Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Health Packages
AllQ&AsTipsQuizzes
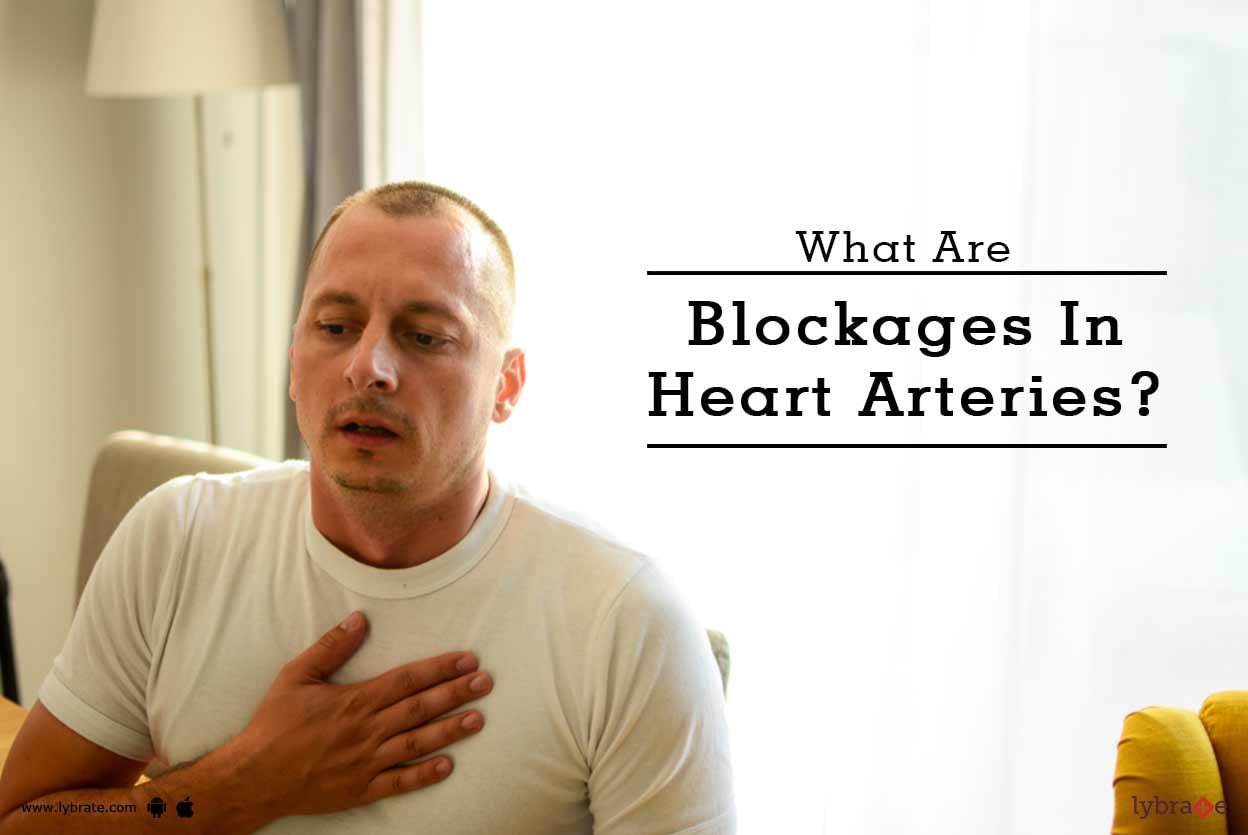
Blocked Arteries Tips
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
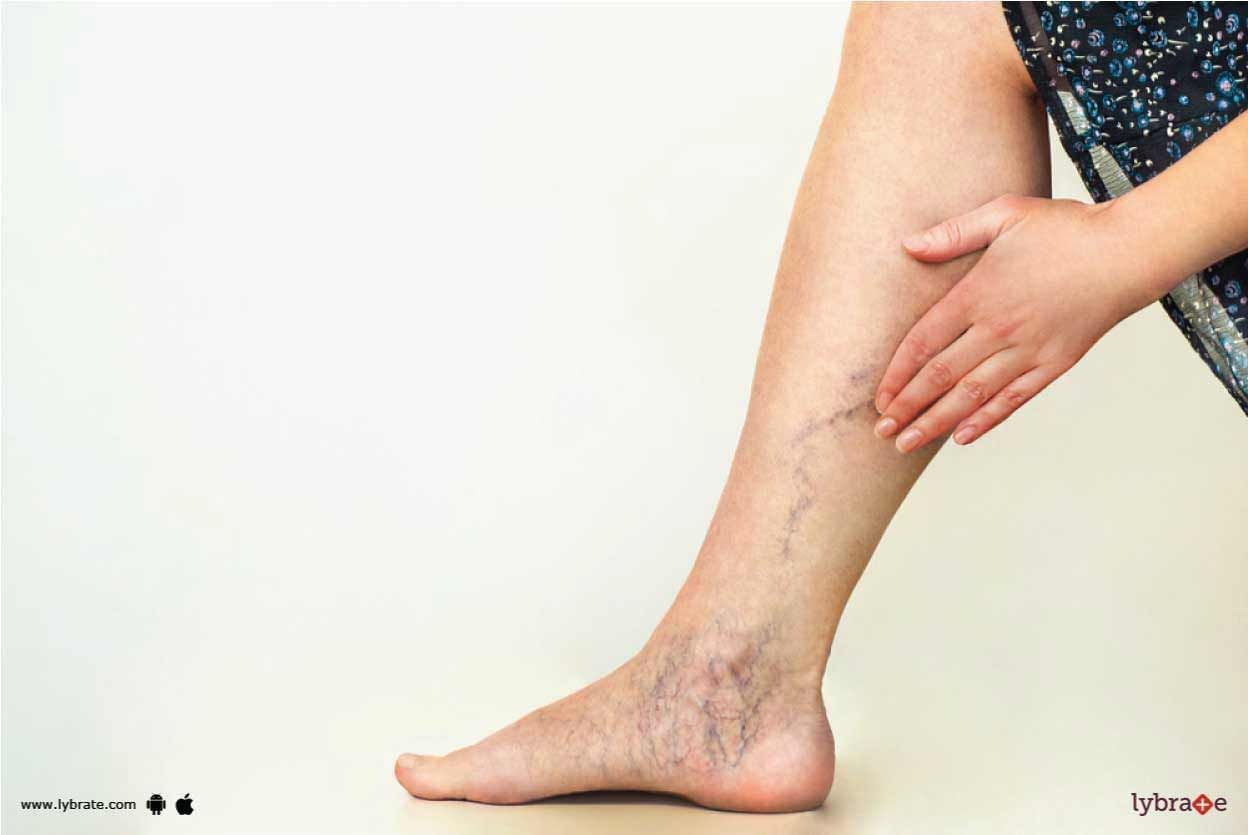
In our bodies, the vascular system is composed of vessels. This system is comprised of a complex network of veins and arteries. The arteries transport oxygenated blood away from the heart and spread it throughout our bodies and veins brings the deoxygenated blood (oxygen-poor) back to the heart for purification. Whenever this complicated process gets disturbed, pain, dysfunction of the system, and other complications may occur.
Most common complications among all are:
1. Abdominal A...more
Most common complications among all are:
1. Abdominal A...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
The blood vessels are elastic tubules controlled by valves through which blood flows. Depending on the organ and the distance from the heart, these vessels should be of a certain thickness to ensure proper blood supply, this maintains a constant normal pressure of the blood flow. In this condition, the blood vessels are narrowed, which results in reduced blood supply, affecting optimal function.
Causes:
With age, the elasticity of these vessels reduce and therefore blood flow a...more
Causes:
With age, the elasticity of these vessels reduce and therefore blood flow a...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Coronary artery disease is one of the major killer diseases of modern society. It is not a solitary problem but brings with it a multitude of issues including obesity, diabetes, stroke, and other metabolic disorders. A thorough understanding of what causes it and how to manage it can help save thousands of lives.
Causes: The circulatory system is mainly made up of the heart and a complex network of arteries and veins. The inner walls of these are lined with smooth muscles, allowing for ...more
Causes: The circulatory system is mainly made up of the heart and a complex network of arteries and veins. The inner walls of these are lined with smooth muscles, allowing for ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Coronary artery disease, also known as coronary heart disease or CHD, is a kind of disease in which a wax-like substance called plaque, builds up in the coronary arteries.
Function of Coronary Artery
The task of coronary arteries is to supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscles. When there is the growth of plaque in these arteries, the condition is termed as atherosclerosis. Plaque builds up over the years, and it hardens or ruptures with time. When plaque gets hardened, it narro...more
Function of Coronary Artery
The task of coronary arteries is to supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscles. When there is the growth of plaque in these arteries, the condition is termed as atherosclerosis. Plaque builds up over the years, and it hardens or ruptures with time. When plaque gets hardened, it narro...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
The heart pumps pure blood to all parts of the body through a network of arteries. These are thicker in the beginning and become finer and thinner as they reach the various organs. These arteries are lined by a layer of epithelial tissues and as blood flows through them, the heavier cholesterol / fat molecules settle down along the walls.
This attracts more and more fat molecules to settle down. This is known as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Over a period of time, ...more
This attracts more and more fat molecules to settle down. This is known as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Over a period of time, ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Heart Blocks are a result of plaque buildup in your arteries, which blocks blood flow and circulation to the heart, causing heart muscle damage and heightens the risk for heart attack and stroke.
Arteries which have smooth and elastic walls become thick and restrict blood flow from the cholesterol deposits over the years. Blood clots can also block the arteries that supply oxygen rich blood to the heart. These can eventually lead to strokes and heart attacks.
Some warning signs that...more
Arteries which have smooth and elastic walls become thick and restrict blood flow from the cholesterol deposits over the years. Blood clots can also block the arteries that supply oxygen rich blood to the heart. These can eventually lead to strokes and heart attacks.
Some warning signs that...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Carotid artery disease occurs when an oily, waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the carotid arteries. These are arteries that supply oxygenated blood to your brain, face, scalp, and neck.
Carotid artery disease is very serious as it can cause a brain stroke. It, in fact, starts with damage to the inner layer of the carotid artery. To stem this damage your body starts a healing process and this leads to a build up of plaque at the point where the artery is damaged.
When thi...more
Carotid artery disease is very serious as it can cause a brain stroke. It, in fact, starts with damage to the inner layer of the carotid artery. To stem this damage your body starts a healing process and this leads to a build up of plaque at the point where the artery is damaged.
When thi...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Blockage in heart is a common term used for narrowing of coronary arteries. Coronary arteries are vessels, which supply blood and thus oxygen and food to continuously working heart muscles. Heart muscles, which are not tired working from the birth till death, however, cannot sustain long without blood supply.
A reduction in blood supply gives rise to ischemia of heart muscles commonly manifested as chest discomfort or angina. A sudden complete shutdown of blood supply leads to heart att...more
A reduction in blood supply gives rise to ischemia of heart muscles commonly manifested as chest discomfort or angina. A sudden complete shutdown of blood supply leads to heart att...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Coronary artery disease is one of the major killer diseases of modern society. It is not a solitary problem but brings with it a multitude of issues including obesity, diabetes, stroke, and other metabolic disorders. A thorough understanding of what causes it and how to manage it can help save thousands of lives.
Causes: The circulatory system is mainly made up of the heart and a complex network of arteries and veins. The inner walls of these are lined with smooth muscles, allowing for ...more
Causes: The circulatory system is mainly made up of the heart and a complex network of arteries and veins. The inner walls of these are lined with smooth muscles, allowing for ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Blockage in heart is a common term used for narrowing of coronary arteries. Coronary arteries are vessels, which supply blood and thus oxygen and food) to continuously working heart muscles. Heart muscles which are not tired working from the birth till death, however, cannot sustain long without blood supply.
A reduction in blood supply gives rise to ischemia of heart muscles commonly manifested as chest discomfort or angina. A sudden complete shutdown of blood supply leads to heart att...more
A reduction in blood supply gives rise to ischemia of heart muscles commonly manifested as chest discomfort or angina. A sudden complete shutdown of blood supply leads to heart att...more
Book appointment with top doctors for Blocked Arteries treatment
View fees, clinic timings and reviews
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously