Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Health Packages
AllQ&AsTipsQuizzes
Genetic Disorders Tips
Last Updated: 3 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
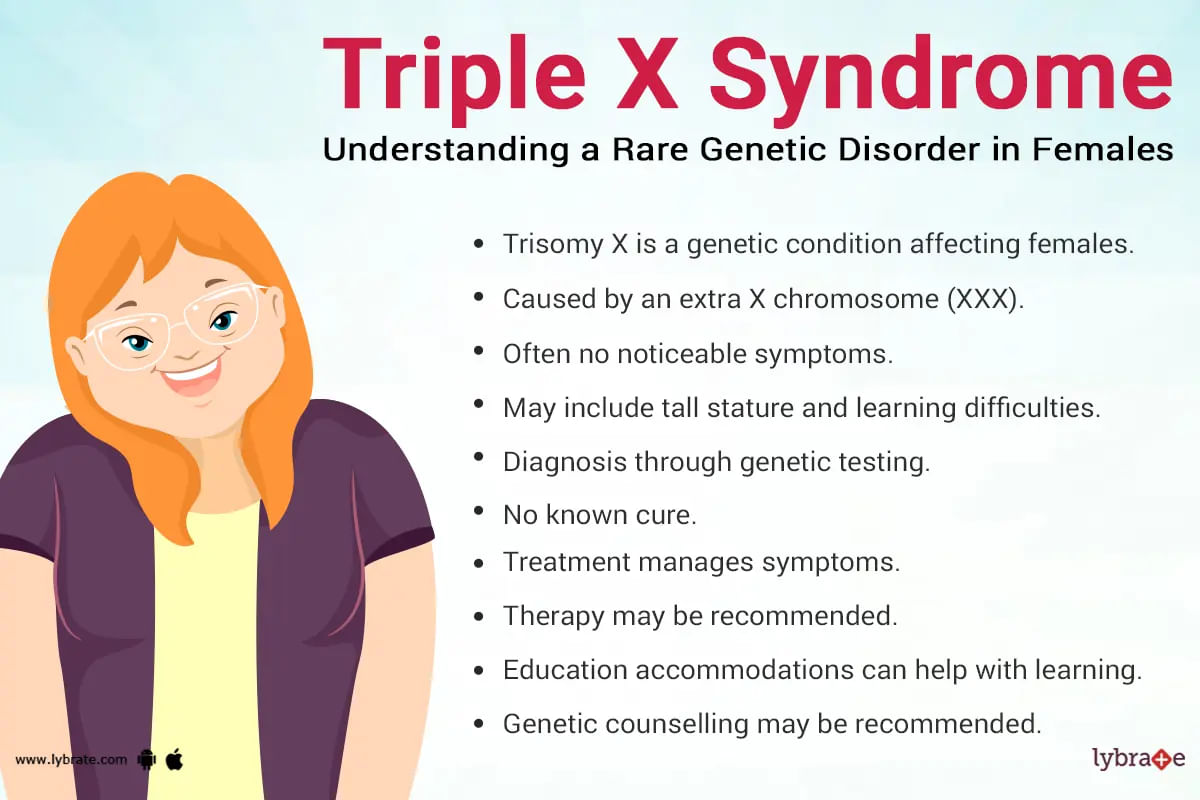
What do you know about" triple x syndrome?
Triple x syndrome, which may also be referred to as trisomy x, is a genetic condition that mainly affects females and is caused by the presence of an extra x chromosome. Typically, females have two x chromosomes, but in this disorder, there are three x chromosomes instead of two, leading to an overabundance of genetic material.
The exact cause of this extra x chromosome is not well known or understood, but it is bel...more
447 people found this helpful
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Delusional disorder refers to the condition in which an individual experiences non-bizarre delusions that are beliefs in things that aren't actually true. The delusions involve situations that take place in real life like being deceived or stalked, conspired against, etc but in actuality, these situations may be highly exaggerated or not true at all as they involve the misinterpretation of experiences or observations. This health problem tends to take place during the middle or later part of you...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Prenatal Diagnosis is the diagnosis of the fetus or unborn baby. By prenatal diagnosis, doctors examine the developing baby. There are two main methods for prenatal diagnosis, Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS), and Amniocentesis. However, the prenatal diagnosis consists of several tests which help doctors to find out the genetic disorder of the fetus.
According to many studies, some parents are at higher risk of having a baby with a genetic problem or disorder. Due to this reason, it is a...more
According to many studies, some parents are at higher risk of having a baby with a genetic problem or disorder. Due to this reason, it is a...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Medical genetics is a branch of medicine that involves identifying the cause of human biological variation. Medical genetics help to determine the health and disease of a person which are hereditary in nature. It involves the study and counseling about the pathogenesis, etiology, and natural history of disorders and diseases that originate genetically.
Medical genetics is different from human genetics in the way that human genetics involves the research and scientific study of the genom...more
Medical genetics is different from human genetics in the way that human genetics involves the research and scientific study of the genom...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Endometriosis is a condition in which the endometrial cells lining the inside wall of the uterus begin to grow outside the uterus. In a majority of the cases, the growth is on the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, or the tissues around the uterus. In rare cases, it occurs in other body parts. Normally, women in the age group of 30 to 40 years are prone to developing this condition and genetics is believed to be the reason behind this disorder. It is a serious medical condition if it causes discomfor...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Usually, when it comes to doing anything or trying something new, we say age doesn t matter at all. But that is not the case with pregnancy. Pregnancy should be planned at earlier ages to keep your baby as well as the conceiving mother healthily. Although it has been observed that those women who conceive their babies at the age of 35 (or maybe even more than that), experience no difficulties but one should take precautionary steps before planning a baby so that no difficulties arise.
I...more
I...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
Wilson s Disease is a rare genetic disorder, affecting one in 30,000 individuals, which leads to an accumulation of copper in different organs of the body, especially in brain, liver, and eyes. Copper is an important mineral that plays an important role in the development of collagen, bones, skin, and nerves. The amount of copper required by the body is obtained from food. In general, excess copper is excreted out with the help of bile juice from the liver. But, in Wilson s Disease, copper from ...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
MBBS, MS - General Surgery, DNB ((Surgic...read more
Surgical Gastroenterologist•Mumbai
Some diseases are inherited genetically and familial polyposis is one such disease. It is a rare condition that typically affects the large intestines and the rectum. In some cases, it can also affect the upper gastrointestinal tract. People suffering from this condition develop extra tissues in the large intestine. If left untreated, it could turn cancerous at a later stage. Hence, surgery is usually recommended to remove the part of the large intestine that has been affected. In cases where it...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
The skin has a protein called keratin that protects it from infections and other harmful toxins. For various reasons, mostly unknown but likely genetic, there could be a buildup of this keratin leading to small, light-colored, hard bumps under the skin that can feel like sandpaper. This condition is medically known as keratosis pilaris. These pillars of keratin block the hair follicles that open onto the surface of the skin, and when a number of follicles are blocked, it leads to dry, bumpy fe...more
Last Updated: 6 years ago• Featured Tip
Share
Bookmark
Report
We all have mood swings but not all mood swings have the same intensity. People who have extreme mood swings ranging from depression to manic highs are said to be suffering from bipolar disorder. These extreme moods are known as episodes and usually, last for a few days or even a few weeks. A person suffering from bipolar disorder could have an episode several times a year. This is a very common psychological problem and can affect both children and adults. Though it cannot be cured, this diseas...more
Book appointment with top doctors for Genetic Disorders treatment
View fees, clinic timings and reviews
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously