Uveitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: May 10, 2023
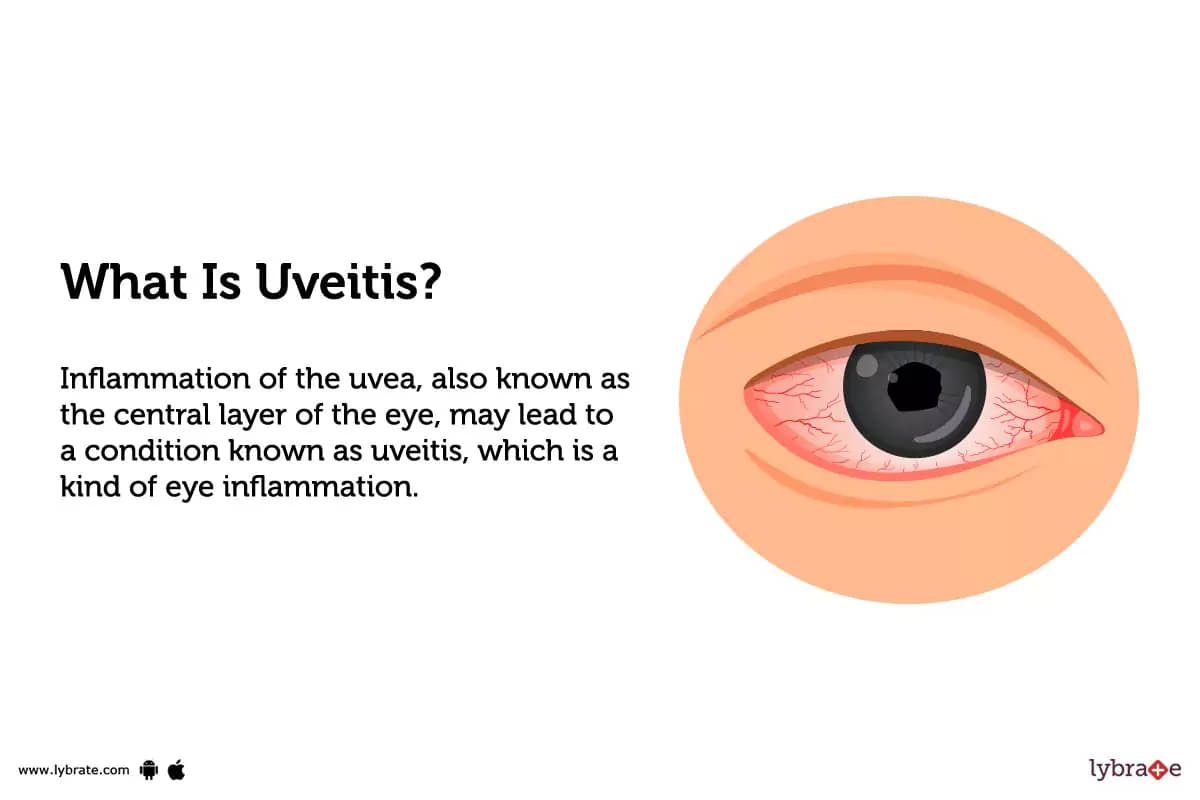
What is Uveitis?
Inflammation of the uvea, also known as the central layer of the eye, may lead to a condition known as uveitis, which is a kind of eye inflammation. It can cause changes in the eye such as redness, pain, and decreased vision.
Types of Uveitis
- Anterior Uveitis (Iridocyclitis): This particular kind of uveitis manifests itself as redness, discomfort, and sensitivity to light. It is caused by inflammation in the anterior segment of the eye.
- Intermediate Uveitis (Pars Planitis): This type of uveitis affects the middle layer of the eye and is characterised by floaters (spots in vision) and blurred vision.
- Posterior Uveitis: This particular kind of uveitis affects the posterior segment of the eye and is characterised by a reduction in one's field of vision as well as the presence of floaters.
- Panuveitis: This type of uveitis affects all layers of the eye, including both anterior and posterior segments. Symptoms include decreased vision, pain, redness, floaters, and sensitivity to light.
What causes Uveitis
Uveitis is caused by an inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, called the uvea. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including autoimmune diseases, infections, and trauma.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Uveitis can be caused by certain autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis. In these cases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, which can lead to inflammation in the uvea.
- Infections: Certain bacteria and viruses can cause uveitis when they enter the eye or spread from nearby tissues. Common infectious causes include herpes simplex virus (HSV), varicella zoster virus (VZV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and toxoplasmosis.
- Trauma: Physical injuries or trauma to the eye can cause uveitis due to irritation or damage to the eye's tissues. This is called traumatic uveitis and may be caused by a direct injury or a foreign body entering the eye such as dirt or dust particles
What are the symptoms of Uveitis?
Eye discomfort, redness, sensitivity to light, and impaired vision are some of the symptoms that may accompany uveitis.
In some cases there may also be floaters in the vision or a loss of vision in the affected eye.Other symptoms may include headache, fever and malaise.
How can you prevent Uveitis?
Have regular eye exams to detect signs of uveitis as early as possible.
- Avoid triggers and known causes of uveitis, such as long-term corticosteroid use or a viral infection.
- Wear protective eyewear during activities that increase your risk for eye injuries, such as contact sports, or to protect from inflammation from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light (UV light).
- Control underlying medical conditions that can lead to uveitis: diabetes, lupus, certain inherited autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions.Follow treatment recommendations closely if you are diagnosed with uveitis, including medications to reduce swelling and suppress autoimmunity (used only when needed).
Uveitis - Diagnosis and Tests
- Visual Acuity Testing: This test is used to measure the sharpness of vision in both eyes. It is performed by having the patient read an eye chart from a specified distance.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: This test uses a special microscope with a light source to examine the eye structures, including the iris, lens, and vitreous gel. It is used to detect inflammation or other problems in the eye.
- Funduscopy: This test uses an ophthalmoscope or retinal camera to examine the interior of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve. It can help identify signs of inflammation that may be present in uveitis cases.
- Tonometry: This procedure is used to determine the intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eye by forcing air into the eye and measuring the amount of force required to cause the cornea to become flatter.High IOP can be an indication of uveitis or glaucoma, both of which require immediate treatment.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound imaging can be used to detect any abnormal areas of fluid buildup in or around the eye that could indicate inflammation or infection associated with uveitis cases.
What are possible complications of Uveitis?
- Blindness: If treatment is not received, uveitis might result in blindness.
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma can develop as a result of inflammation in the eye, leading to nerve damage and vision loss.
- Cataracts: If uveitis is not treated promptly, it can worsen and cause cataracts, or cloudiness of the eye's lens which can result in blurred vision and eventual vision loss.
- Damage to Retina: Inflammation in the eye due to uveitis can cause damage to the retina which lines the back of the eye and is responsible for transmitting images from the eye to your brain for interpretation.Damage to the retina over a prolonged period of time may result in irreversible loss of eyesight.
- Macular Degeneration: Uveitis may also increase an individual’s risk of developing age-related macular degeneration, a condition that leads to a decrease in sharp central vision due to deterioration of the macula (the imaging portion of your retina).
Home Remedies for Uveitis
- Triphala: Triphala is an Ayurvedic herb that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It can be taken as a powder or capsule form to reduce inflammation and improve eye health.Ghee: Ghee is a clarified butter that has cooling and soothing properties.Uveitis may cause irritation and inflammation in the eye, which can be reduced by using this substance either topically or orally.
- Amalaki: Amalaki is an Ayurvedic herb that has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce the symptoms of uveitis. In order to lessen inflammation and promote better eye health, you may take it in either powder or capsule form.
- Ashwagandha: Ashwagandha is a plant used in Ayurveda medicine that is known to help alleviate feelings of stress and anxiety. This, in turn, may make it easier to cope with the symptoms of uveitis. For optimal benefits, it is recommended to consume it in either powder or capsule form.
- Anjana: Anjana is an Ayurvedic herbal preparation used for treating various inflammatory conditions, including uveitis. It can be applied directly on the eyes to reduce swelling and irritation caused by uveitis.
What to eat in Uveitis?
- Consume a diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products that are low in fat. This will help you maintain a healthy weight.
- Staying hydrated requires that you consume a lot of water throughout the day.
- It is recommended that you include omega-3 fatty acids into your diet since they may assist in reducing the inflammation that eyes linked with uveitis.
What not to eat in Uveitis?
- Fried food: Fried food can increase inflammation, leading to more severe uveitis symptoms.
- Refined grains: Eating processed grains such as white bread, white rice and other refined products can worsen inflammation in people with uveitis.
- Sugary foods: Eating too much sugar can be a trigger for some forms of uveitis, as well as contribute to inflammation in general.
- Processed meats: Eating processed meats that are high in sodium and preservatives can exacerbate symptoms associated with uveitis.
- Alcoholic beverages: Drinking alcohol has been linked to an increased risk of ocular diseases including uveitis and could make existing symptoms worse if consumed in large quantities over time.
Uveitis Treatment
- Immunosuppressive therapy: This type of therapy uses medications that suppress the body’s immune system and can help to reduce inflammation in the eye.
- Intravitreal injections: These are injections of medications into the eye that can help to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the retina and other parts of the eye.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT): This is a relatively new treatment for uveitis that uses a light-sensitive drug to target abnormal blood vessels in the eye that are causing inflammation.
- Laser treatment: A special type of laser called photocoagulation may be used to treat certain types of uveitis by destroying abnormal
- Surgery: When other treatments fail, surgical approaches may be necessary to treat Uveitis. Surgical interventions range from removing a portion of the iris to transplanting sclera or repositioning a lens implant.
Which doctor to consult for Uveitis?
It is important to consult an ophthalmologist if symptoms of uveitis are present.
Ophthalmologists are medical doctors that specialise in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of eye-related disorders such as uveitis. Uveitis is one of these eye-related conditions.
Which are the best medicines for Uveitis?
- Corticosteroids: These are the most commonly used medicines for treating uveitis. They help reduce inflammation and prevent scarring of the eye tissues.
- Immunosuppressants: These medicinal substances function by dampening the immunological response of the body and bringing down levels of inflammation.Examples include methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclosporine A.
- Biologics: There are more recent biologic medications like secukinumab, adalimumab, infliximab, and aflibercept that target particular components of the immune system to decrease inflammation in the eye.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): This group includes ibuprofen and celecoxib, which can help relieve symptoms like pain due to uveitis or other forms of inflammation in the eye or around it.
- Other medications: such as cycloplegics (atropine) and antibiotics can be used to reduce inflammation or infection associated with uveitis depending on its underlying cause.
How long does it take to recover from Uveitis?
Generally, some forms of uveitis can take weeks to months to resolve with appropriate treatment, while others may have an indeterminate course.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
In many instances, therapy may result in a noticeable increase in the patient's level of comfort as well as their eyesight. However, due to its chronic nature, uveitis may require ongoing management with medication or other treatments in some cases.
There is no guarantee that a particular course of treatment will provide permanent relief; it is important to work with your doctor or specialist to determine the best plan for ongoing symptom management.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Use artificial tears or preservative-free eye drops frequently throughout the day to keep eyes lubricated to help prevent further damage and control pain caused by dryness and irritability.
- Wear sunglasses when going outside, as UV rays can cause further damage and exacerbate symptoms.
- Depending on the type of uveitis being treated, certain lifestyle modifications may be recommended by a doctor including taking nutritional supplements, avoiding excessive screen use or getting more sleep.
- Don’t ignore any warning signs such as flu-like symptoms, soreness around the eyes or blurred vision; instead seek medical help right away if any such issues occur so that prompt action can be taken to prevent further deterioration of ocular health.
What is the cost of Uveitis treatments in India?
- Generally, treatment for uveitis includes types of medications, such as steroids, biologic agents and other immunomodulators, which can range from Rs 5,000 to Rs. 25000 per month.
- Other treatments such as laser photocoagulation and vitrectomy may range from Rs 20,000 to Rs 2 lakhs depending on various factors like type of procedure required and degree of complications.
- Surgery may additionally require costs for an anaesthesia fee and hospital stay charges.
What are side-effects of Uveitis treatments?
- Common side effects of uveitis treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition and can include blurred vision, eye pain, and sensitivity to light.
- Other side effects that may occur include headaches, fatigue, nausea or vomiting, dizziness, dryness or irritation in the eyes, increased risk of infection, glaucoma and cataracts.
- Long-term use of steroid treatments may be associated with additional side effects such as weight gain, thinning skin and osteoporosis.
Uveitis - Outlook/ Prognosis
You should see a local doctor if you have any uveitis-related symptoms since they may lead to other issues including macular edema, scarring on the retina, and glaucoma.
Depending on the severity of the condition, therapy regimens may last anywhere from a few months to years for conditions including cataracts and optic nerve damage.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Ophthalmologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors