Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Health Packages
AllQ&AsTipsQuizzes
Gestational Diabetes Tips
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
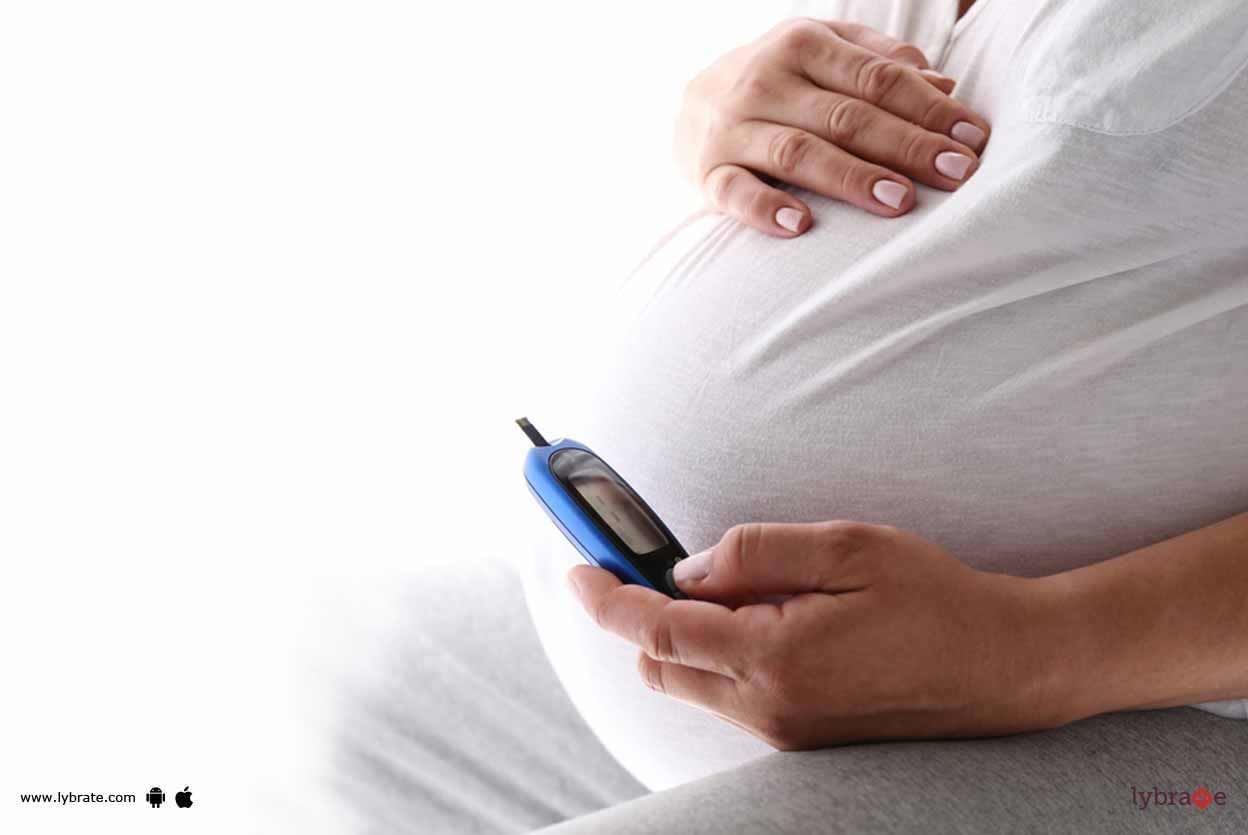
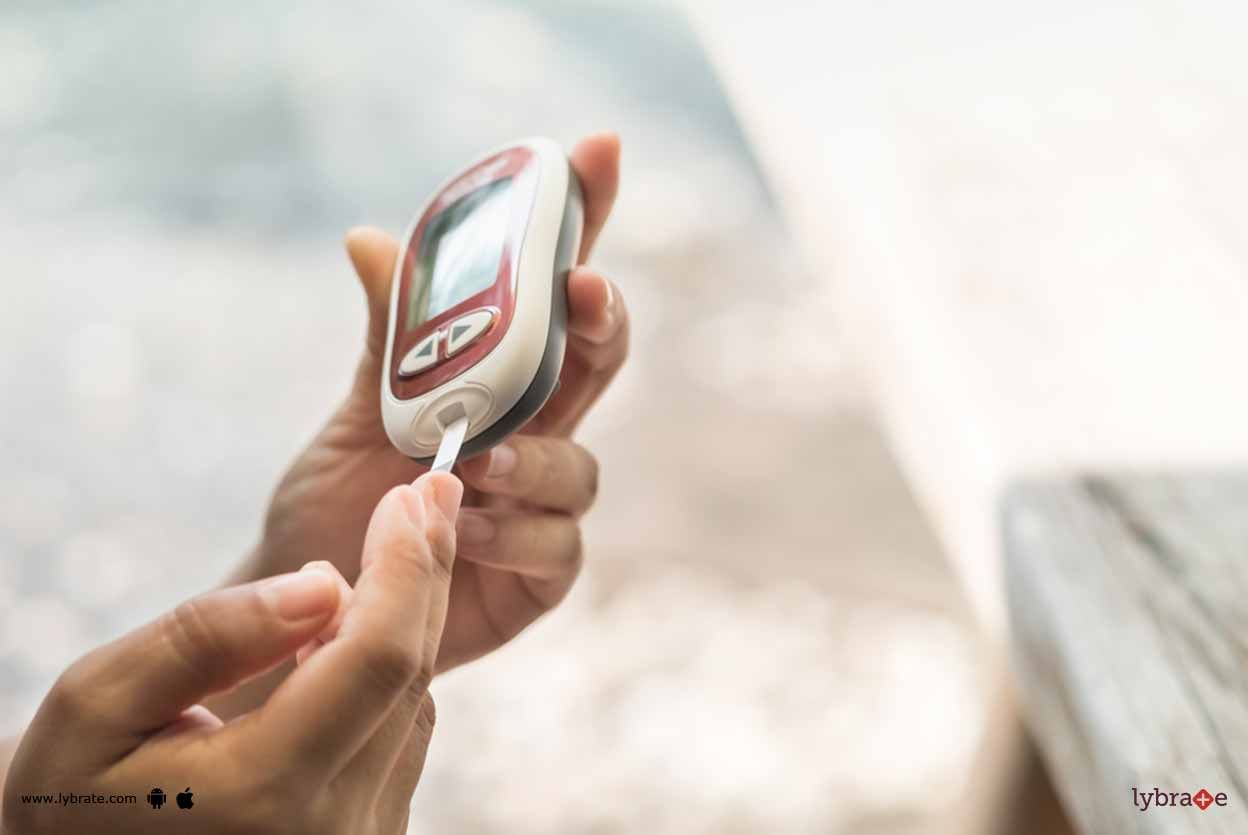
Gestational diabetes, as the name suggests, occurs during gestation or pregnancy when the blood sugar levels exceed the normal level. Gestational diabetes, like other form of diabetes, affects how your body cells use glucose or sugar during pregnancy, and usually disappears after you ve given birth.
Causes and symptoms to look out for!
During gestation, the placenta produces hormones that lead to the accumulation of blood glucose. Under normal condition, the pancreas forms enou...more
Causes and symptoms to look out for!
During gestation, the placenta produces hormones that lead to the accumulation of blood glucose. Under normal condition, the pancreas forms enou...more
Last Updated: 5 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
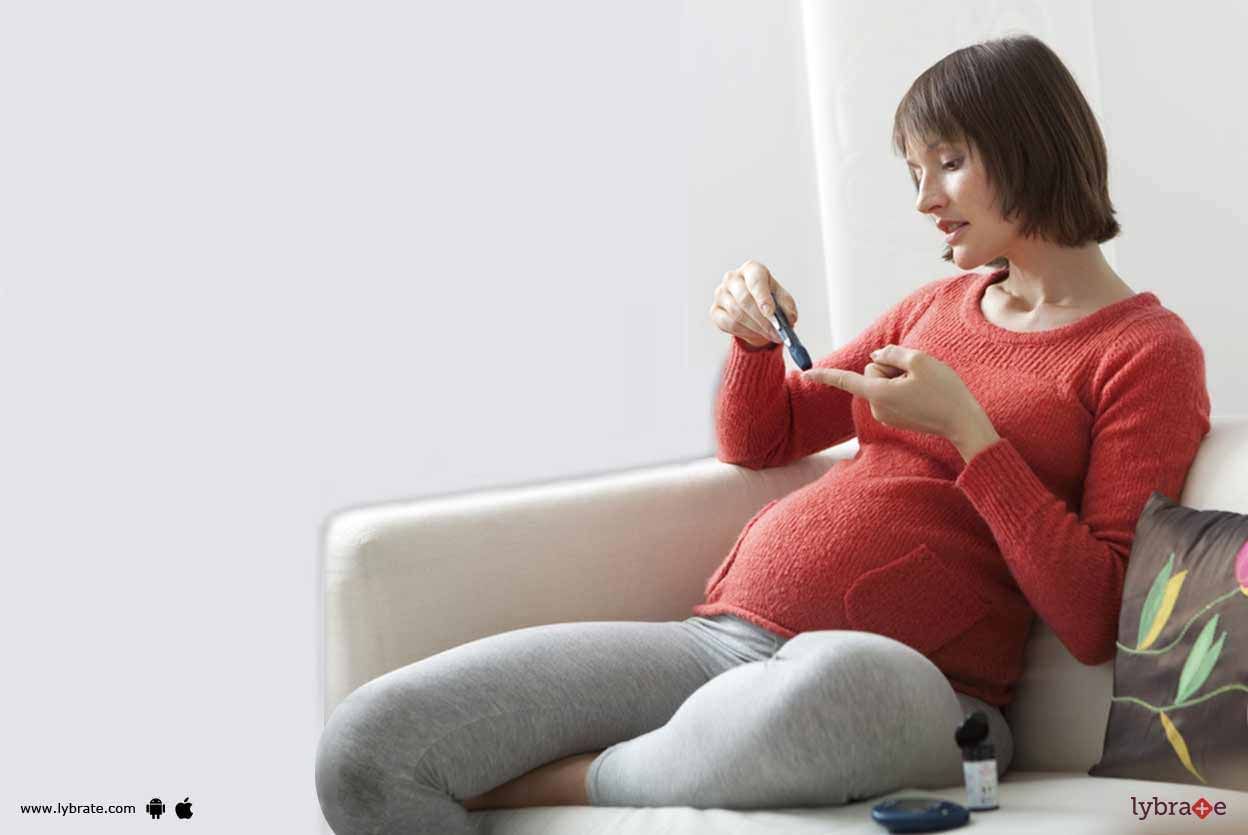
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that arises during the pregnancy and disappears after giving birth. It is usually diagnosed in the second stage by screening or blood test. It mostly occurs in the women who previously have some traits of diabetes. Gestational diabetes affects your pregnancy and your newborn baby health, but risk can be reduced if detected before and manage well.
Gestational diabetes is caused due to an excessive amount of blood sugar level, as at the time of pregnancy p...more
Gestational diabetes is caused due to an excessive amount of blood sugar level, as at the time of pregnancy p...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Gestational diabetes is a condition characterized by higher than normal blood sugar levels during pregnancy. The symptoms of this disorder are mild and a blood test has to be conducted as a part of the diagnosis. In all cases, the women should be administered treatment to avoid medical complications associated with it and to be on the safer side. Proper diagnosis is absolutely essential in the case of women with prediabetes or those women who had diabetes prior to pregnancy.
When the in...more
When the in...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Gestational trophoblastic disease is a rare condition. It only happens when trophoblast cells abnormally grow inside the uterus. Also, this only happens after conception. These cells surround the egg which has been fertilized in the uterus. It is also worth note that the trophoblast cells usually connect the fertilized eggs to the uterus' walls and also form a part of the placenta. It is only when there is a tumor that this disease is diagnosed. There are many forms of gestational trophoblastic ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Gestational diabetes is a kind of diabetes that happens during pregnancy. Diabetes is referred to a condition where your blood glucose or blood sugar is very high. Although, glucose is good as it used by your body for energy, but excessive glucose in your blood can be harmful for both you and your child.
Gestational diabetes is mostly diagnosed in the later stages of pregnancy. If gestational diabetes is diagnosed in the early stages of pregnancy, then it is quite possible that you may...more
Gestational diabetes is mostly diagnosed in the later stages of pregnancy. If gestational diabetes is diagnosed in the early stages of pregnancy, then it is quite possible that you may...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
During the time between 24th to 28th weeks of your pregnancy, you might develop a high level of glucose in your blood stream; this is known as gestational diabetes, and it affects the cells in the blood and how they absorb and use the glucose.
Ten best remedies which can prevent or control this problem are as follows:
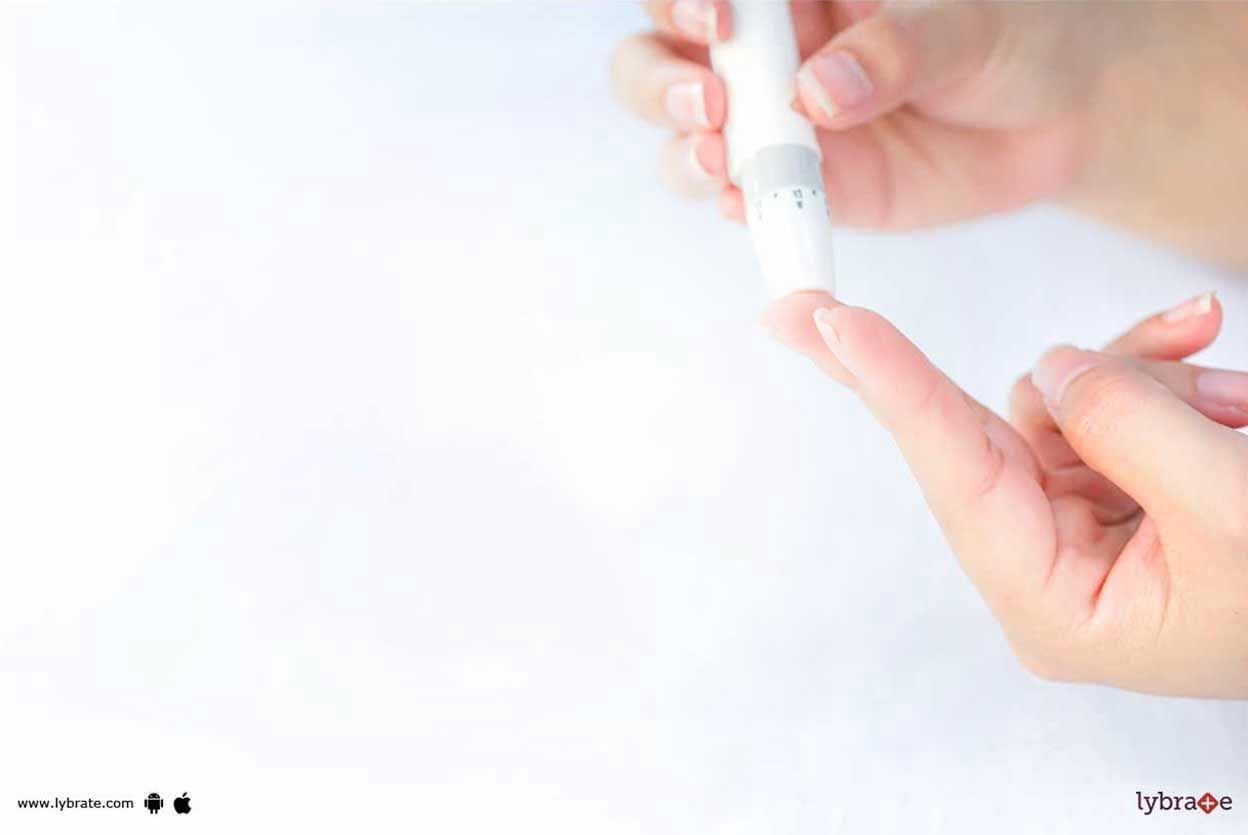
Regular monitoring of the level of blood sugar: Prevention is always better than cure, especially if you are at risk. When you are an expecting mother, you need t...more
Ten best remedies which can prevent or control this problem are as follows:
Regular monitoring of the level of blood sugar: Prevention is always better than cure, especially if you are at risk. When you are an expecting mother, you need t...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
MBBS Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor o...read more
Internal Medicine Specialist•Hyderabad
Diabetes is often referred to as diabetes mellitus by physicians, which is used for describing a group of metabolic-related diseases. Diabetic patients have high blood sugar (blood glucose) in the blood, the cause of which might be either the inadequate production of insulin or because the body is unable to use the insulin properly. Diabetes might also be a result of the combination of both.
There are three types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes which was formerly known as insulin-...more
There are three types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes which was formerly known as insulin-...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Gestational trophoblastic disease is a rare condition. It only happens when trophoblast cells abnormally grow inside the uterus. Also, this only happens after conception. These cells surround the egg which has been fertilized in the uterus. It is also worth note that the trophoblast cells usually connect the fertilized eggs to the uterus' walls and also form a part of the placenta. It is only when there is a tumor that this disease is diagnosed. There are many forms of the gestational trophoblas...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
'Congratulations! You're pregnant!' Almost all women long to hear these words and nothing should come in the way, even diabetes. So, if you are a Type 1 or Type 2 diabetic, here are a few things you should keep in mind to have a healthy baby.
Your blood sugar must be monitored regularly
The most important thing you can do to have a healthy baby is to keep your blood sugar as close to normal before and during your pregnancy. Testing is recommended a minimum of four times a day. ...more
Your blood sugar must be monitored regularly
The most important thing you can do to have a healthy baby is to keep your blood sugar as close to normal before and during your pregnancy. Testing is recommended a minimum of four times a day. ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Are you experiencing high blood sugar during pregnancy? This condition is known as gestational diabetes. It is associated with hormonal changes, which occur in your body during pregnancy. Women who are overweight, above the age of 25, and have a family history of diabetes are more likely to experience gestational diabetes. In most cases, the blood sugar levels return to normal after giving birth, and proper management enables you to keep away from any complications during pregnancy as well.
...more
...more
Book appointment with top doctors for Gestational Diabetes treatment
View fees, clinic timings and reviews
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously