Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Health Packages
AllQ&AsTipsQuizzes
Alcoholic Liver Disease Tips
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
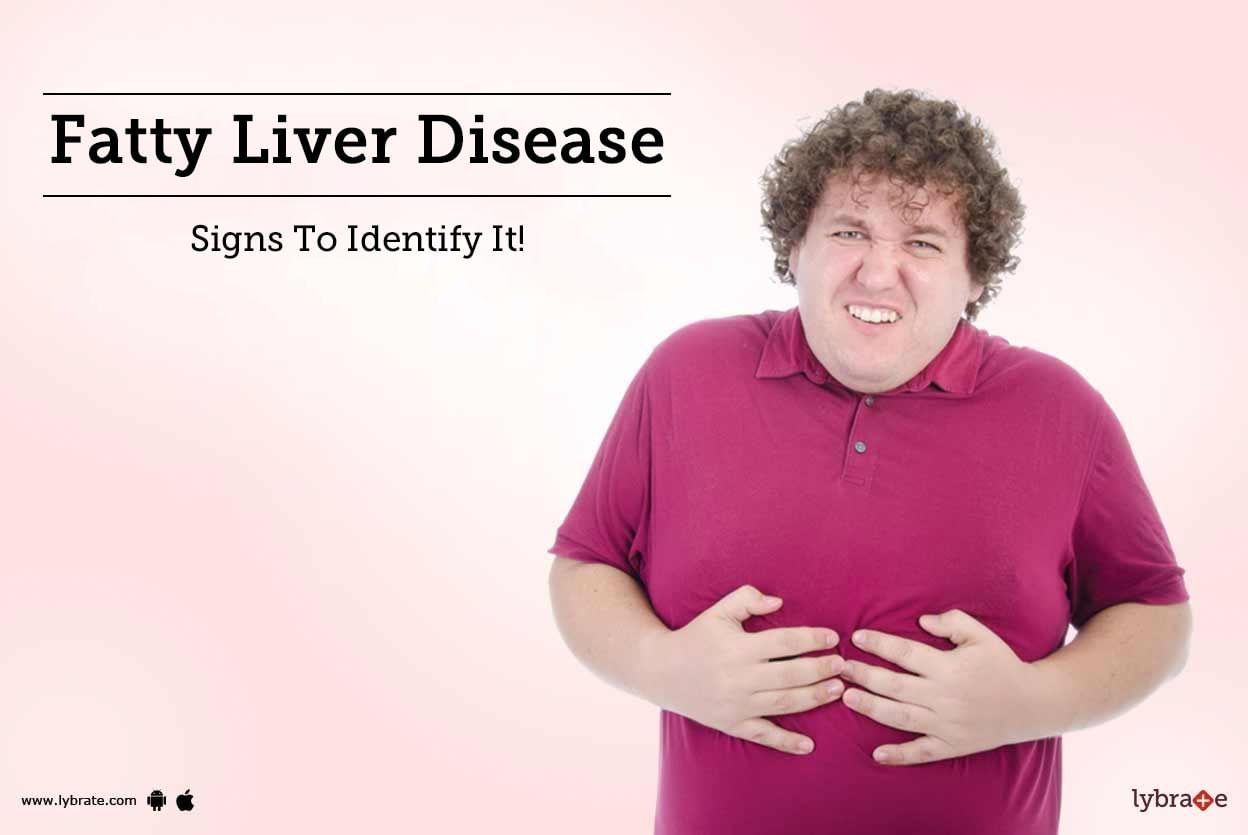
Fatty liver or steatosis refers to the condition in which excess fat gets accumulated in the liver causing the liver to dysfunction. Some percentage of fat in the liver is normal but if it gets beyond the figure of 5 to 10 percent, then it is surely a cause of concern. Such a condition warrants treatment and if fatty liver is not treated on time, it can lead to liver cirrhosis or cancer. Therefore, the signs and symptoms of fatty liver should be taken seriously.
Some of the common sympt...more
Some of the common sympt...more
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Cirrhosis is a severe problem of the liver, wherein the liver stops functioning properly due to long-term damage caused by its exposure to toxic substances like alcohol or viral infections. Every time the liver gets affected, it tries to repair itself through the body s natural healing process. Now, due to this continuous healing process, scar tissue gets formed. With the progress of cirrhosis, resulting in the formation of more and more scar tissue, the liver becomes unable to function properly...more
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Who is at risk?
All patients having cirrhosis.
It happens in non cirrhotics too.
What causes of cirrhosis commonly lead to hcc?
Hepatitis b related cirrhosis (most likely), hepatitis c, alcoholic cirrhosis, nash.
Is liver cancer curable?
Yes if diagnosed at an early stage.
Is there any treatment option for advanced hcc?
Yes there are options which can prolong the survival.
How to screen?
All cirrhotics need to get and ultrasound once a ...more
All patients having cirrhosis.
It happens in non cirrhotics too.
What causes of cirrhosis commonly lead to hcc?
Hepatitis b related cirrhosis (most likely), hepatitis c, alcoholic cirrhosis, nash.
Is liver cancer curable?
Yes if diagnosed at an early stage.
Is there any treatment option for advanced hcc?
Yes there are options which can prolong the survival.
How to screen?
All cirrhotics need to get and ultrasound once a ...more
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) most commonly affects patients with cirrhosis.
Can even occur in non cirrhotics.
More common in males.
Most commonly occurs in cirrhosis due to hepatitis b virus.
Other causes of cirrhosis that commonly lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc)- hepatitis c virus, alcohol associated, non alcoholic fatty liver.
Is hcc curable?
Yes if detected at at early stage treatment options do exist.
If a patient i...more
Can even occur in non cirrhotics.
More common in males.
Most commonly occurs in cirrhosis due to hepatitis b virus.
Other causes of cirrhosis that commonly lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc)- hepatitis c virus, alcohol associated, non alcoholic fatty liver.
Is hcc curable?
Yes if detected at at early stage treatment options do exist.
If a patient i...more
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Alcoholic liver disease or cirrhosis is one of the most common disorders of the liver. Since the liver performs a vital function in the body, it is essential to maintain its health. There can be several causes for the cirrhosis of the liver. Here are some of the factors that you need to watch out for if you want to steer clear of alcoholic liver disease.
Excess alcohol consumption: While limited alcohol consumption does not cause major health issues, you need to understand how much is t...more
Excess alcohol consumption: While limited alcohol consumption does not cause major health issues, you need to understand how much is t...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common form of liver disease as it affects about 80 to 100 million people in the US alone. It is described as a range of liver conditions which may affect people who either don t drink alcohol or drink too little of it. The distinguishing feature of this disease is the presence of too much fat in the liver. It can occur in every age group. However, people in age groups of the 40s and 50s, who are susceptible to heart diseases because of diabetes and ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic and progressive condition in which the liver gets damaged and healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, ultimately causing dysfunction of the liver. Liver damage obstructs the circulation to the liver and also hinders the processing of nutrients, hormones, drugs, toxins as well as the production of proteins and other substances made by the liver. Liver cirrhosis is caused due to hepatitis C, fatty liver, alcohol abuse, viral infections, inherited dise...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Just like the name suggests, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a set of diseases that can affect the liver due to excess accumulation of fat. One common disease that arises from this condition is known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. This can lead to cirrhosis as well. NAFLD is very common in the Western Countries affecting close to 100 million people annually. Although it can occur in any age group, the most affected age group being the one between 40-50 million. With this condition...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Having some fat in your liver is legit. But, if you have too much of fat say more than 5%-10% of the organ's weight then you are at risk of getting fatty liver disease. At the onset, you can do one important thing to help your liver stop drinking. It causes fatty liver disease.
There are two main types of fatty liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease or ALD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or NAFLD
If you are a woman who is pregnant, you can also get fatty liver disease....more
There are two main types of fatty liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease or ALD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or NAFLD
If you are a woman who is pregnant, you can also get fatty liver disease....more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
MBBS, MS - General Surgery, DNB ((Surgic...read more
Surgical Gastroenterologist•Mumbai
Liver Cirrhosis is a medical condition that results in severe scarring (often permanent and irreversible) of the liver. While there can be a myriad of factors giving rise to cirrhosis (such as repeated liver injury or unhealthy diet), the most common triggers include Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Alcohol, NASH (non-alcoholics teatohepatitis ). In addition to interfering with the healthy functioning of the liver, cirrhosis also gives rise to many serious and life-threatening complications such as Blo...more
Book appointment with top doctors for Alcoholic Liver Disease treatment
View fees, clinic timings and reviews
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously