Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes!
Uncontrolled diabetes can be life-threatening. Prevent these serious diabetes complications by learning the warning signs.
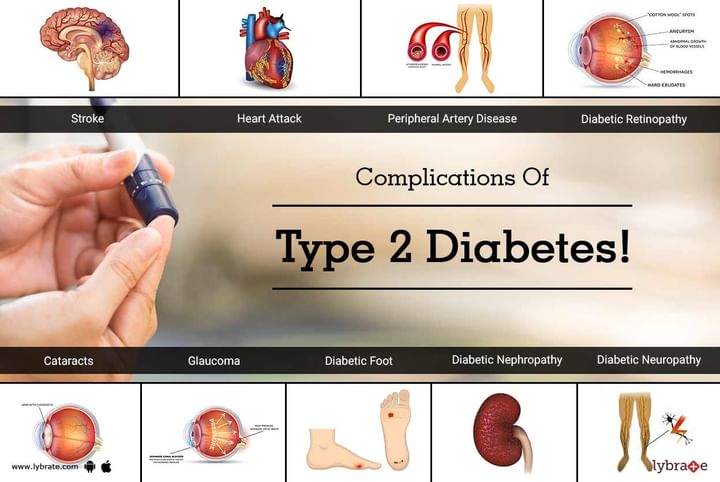
People with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of many serious health problems, including heart attack, kidney failure, nerve damage, stroke, vision loss, amputation. But by keeping your diabetes in check — that means maintaining good blood sugar control, you can prevent many of these.
HEART ATTACK
- Chest discomfort that feels like pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain in the center of your chest, lasting for a short time or going away and returning.
- Pain elsewhere, including the back, jaw, stomach, or neck; or pain in one or both arms.
- Shortness of breath.
STROKE
Stroke warning signs may include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially if it occurs on one side of the body.
- Feeling confused.
- Difficulty walking, talking and lacking coordination.
NERVE DAMAGE
People with diabetes are at increased risk of nerve damage, or diabetic neuropathy, due to uncontrolled high blood sugar. Nerve damage associated with type 2 diabetes can cause a loss of feeling in your feet, which makes you more vulnerable to injury and infection. You may get a blister or cut on your foot that you don't feel and, unless you check your feet regularly, an infection can develop. Untreated infections can result in gangrene (death of tissue) and ultimately amputation of the affected limb.
ALTERED IMMUNE SYSTEM
Diabetes can also make it more difficult for your body to fight infections, causing skin problems. Various skin conditions are linked to diabetes, and even the most minor cuts or sores can turn serious fast. Any bumps, cuts, or scrapes should be cleaned and treated with an antibiotic cream and monitored carefully.
Type 2 diabetes increases your risk of kidney disease, or diabetic nephropathy, a condition in which the blood vessels in your kidneys are damaged to the point that they cannot filter out waste properly. If left untreated, dialysis (a treatment to filter out waste products from the blood) and ultimately a kidney transplant may be needed.
Typically, you won’t notice symptoms of kidney disease until it has advanced. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, visit your doctor:
- Swelling in your ankles and legs.
- Leg cramps.
- A need to go to the bathroom more often at night.
- A reduction in your need for insulin.
- Weakness and paleness.
- Itching.
The best way to prevent type 2 diabetes-related kidney problems is to have your urine, blood, and blood pressure monitored regularly and to keep your blood sugar and blood pressure under control.
EYE PROBLEMS
People with type 2 diabetes are at risk of several eye conditions, including diabetic retinopathy (which affects the blood vessels in the eye), glaucoma, and cataracts. If left untreated, these conditions can cause vision loss.
Visit your doctor if you notice any of these warning signs:
- Blurry vision that lasts for more than two days.
- Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Floaters, black or gray spots, cobwebs, or strings that move when you move your eyes.
- A sensation of seeing "flashing lights".
- Pain or pressure in one or both eyes.
HIGH BLOOD SUGAR (HYPERGLYCEMIA)
Hyperglycemia means you have too much sugar in your blood. High blood sugar doesn't always produce symptoms; therefore, it is important to check your blood sugar regularly, as indicated by your doctor. When symptoms of hyperglycemia occur, they may include:
- Frequent urination.
- Extreme thirst.
- Feeling tired and weak.
- Blurry vision.
The key to preventing many of the complications of diabetes is to keep your blood sugar at a healthy level. To do this eat right, exercise, monitor your blood sugar as recommended by your doctor, and don't smoke.
A healthy lifestyle is your road map for managing diabetes, which is the key to preventing or delaying complications:
-
Follow a healthy eating plan.
-
Be physically active for at least 150 minutes a week (just 30 minutes, 5 days a week).
-
Manage your ABCs:
-
A regular A1C test to measure your average blood sugar over 2 to 3 months; aim to stay in your target range as much as possible.
-
Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg (or the target your doctor sets).
-
Control your cholesterol levels.
-
- Stop smoking or don’t start.
For people with diabetes, controlling blood pressure has big benefits: it reduces the risk of heart disease by as much as 50% and the risk of kidney, eye, and nerve disease by about 33%.
Lose weight if you’re overweight—just a 5% to 7% weight loss lowers the risk for complications. That’s 10 to 14 pounds for someone who weighs 200 pounds.
Take medicines as prescribed.
In case you have a concern or query you can always consult an expert & get answers to your questions!


+1.svg)
