection of ankle muscles and bones.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Where is are ankle?
Ankles are found at the junction of the leg and foot.
What are the 5 ankle bones?
Three bones make up the majority of the ankle: the fibula, talus, and tibia.
What does my ankle pain mean?
Ankle pain is caused due to discomfort in the ankle which may have been caused by normal wear and tear or injury or due to arthritis.
What are the most common ankle problems?
Most common ankle problems-Ankle fracture/Sprain/Stains, Arthritis, or inflammation of a tendon (Achilles tendinitis).
How do I know if my ankle pain is serious?
Your ankle pain is serious if there is severe ankle pain or a person is unable to put weight on the foot or signs of infection or misshapen.
How do you fix ankle pain?
It takes a lot of time to fix ankle pain, however giving rest to your ankles and applying ice can reduce the pain. Medicines like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can also be used to relieve pain. During acute pain, a doctor should be consulted.
What disease causes ankle pain?
Diseases such as Arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Osteoarthritis cause ankle pain
What causes ankle pain without an injury?
Ankle pain can be caused without injury due to diseases such as arthritis or osteoarthritis. Other causes are sprains, strains, and wearing high heels.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously