Prostate Surgery Blood In Urine
Hi, i'm a 31 years old virgin male. Last 2 years I have had pain and swelling in scrotum during travel, weight left, som ...
Ask Free Question
Hello- the pain you experience will determine the problem you may be suffering from. For example, pain from testicular torsion occurs suddenly, while pain from an infection of the testicle sets in gradually. Like pain from any source, you may notice swelling or redness of the testicles or scrotum as well as nausea and vomiting. You may experience fever or chills with epididymitis but less frequently with torsion. Pains during urination or involuntary penile discharge are also common with epididymitis but less frequent with torsion. Pain with intercourse, pain with ejaculation, or blood in the semen is also possible. With testicular pain, the first goal is to determine whether or not the pain is caused by torsion, which is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgery.
I am having dry orgasms while being treated for urine infection and post voided vol. 77mls. When I masturbate I do not e ...
Ask Free Question
Hello- Dry orgasm occurs when a man reaches sexual climax but doesn't release (ejaculate) semen from the penis or releases very little semen. Semen is the thick, white fluid that carries sperm. Dry orgasm usually isn't harmful, but it can interfere with a man's ability to father a child. Fortunately, it is curable in ayurveda. Underlying causes of dry orgasm include: Bladder removal surgery (cystectomy) Blocked sperm duct (ejaculatory duct obstruction) Certain medications used to treat high blood pressure, enlarged prostate and mood disorders Diabetes Genetic abnormalities of the reproductive system Male hypogonadism (testosterone deficiency) Multiple sclerosis Open prostatectomy Prostatectomy (radical) Prostate laser surgery Radiation therapy Retrograde ejaculation Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection Spinal cord injury TUIP (transurethral incision of the prostate) TUMT (transurethral microwave therapy) TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate)
I'm 22 year old male. 4 months back I have put oil into my urethra. I used to get pain in my penis after urinating. But ...
Ask Free Question
Hello- A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra caused by inflammation or scar tissue from surgery, disease, or injury. It may also be caused by external pressure from an enlarging tumor near the urethra. Increased risk is associated with men who have a history of sexually transmitted disease (STD), repeated episodes of urethritis, having history of excessive masturbation or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Common symptoms of urethral stricture includes: - Weak urine flow or reduction in the volume of urine. - Sudden, frequent urges to urinate. - A feeling of incomplete bladder emptying after urination. - Frequent starting and stopping urinary stream. - Pain or burning during urination. - Inability to control urination (incontinence) As per old saying 'once a stricture always a stricture' in present era there are different modalities for Stricture Urethra are practiced such as Dilatation, Urethroplasty, Stent etc. but it involves many potential complications such as recurrence, bleeding, infection, wound breakdown, tightness with erections, dribbling, etc. Even any instrument inserted into the urethra for diagnosis (such as a catheter or cystoscope) further increases the pathogenesis and can make the condition worse. Ayurveda is a choice of treatment in Urethral stricture due to its non-invasive action. Ayurvedic medicines, which are sourced from natural substances, are very beneficial in the treatment of Urethral Stricture. Herbs used are completely safe and natural, with no side effects, and ensure complete recovery.
My father 79 years old got his usg abdomen n pelvis done he got psa blood test normal in usg report he got 1. Prostate m ...
Ask Free Question
Yes your father is suffering with BPH Cholilithiasis which needs operation
Hi my name is amit my age is 30 my sperm count is nill prostatic secretion when I talk to girl my semen is thin what sho ...
