Fungal Infections - What Should You Know?
Fungi are organisms that can grow in or on the body, causing infections of internal organs or of the skin, nails, and hair. These fungi are common in the environment and can affect anyone causing a wide range of illnesses, from minor skin conditions to life-threatening diseases. Learning about them can help you and your doctor recognize the symptoms of a fungal disease early and may help prevent serious complications.
Fungal infections are often described as opportunistic or primary. They can affect many areas of the body (systemic) or only one area (localized).
- Opportunistic fungal infections take advantage of a weakened immune system. Thus, they usually occur in people with a weakened immune system, such as those with AIDS. Opportunistic fungal infections can be very aggressive, spreading quickly to other organs and often leading to death.
- Primary fungal infections occur in people with the normal immune system and generally do not spread to organs deep in the body. They are more common in certain geographic areas. Because many primary fungal infections develop slowly, months or years may pass before people seek medical attention.
- Localised fungal infections typically involve the skin and nails, vagina, mouth, or sinuses.
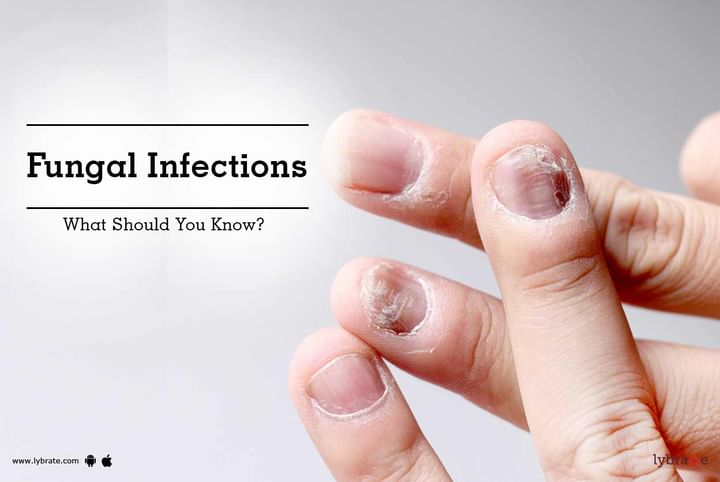
Fungal infections of the skin
For those who like to spend time outdoors, at the gym, or other places that may cause the skin to become sweaty and dirty, it is important to understand the risk of contracting a fungal infection of the skin. Fungi usually make their homes in moist areas of the body where skin surfaces meet: between the toes, in the genital area, and under the breasts. Fungal infections of the skin are often diagnosed on the basis of their appearance and their location on the body.
Common fungal skin infections are caused by yeasts (such as Candida or Malassezia furfur) or dermatophytes, such as Epidermophyton, Microsporum, and Trichophyton. Many such fungi live only in the topmost layer of the epidermis (stratum corneum) and do not penetrate deeper. Obese people are more likely to get these infections because they have excessive skin folds, especially if the skin within a skin fold becomes irritated and broken down (intertrigo). People with diabetes tend to be more susceptible to fungal infections as well.
Strangely, fungal infections on one part of the body can cause rashes on other parts of the body that are not infected. For example, a fungal infection on the foot may cause an itchy, bumpy rash on the fingers. These eruptions (Dermatophytids, or identity or id reactions) are allergic reactions to the fungus. They do not result from touching the infected area.
Antifungal drugs may also be taken by mouth. Keeping the skin dry and clean is helpful. Other skin infections, however, do not respond to such treatment. They require a doctor's attention and systemic treatment with prescription antifungal medications.
In case you have a concern or query you can always consult an expert & get answers to your questions!


+1.svg)