Ask Free Question
Tests for a low sperm count depending on initial findings, your doctor might recommend additional tests to look for the cause of your low sperm count and other possible causes of male infertility. These can include: 1) semen analysis scrotal ultrasound. this test uses high-frequency sound waves to look at the testicles and supporting structures. Hormone testing. your doctor might recommend a blood test to determine the level of hormones produced by the pituitary gland and testicles, which play a key role in sexual development and sperm production. Post-ejaculation urinalysis. sperm in your urine can indicate your sperm are traveling backward into the bladder instead of out your penis during ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation). Genetic tests. when sperm concentration is extremely low, genetic causes could be involved. A blood test can reveal whether there are subtle changes in the y chromosome — signs of a genetic abnormality. Genetic testing might also be ordered to diagnose various congenital or inherited syndromes. Testicular biopsy. this test involves removing samples from the testicle with a needle. The results of the testicular biopsy can tell if sperm production is normal. If it is, your problem is likely caused by a blockage or another problem with sperm transport. However, this test is typically only used in certain situations and is not commonly used to diagnose the cause of infertility. Anti-sperm antibody tests. these tests, which are used to check for immune cells (antibodies) that attack sperm and affect their ability to function, are not common. Specialized sperm function tests. a number of tests can be used to check how well your sperm survive after ejaculation, how well they can penetrate an egg and whether there's any problem attaching to the egg. These tests are rarely performed and often do not significantly change treatment recommendations. Transrectal ultrasound. a small lubricated wand is inserted into your rectum to check your prostate and check for blockages of the tubes that carry semen (ejaculatory ducts and seminal vesicles). Treatment treatments for low sperm count include: surgery. for example, a varicocele can often be surgically corrected or an obstructed vas deferens can be repaired. Prior vasectomies can be reversed. In cases where no sperm are present in the ejaculate, sperm can often be retrieved directly from the testicles or epididymis using sperm retrieval techniques. Treating infections. antibiotics can cure an infection of the reproductive tract, but this doesn't always restore fertility. Treatments for sexual intercourse problems. Medication or counseling can help improve fertility in conditions such as erectile dysfunction or premature ejaculation. Hormone treatments and medications. your doctor might recommend hormone replacement or medications in cases where infertility is caused by high or low levels of certain hormones or problems with the way the body uses hormones. Assisted reproductive technology (art). art treatments involve obtaining sperm through normal ejaculation, surgical extraction or from donor individuals, depending on your specific situation and wishes. The sperm are then inserted into the female genital tract, or used for ivf or intracytoplasmic sperm injection.
I am 76. I am having erectile dysfunction. I am on telmisartan 40 - 1xbd, amlodipine 2.5 mg - 1xbd, gabapentin 300 mg - ...
Ask Free Question
Erectile dysfunction affects older men more than younger men. About 1% of men in their 40s, 17% of men in their 60s, and nearly 50% of men 75 or older aren't able to achieve an erection sufficient for intercourse. Sometimes erectile dysfunction develops gradually. One night it may take longer or require more stimulation to get an erection. Another time, an erection may not be as firm as usual, or it may end before orgasm. When such difficulties occur regularly, it's time to talk to a doctor. The culprit behind erectile dysfunction is often clogged arteries. In fact, in nearly one-third of men who see their doctors about trouble getting or keeping an erection, erectile dysfunction is the first hint that they have cardiovascular disease. Other possible causes of erectile dysfunction include medications and prostate surgery, as well as illnesses and accidents. Stress, relationship problems, or depression can also lead to it. Regardless of the cause, erectile dysfunction often can be effectively treated. For some men, simply losing weight may help. Others may need medications. If these steps aren’t effective, a number of other options, including injections and vacuum devices, are available. Given the variety of options, the possibility of finding the right solution is now greater than ever before. Tests for underlying conditions might include: physical exam. this might include careful examination of your penis and testicles and checking your nerves for sensation. Blood tests. a sample of your blood might be sent to a lab to check for signs of heart disease, diabetes, low testosterone levels and other health conditions. Urine tests (urinalysis). like blood tests, urine tests are used to look for signs of diabetes and other underlying health conditions. Ultrasound. this test is usually performed by a specialist in an office. It involves using a wandlike device (transducer) held over the blood vessels that supply the penis. It creates a video image to let your doctor see if you have blood flow problems. This test is sometimes done in combination with an injection of medications into the penis to stimulate blood flow and produce an erection. Psychological exam. your doctor might ask questions to screen for depression and other possible psychological causes of erectile dysfunction. Oral medications oral medications are a successful erectile dysfunction treatment for many men. They include: sildenafil (viagra) tadalafil (adcirca, cialis) vardenafil (levitra, staxyn) avanafil (stendra) all four medications enhance the effects of nitric oxide — a natural chemical your body produces that relaxes muscles in the penis. This increases blood flow and allows you to get an erection in response to sexual stimulation. Taking one of these tablets will not automatically produce an erection. Sexual stimulation is needed first to cause the release of nitric oxide from your penile nerves. These medications amplify that signal, allowing some men to function normally. Oral erectile dysfunction medications are not aphrodisiacs, will not cause excitement and are not needed in men who get normal erections. The medications vary in dosage, how long they work and side effects. Possible side effects include flushing, nasal congestion, headache, visual changes, backache and stomach upset. Your doctor will consider your particular situation to determine which medication might work best. These medications might not treat your erectile dysfunction immediately. You might need to work with your doctor to find the right medication and dosage for you. Before taking any medication for erectile dysfunction, including over-the-counter supplements and herbal remedies, get your doctor's ok. Medications for erectile dysfunction do not work in all men and might be less effective in certain conditions, such as after prostate surgery or if you have diabetes. Testosterone replacement. some men have erectile dysfunction that might be complicated by low levels of the hormone testosterone. In this case, testosterone replacement therapy might be recommended as the first step or given in combination with other therapies. Penis pumps. a penis pump (vacuum erection device) is a hollow tube with a hand-powered or battery-powered pump. The tube is placed over your penis, and then the pump is used to suck out the air inside the tube. This creates a vacuum that pulls blood into your penis. Once you get an erection, you slip a tension ring around the base of your penis to hold in the blood and keep it firm. You then remove the vacuum device. The erection typically lasts long enough for a couple to have sex. You remove the tension ring after intercourse. Psychological counseling if your erectile dysfunction is caused by stress, anxiety or depression — or the condition is creating stress and relationship tension — your doctor might suggest that you, or you and your partner, visit a psychologist or counselor. Alternative medicine before using any supplement, check with your doctor to make sure it's safe for you — especially if you have chronic health conditions. Some alternative products that claim to work for erectile dysfunction can be dangerous.
Hi, im a 17 years old boy. Since 3 months, I have been suffering from staphylococcus aureus in urine due to which my spe ...
Ask Free Question
Male factors account for 20% to 50% of infertility cases, and infection in the genitourinary tract may play a contributing role in up to 15% of male infertility. Leukocytospermia is a well-known indicator of infection or inflammation in the male sex glands and the urogenital tract. Although great deal of effort has been expended to elucidate definite management strategies in infertile men with leukocytospermia, the gold standard of treatment remains unclear. Until recently, broad spectrum antibiotics and antioxidants have been used in the treatment of leukocytospermia for male infertility to eliminate infection and reduce reactive oxygen free radicals produced inside cellular mitochondria as a result of inflammation. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (nsaids) are also prescribed for patients with pyospermia, and may also improve sperm count. Pyospermia may also get better on its own. There are other things men can do to try to eliminate excess white blood cells from semen, including: stopping the use of any tobacco product; avoiding the use of too much alcohol; stopping the use of marijuana; more frequent ejaculation. The use of the antioxidant nutritional supplements can reduce sperm production and lessen the effects of white blood cells in the semen. Men who are trying to make a pregnancy and who have pyospermia should consider taking antioxidant nutritional supplements, including vitamin e, vitamin c, coenzyme ubiquinol-10 (coq10), glutathione, and others. Pyospermia can also be treated by correcting genitourinary abnormalities that may cause infection or inflammation. Methods of correction include varicocelectomy, the surgery to correct a varicocele, which can improve semen production and reduce white blood cells in the semen. Other abnormalities that can be treated include prostatic obstruction with infection and urethral valves. Follow-up another semen analysis three months after the antibiotics are completed is recommended as a follow-up. If the pyospermia has not been treated successfully, other measures include semen cultures, antisperm antibody testing, x-rays of the genitourinary tract, and/or urine flow tests. In many cases, treatment for 30 days with an over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication may be recommended.
Wbc pus cell in semen 40 to 60 hpf is this cure we take one-month cefixime and doxxyxline medicine one and half months b ...
Ask Free Question
Eliminating white blood cells from the semen can improve the function of the sperm and improve pregnancy rates. Because antibiotics may help treat pyospermia, men may receive a prescription for antibiotics and told to take the entire course, even if no organisms are found in the urine. In rare cases, a culture of the semen may be taken. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (nsaids) are also prescribed for patients with pyospermia, and may also improve sperm count. Pyospermia may also get better on its own. There are other things men can do to try to eliminate excess white blood cells from semen, including: stopping the use of any tobacco product; avoiding the use of too much alcohol; stopping the use of marijuana; more frequent ejaculation. The use of the antioxidant nutritional supplements can reduce sperm production and lessen the effects of white blood cells in the semen. Men who are trying to make a pregnancy and who have pyospermia should consider taking antioxidant nutritional supplements, including vitamin e, vitamin c, coenzyme ubiquinol-10 (coq10), glutathione, and others. Pyospermia can also be treated by correcting genitourinary abnormalities that may cause infection or inflammation. Methods of correction include varicocelectomy, the surgery to correct a varicocele, which can improve semen production and reduce white blood cells in the semen. Other abnormalities that can be treated include prostatic obstruction with infection and urethral valves. Follow-up another semen analysis three months after the antibiotics are completed is recommended as a follow-up. If the pyospermia has not been treated successfully, other measures include semen cultures, antisperm antibody testing, x-rays of the genitourinary tract, and/or urine flow tests. In many cases, treatment for 30 days with an over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication may be recommended.
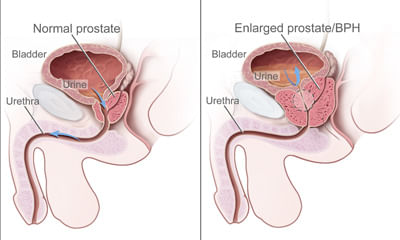
I am 60 years old. Since 6 months I have an issue of prostate enlargement. Is there a remedy other than the surgery? Whe ...
Ask Free Question
There are many treatments for enlarged prostates or bph, but most of them have side effects and possible complications. The symptoms may include trouble starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. And, like gray hair, an enlarged prostate is a natural by-product of getting older. When the bladder does not empty completely, you become at risk for developing urinary tract infections. Other serious problems can also develop over time, including bladder stones, blood in the urine, incontinence, and acute urinary retention. You should discuss it in detail to get right diagnosis.
Hi, I want to know how erectile dysfunction test is performed. Can you please provide the details? Further do the tests ...
Ask Free Question
For many men, a physical exam and answering questions (medical history) are all that's needed for a doctor to diagnose erectile dysfunction and recommend a treatment. If you have chronic health conditions or your doctor suspects that an underlying condition might be involved, you might need further tests or a consultation with a specialist. Tests for underlying conditions might include: physical exam. This might include careful examination of your penis and testicles and checking your nerves for sensation. Blood tests. A sample of your blood might be sent to a lab to check for signs of heart disease, diabetes, low testosterone levels and other health conditions. Urine tests (urinalysis). Like blood tests, urine tests are used to look for signs of diabetes and other underlying health conditions. Ultrasound. This test is usually performed by a specialist in an office. It involves using a wandlike device (transducer) held over the blood vessels that supply the penis. It creates a video image to let your doctor see if you have blood flow problems. This test is sometimes done in combination with an injection of medications into the penis to stimulate blood flow and produce an erection. Psychological exam. Your doctor might ask questions to screen for depression and other possible psychological causes of erectile dysfunction.